
Before you go, check this out!
We have lots more on the site to show you. You've only seen one page. Check out this post which is one of the most popular of all time.

Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability: How do they differ?

Probability is the study of chances and is an important topic in mathematics. There are two types of probability: theoretical and experimental.
So, how to define theoretical and experimental probability? Theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas, while experimental probability is based on results from experiments or surveys. In order words, theoretical probability represents how likely an event is to happen. On the other hand, experimental probability illustrates how frequently an event occurs in an experiment.
Read on to find out the differences between theoretical and experimental probability. If you wonder How to Understand Statistics Easily , I wrote a whole article where I share 9 helpful tips to help you Ace statistics.
Table of Contents
What Is Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas. In other words, a theoretical probability is a probability that is determined based on reasoning. It does not require any experiments to be conducted. Theoretical probability can be used to calculate the likelihood of an event occurring before it happens.
Keep in mind that theoretical probability doesn’t involve any experiments or surveys; instead, it relies on known information to calculate the chances of something happening.
For example, if you wanted to calculate the probability of flipping a coin and getting tails, you would use the formula for theoretical probability. You know that there are two possible outcomes—heads or tails—and that each outcome is equally likely, so you would calculate the probability as follows: 1/2, or 50%.
How Do You Calculate Theoretical Probability?
- First, start by counting the number of possible outcomes of the event.
- Second, count the number of desirable (favorable) outcomes of the event.
- Third, divide the number of desirable (favorable) outcomes by the number of possible outcomes.
- Finally, express this probability as a decimal or percentage.
The theoretical probability formula is defined as follows: Theoretical Probability = Number of favorable (desirable) outcomes divided by the Number of possible outcomes.
How Is Theoretical Probability Used in Real Life?
Probability plays a vital role in the day to day life. Here is how theoretical probability is used in real life:
- Sports and gaming strategies
- Analyzing political strategies.
- Buying or selling insurance
- Determining blood groups
- Online shopping
- Weather forecast
- Online games
What Is Experimental Probability?
Experimental probability, on the other hand, is based on results from experiments or surveys. It is the ratio of the number of successful trials divided by the total number of trials conducted. Experimental probability can be used to calculate the likelihood of an event occurring after it happens.
For example, if you flipped a coin 20 times and got heads eight times, the experimental probability of obtaining heads would be 8/20, which is the same as 2/5, 0.4, or 40%.
How Do You Calculate Experimental Probability?
The formula for the experimental probability is as follows: Probability of an Event P(E) = Number of times an event happens divided by the Total Number of trials .
If you are interested in learning how to calculate experimental probability, I encourage you to watch the video below.
How Is Experimental Probability Used in Real Life?
Knowing experimental probability in real life provides powerful insights into probability’s nature. Here are a few examples of how experimental probability is used in real life:
- Rolling dice
- Selecting playing cards from a deck
- Drawing marbles from a hat
- Tossing coins
The main difference between theoretical and experimental probability is that theoretical probability expresses how likely an event is to occur, while experimental probability characterizes how frequently an event occurs in an experiment.
In general, the theoretical probability is more reliable than experimental because it doesn’t rely on a limited sample size; however, experimental probability can still give you a good idea of the chances of something happening.
The reason is that the theoretical probability of an event will invariably be the same, whereas the experimental probability is typically affected by chance; therefore, it can be different for different experiments.
Also, generally, the more trials you carry out, the more times you flip a coin, and the closer the experimental probability is likely to be to its theoretical probability.
Also, note that theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas, while experimental probability is found by conducting experiments.
What to read next:
- Types of Statistics in Mathematics And Their Applications .
- Is Statistics Harder Than Algebra? (Let’s find out!)
- Should You Take Statistics or Calculus in High School?
- Is Statistics Hard in High School? (Yes, here’s why!)
Wrapping Up
Theoretical and experimental probabilities are two ways of calculating the likelihood of an event occurring. Theoretical probability uses mathematical formulas, while experimental probability uses data from experiments. Both types of probability are useful in different situations.
I believe that both theoretical and experimental probabilities are important in mathematics. Theoretical probability uses mathematical formulas to calculate chances, while experimental probability relies on results from experiments or surveys.
I am Altiné. I am the guy behind mathodics.com. When I am not teaching math, you can find me reading, running, biking, or doing anything that allows me to enjoy nature's beauty. I hope you find what you are looking for while visiting mathodics.com.
Recent Posts
How to Find the Y-Value of Stationary Points with TI-84 Plus CE
TI-84 Plus CE Calculator If you’re studying calculus or any advanced math course, you will certainly come across the concept of stationary points. So, what is a stationary point? A...
IB Maths Vs. A-Level Maths - Which One is Harder?
Maths is a subject that can be demanding for many students. It not only requires strong analytical skills but also an ability to handle complex concepts with ease. Students looking to further their...
Theoretical Probability: Definition + Examples
Probability is a topic in statistics that describes the likelihood of certain events happening. When we talk about probability, we’re often referring to one of two types:
1. Theoretical probability
Theoretical probability is the likelihood that an event will happen based on pure mathematics. The formula to calculate the theoretical probability of event A happening is:
P( A ) = number of desired outcomes / total number of possible outcomes
For example, the theoretical probability that a dice lands on “2” after one roll can be calculated as:
P( land on 2 ) = (only one way the dice can land on 2) / (six possible sides the dice can land on) = 1/6
2. Experimental probability
Experimental probability is the actual probability of an event occurring that you directly observe in an experiment. The formula to calculate the experimental probability of event A happening is:
P( A ) = number of times event occurs / total number of trials
For example, suppose we roll a dice 11 times and it lands on a “2” three times. The experimental probability for the dice landing on “2” can be calculated as:
P( land on 2 ) = (lands on 2 three times) / (rolled the dice 11 times) = 3/11
How to Remember the Difference
You can remember the difference between theoretical probability and experimental probability using the following trick:
- The theoretical probability of an event occurring can be calculated in theory using math.
- The experimental probability of an event occurring can be calculated by directly observing the results of an experiment .
The Benefit of Using Theoretical Probability
Statisticians often like to calculate the theoretical probability of events because it’s much easier and faster to calculate compared to actually conducting an experiment.
For example, suppose it’s known that 1 out of every 30 students at a particular school will need additional help with their math homework after school. Instead of waiting to see how many students show up for homework help after school, a school administrator could instead calculate the total number of students at the school (suppose it’s 300) and multiply by the theoretical probability (1/30) to know that he will likely need 10 people present to help each of the students one-on-one.
Examples of Theoretical Probability
Experimental probabilities are usually easier to calculate than theoretical probabilities because it just involves counting the number of times that a certain event actually occurred relative to the total number of trials.
Conversely, theoretical probabilities can be trickier to calculate. So, here are several examples of how to calculate theoretical probabilities to help you master the topic.
A bag contains the following:
- 3 red balls
- 4 green balls
- 2 purple balls
Question: If you close your eyes and randomly pull out one ball, what is the probability that it will be green?
Answer: We can use the following formula to calculate the theoretical probability of pulling out a green ball:
P( green ) = (4 green balls) / (9 total balls) = 4/9
You own a 9-sided dice that contains the numbers 1 through 9 on the sides.
Question: What is the probability that the dice lands on “7” if you were to roll it one time?
Answer: We can use the following formula to calculate the theoretical probability that the dice lands on 7:
P( lands on 7 ) = (only one way the dice can land on 7) / (9 possible sides) = 1/9
A bag contains the name of 3 boys and 7 seven girls.
Question: If you close your eyes and randomly pull one name out of the bag, what is the probability that you pull out a girl’s name?
Answer: We can use the following formula to calculate the theoretical probability that you pull out a girl’s name:
P( girls name ) = (7 possible girl names) / (10 total names) = 7/10
Featured Posts
Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for professional businesses in both healthcare and retail. I’m passionate about statistics, machine learning, and data visualization and I created Statology to be a resource for both students and teachers alike. My goal with this site is to help you learn statistics through using simple terms, plenty of real-world examples, and helpful illustrations.
One Reply to “Theoretical Probability: Definition + Examples”
The first place to be ! If you are dreaming of understanding Applied Statistics If you are shifting your career to Machine Learning / Data Science And I’m …. Loving it !
Regards Majid Lecturer Computer Science PhD Computer Science
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Join the Statology Community
Sign up to receive Statology's exclusive study resource: 100 practice problems with step-by-step solutions. Plus, get our latest insights, tutorials, and data analysis tips straight to your inbox!
By subscribing you accept Statology's Privacy Policy.

- Kindergarten
- Middle School
- High School
- Math Worksheets
- Language Arts
- Social Studies
Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability

More Topics
- Handwriting
- Difference Between
- 2020 Calendar
- Online Calculators
- Multiplication
Educational Videos
- Coloring Pages
- Privacy policy
- Terms of Use
© 2005-2020 Softschools.com
Theoretical Probability
Theoretical probability as the name suggests is the theory behind probability. Theoretical probability gives the outcome of the occurrence of an event based on mathematics and reasoning. It tells us about what should happen in an ideal situation without conducting any experiments.
Theoretical probability is extremely useful in situations, such as in the launching of a satellite, where it is not feasible to conduct an actual experiment to arrive at a sound conclusion. In this article, we will learn more about the meaning of theoretical probability, the differences between the types of probabilities, and see some associated examples.
What is Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is an approach in probability theory that is used to calculate the probability of an outcome of a specific event. Probability theory is a branch of mathematics that is concerned with finding the likelihood of occurrence of a random event. The probability that an event will occur lies between 0 and 1. If the probability is closer to 0 it implies that the event is less likely to take place. Similarly, if the probability is closer to 1 it denotes that the event has a higher chance of occurring.
Theoretical Probability Definition
Theoretical probability can be defined as the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes. To determine the theoretical probability there is no need to conduct an experiment. However, knowledge of the situation is required to find the probability of occurrence of that event. Theoretical probability predicts the probability of occurrence of an event by assuming that all events are equally likely to occur.
Theoretical Probability Example
Suppose there are a total of 5 cards and the probability of drawing 2 cards needs to be determined. Then by using the concept of theoretical probability, the number of favorable outcomes (2) is divided by the total possible outcomes (5) to get the probability as 0.4.
Theoretical Probability Formula

Theoretical probability can be calculated either by using logical reasoning or by using a simple formula. The result of such a type of probability is based on the number of possible outcomes. The theoretical probability formula is equal to the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of probable outcomes. This formula is expressed as follows:
Theoretical Probability = Number of favorable outcomes / Number of possible outcomes.
How to Find Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is used to express the likelihood of occurrence of an event without conducting any experiments. Suppose a person has 30 raffle tickets and, in total, 500 tickets were sold. The steps to calculate the theoretical probability of the person winning a prize are as follows:
- Step 1: Identify the number of favorable outcomes. As there are 30 raffle tickets thus, 30 will be the number of desired outcomes.
- Step 2: Determine the total possible outcomes. Since 500 total tickets were sold thus, 500 will be the number of total possible outcomes.
- Step 3: To calculate the theoretical probability divide the value from step 1 by step 2. Thus, 30 / 500 = 0.06. This shows that the probability of a person winning a raffle prize is 0.06.

Theoretical Probability vs Empirical Probability
Empirical probability is also known as experimental probability . Both theoretical probability and empirical probability are approaches to calculating the chance that a random event will occur. The difference between theoretical probability and empirical probability is given in the table below:
Related Articles:
- Probability Rules
- Probability and Statistics
- Poisson Distribution Formula
- Event Probability Calculator
Important Notes on Theoretical Probability
- Theoretical probability is used to calculate the probability of occurrence of an event without performing an experiment.
- Theoretical probability assumes that all events have an equal likelihood of occurrence.
- The theoretical probability formula is given as \(\frac{Number\: of\: favorable \:outcomes}{Number\: of \:possible \:outcomes}\).
Examples on Theoretical Probability
Example 1: If a bag contains 5 red and 7 blue balls then what is the probability of picking up a red ball?
Solution: To calculate the theoretical probability the following formula is used.
Number of favorable outcomes = 5
Number of possible outcomes = 5 + 7 = 12
P(red) = 5 / 12 = 0.4167
Answer: The probability of picking up a red ball is 0.4167.
Example 2: Find the probability of getting 3 on a fair die.
Solution: The possible outcomes of rolling a die are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
In other words, the total number of outcomes = 6
As we want to calculate the probability of getting only number 3 thus, the number of favorable outcomes = 1
P(3) = 1 / 6 = 0.167
Answer: The probability of getting 3 on a fair die is 0.167.
Example 3: The letters of the word "MATHEMATICS" are placed in a bag. What is the probability of drawing the letter "T" from the bag?
Solution: The total number of letters = 11
As there are two T's placed in the bag thus, the number of favorable outcomes = 2.
P(T) = 2 / 11 = 0.182
Answer: The probability of drawing the letter "T" is 0.182
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Theoretical Probability
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Theoretical Probability
What is theoretical probability in math.
Theoretical probability in math refers to the probability that is calculated without any experiment being performed. It can be defined as the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes.
What is the Formula for Theoretical Probability?
The theoretical probability formula is given as follows:
Theoretical probability = \(\frac{Number\: of\: favorable \:outcomes}{Number\: of \:possible \:outcomes}\)
How Do You Calculate Theoretical Probability?
To calculate the theoretical probability the steps are as follows:
- Find the number of desired or favorable outcomes.
- Find the total number of outcomes.
- Divide the value obtained in step 1 by the value from step 2.
What is the Difference Between Theoretical Probability and Experimental Probability?
Theoretical probability is calculated when conducting an experiment is not possible. It gives a fair idea of the likelihood of occurrence of an outcome. In contrast, experimental probability is calculated based on experiments that have been conducted in the past.
Is Classical Probability the Same as Theoretical Probability?
Yes, theoretical probability is the same as classical probability. It is an approach used to calculate the outcome of an event based on the assumption that each outcome of the given event is equally likely to occur.
Why Do You Use Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is required in situations where it is not possible to conduct repeated experiments due to its impracticality or lack of finance. For example, direct experiments cannot be performed when determining the various probabilities associated with subatomic particles. In such a case theoretical probability is used.
What is a Theoretical Probability Distribution?
Theoretical distributions that are designed based on certain assumptions are known as theoretical probability distributions. They are required for the quick analysis of the distribution of random variables. For example, Bernoulli distribution , normal distribution , binomial distribution , etc. are theoretical probability distributions.
Theoretical Probability & Experimental Probability
Related Pages Probability Tree Diagrams Probability Without Replacement Probability Word Problems More Lessons On Probability
In these lessons, we will look into experimental probability and theoretical probability.
The following table highlights the difference between Experimental Probability and Theoretical Probability. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
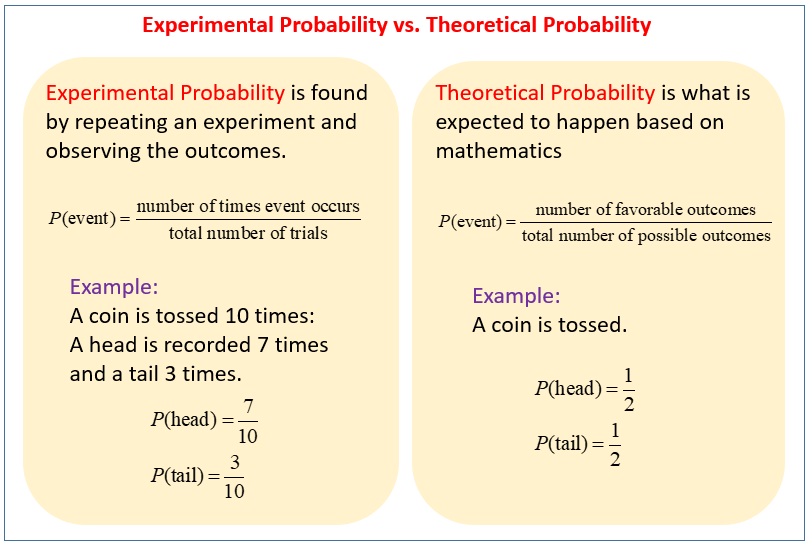
Printable Probability (Equally Likely Outcomes) Probability (Not Equally Likely Outcomes) Probability Tree Diagrams
Online Probability Problems Complementary Probability Probability Problems Probability & Geometry Mutually Exclusive Probability Independent Events Probability Dependent Events Probability
How To Find The Experimental Probability Of An Event?
Step 1: Conduct an experiment and record the number of times the event occurs and the number of times the activity is performed.
Step 2: Divide the two numbers to obtain the Experimental Probability.
How To Find The Theoretical Probability Of An Event?
The Theoretical Probability of an event is the number of ways the event can occur (favorable outcomes) divided by the number of total outcomes.
What Is The Theoretical Probability Formula?
The formula for theoretical probability of an event is
Experimental Probability
One way to find the probability of an event is to conduct an experiment.
Example: A bag contains 10 red marbles, 8 blue marbles and 2 yellow marbles. Find the experimental probability of getting a blue marble.
Solution: Take a marble from the bag. Record the color and return the marble. Repeat a few times (maybe 10 times). Count the number of times a blue marble was picked (Suppose it is 6).
How to find and use experimental probability?
The following video gives another example of experimental probability.
How the results of the experimental probability may approach the theoretical probability?
Example: The spinner below shows 10 equally sized slices. Heather spun 50 times and got the following results. a) From Heather’s’ results, compute the experimental probability of landing on yellow. b) Assuming that the spinner is fair, compute the theoretical probability of landing in yellow.
Theoretical Probability
We can also find the theoretical probability of an event.
Example: A bag contains 10 red marbles, 8 blue marbles and 2 yellow marbles. Find the theoretical probability of getting a blue marble.
Solution: There are 8 blue marbles. Therefore, the number of favorable outcomes = 8. There are a total of 20 marbles. Therefore, the number of total outcomes = 20
Example: Find the probability of rolling an even number when you roll a die containing the numbers 1-6. Express the probability as a fraction, decimal, ratio and percent.
Solution: The possible even numbers are 2, 4, 6. Number of favorable outcomes = 3. Total number of outcomes = 6
Comparing Theoretical And Experimental Probability
The following video gives an example of theoretical and experimental probability.
Example: According to theoretical probability, how many times can we expect to land on each color in a spinner, if we take 16 spins? Conduct the experiment to get the experimental probability.
We will then compare the Theoretical Probability and the Experimental Probability.
The following video shows another example of how to find the theoretical probability of an event.
A spinner is divided into eight equal sectors, numbered 1 through 8. a) What is the probability of spinning an odd numbers? b) What is the probability of spinning a number divisible by 4? b) What is the probability of spinning a number less than 3?
A spinner is divided into eight equal sectors, numbered 1 through 8. a) What is the probability of spinning a 2? b) What is the probability of spinning a number from 1 to 4? b) What is the probability of spinning a number divisible by 2?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- Pre-Algebra Topics
- Algebra Topics
- Algebra Calculator
- Algebra Cheat Sheet
- Algebra Practice Test
- Algebra Readiness Test
- Algebra Formulas
- Want to Build Your Own Website?
Sign In / Register
Theoretical Probability versus Experimental Probability
You've heard the terms, theoretical probability and experimental probability , but what do they mean?
Are they in anyway related? This is what we are going to discover in this lesson.
If you've completed the lessons on i ndependent and dependent probability , then you've already found the theoretical probability for numerous problems.
Theoretical Probability
Theoretical probability is the probability that is calculated using math formulas. This is the probability based on math theory.
Experimental Probability
Experimental probability is calculated when the actual situation or problem is performed as an experiment. In this case, you would perform the experiment, and use the actual results to determine the probability.
In order to accurately perform an experiment, you must:
- Identify what constitutes a " trial ".
- Perform a minimum of 25 trials
- Set up an organizer (table or chart) to record your data.
Let's take a look at an example where we first calculate the theoretical probability, and then perform the experiment to determine the experimental probability.
It will be interesting to compare the theoretical probability and the experimental probability. Do you think the two calculations will be close?
Example 1 - Theoretical Versus Experimental
This problem is from Example 1 in the independent events lesson. We calculated the theoretical probability to be 1/12 or 8.3%. Take a look:
Since we know that the theoretical probability is 8.3% chance of flipping a head and rolling a 6, let's see what happens when we actually perform the experiment.
Identify a trial: A trial consists of flipping a coin once and rolling a die once.
Conduct 25 trials and record your data in the table below.
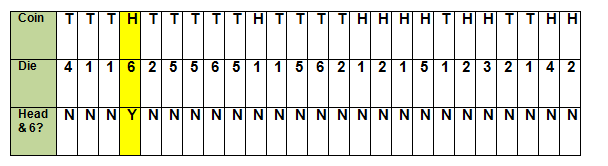
For each trial, I flipped the coin once and rolled the die. I recorded and H for heads and a T for tails in the row labeled "Coin."
I recorded the number on the die in the row labeled "Die".
In the last row I determined whether the trial completed the event of flipping a head and rolling a six.
In this experiment, there was only 1 trial (out of 25) where a head was flipped on the coin and a 6 was rolled on the die.
This means that the experimental probability is 1/25 or 4%.
Please note that everyone's experiment will be different; thus allowing the experimental probability to differ.
Also, the more trials that you conduct in your experiment, the closer your calculations will be for the experimental and theoretical probabilities.
Conclusions
The theoretical probability is 8.3% and the experimental probability is 4%. Although the experimental probability is slightly lower, this is not a significant difference.
In most experiments, the theoretical probability and experimental probability will not be equal; however, they should be relatively close.
If the calculations are not close, then there's a possibility that the experiment was conducted improperly or more trials need to be completed.
I hope this helps to give you a sense of how to set up an experiment in order to compare theoretical versus experimental probabilities.
- Probability
- Theoretical/Experimental Probability

Need More Help With Your Algebra Studies?
Get access to hundreds of video examples and practice problems with your subscription!
Click here for more information on our affordable subscription options.
Not ready to subscribe? Register for our FREE Pre-Algebra Refresher course.
ALGEBRA CLASS E-COURSE MEMBERS

Click here for more information on our Algebra Class e-courses.

Need Help? Try This Online Calculator!
Affiliate Products...
On this site, I recommend only one product that I use and love and that is Mathway If you make a purchase on this site, I may receive a small commission at no cost to you.
Privacy Policy
Let Us Know How we are doing!
send us a message to give us more detail!
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Copyright © 2009-2020 | Karin Hutchinson | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Experimental Probability vs. Theoretical Probability
What's the difference.
Experimental probability is based on actual observations and data collected from experiments or real-life events. It is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of outcomes. On the other hand, theoretical probability is based on mathematical calculations and predictions. It is determined by analyzing the possible outcomes and their likelihood in a given situation. While experimental probability provides an estimate of the likelihood of an event based on real-world data, theoretical probability provides a more precise and accurate prediction based on mathematical principles.
Further Detail
Introduction.
Probability is a fundamental concept in mathematics and statistics that allows us to quantify the likelihood of an event occurring. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including science, finance, and everyday decision-making. When discussing probability, two important terms often come up: experimental probability and theoretical probability. While both concepts deal with the likelihood of events, they differ in their approach and application. In this article, we will explore the attributes of experimental probability and theoretical probability, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Experimental Probability
Experimental probability, also known as empirical probability, is based on observations and data collected from experiments or real-life events. It involves conducting experiments or observations to determine the likelihood of an event occurring. The experimental probability of an event is calculated by dividing the number of times the event occurs by the total number of trials or observations.
One of the key attributes of experimental probability is its reliance on real-world data. By conducting experiments or observations, we can gather empirical evidence to estimate the probability of an event. This makes experimental probability particularly useful when dealing with situations where theoretical calculations may be challenging or impractical.
Another attribute of experimental probability is its subjectivity. Since it is based on observed data, the results can vary depending on the specific experiments or observations conducted. The more trials or observations we perform, the more reliable the experimental probability becomes. However, it is important to note that experimental probability is still an estimation and may not always accurately reflect the true probability of an event.
Experimental probability is often used in fields such as psychology, biology, and social sciences, where controlled experiments or observations can provide valuable insights into the likelihood of certain outcomes. For example, in a psychology study, researchers may conduct experiments to determine the probability of a specific behavior occurring in response to certain stimuli.
Theoretical Probability
Theoretical probability, also known as classical probability, is based on mathematical principles and calculations. It involves analyzing the underlying structure of a given situation or event to determine the probability of specific outcomes. Theoretical probability relies on assumptions and mathematical models to make predictions about the likelihood of events.
One of the key attributes of theoretical probability is its objectivity. Since it is based on mathematical calculations, the results are not influenced by specific experiments or observations. Theoretical probability provides a systematic and consistent approach to quantifying probabilities, making it particularly useful in situations where empirical data may be limited or unavailable.
Another attribute of theoretical probability is its precision. By using mathematical formulas and principles, we can calculate the exact probability of an event occurring. This allows for precise predictions and analysis, which can be valuable in fields such as finance, engineering, and physics.
Theoretical probability is often used in situations where the outcomes are well-defined and the underlying probabilities can be determined with certainty. For example, in a fair six-sided die, the theoretical probability of rolling a specific number is 1/6, as there are six equally likely outcomes.
While experimental probability and theoretical probability differ in their approach and application, they share some common attributes. Both concepts deal with the likelihood of events and aim to quantify probabilities. Additionally, both experimental and theoretical probabilities range from 0 to 1, where 0 represents an impossible event and 1 represents a certain event.
However, there are also notable differences between experimental and theoretical probability. Experimental probability relies on observed data, making it subjective and dependent on the specific experiments or observations conducted. On the other hand, theoretical probability is objective and based on mathematical calculations, providing a more systematic and consistent approach.
Another difference lies in the precision of the probabilities. Experimental probability provides an estimation of the likelihood of an event based on observed data, which may not always accurately reflect the true probability. Theoretical probability, on the other hand, allows for precise calculations and predictions, assuming the underlying assumptions and mathematical models are accurate.
Furthermore, experimental probability is often used in situations where real-world data is available or when conducting experiments is feasible. It is particularly useful in fields such as social sciences, where controlled experiments or observations can provide valuable insights. Theoretical probability, on the other hand, is more suitable for situations where the underlying probabilities can be determined with certainty or when empirical data is limited or unavailable. It is commonly used in fields such as mathematics, finance, and physics.
Experimental probability and theoretical probability are two important concepts in the study of probability. While both aim to quantify the likelihood of events, they differ in their approach and application. Experimental probability relies on observed data and provides an estimation of probabilities based on experiments or observations. Theoretical probability, on the other hand, is based on mathematical calculations and provides precise predictions assuming the underlying assumptions and models are accurate.
Understanding the attributes of experimental and theoretical probability is crucial for making informed decisions and analyzing probabilities in various fields. By recognizing the strengths and limitations of each approach, we can effectively apply probability concepts to real-world situations and enhance our understanding of uncertain events.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main difference between theoretical and experimental probability is that theoretical probability expresses how likely an event is to occur, while experimental probability characterizes how frequently an event occurs in an experiment.
Theoretical probability is the likelihood that an event will happen based on pure mathematics. The formula to calculate the theoretical probability of event A happening is: P( A ) = number of desired outcomes / total number of possible outcomes
Theoretical probability is what we expect to happen, where experimental probability is what actually happens when we try it out. The probability is still calculated the same way, using the number of possible ways an outcome can occur divided by the total number of outcomes.
The results of experimental probability are close to theoretical only if the number of trials are more in number. Learn to calculate the Experimental Probability through various examples and solved problems. Know the differences between theoretical and experimental probability.
This Khan Academy video compares theoretical and experimental probabilities for seventh-grade math students.
Theoretical Probability is the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total possible outcomes of an event. Understand theoretical probability using solved examples.
Lessons distinguishing between theoretical probability and experimental probability, How to find and use experimental probability, How to find the theoretical probability of an event, How to use the formula for theoretical probability, with video lessons, examples and step-by-step solutions.
The difference between theoretical and experimental probability is that theoretical is based on knowledge and mathematics. Experimental probability is based on trials or experiments.
Theoretical probability is the probability that is calculated using math formulas. This is the probability based on math theory. Experimental Probability. Experimental probability is calculated when the actual situation or problem is performed as an experiment.
While experimental probability provides an estimate of the likelihood of an event based on real-world data, theoretical probability provides a more precise and accurate prediction based on mathematical principles.