Essay Papers Writing Online
Get the ultimate guide on writing an expository essay – step-by-step tips and examples.

Are you grappling with the challenge of composing a compelling expository essay? Look no further, as this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the essential tools and techniques to effectively convey your ideas and captivate your readers. By employing powerful writing strategies and supplementing your work with concrete examples and real-life anecdotes, you will unlock the true potential of your explanatory essay.
Begin your writing journey by harnessing the power of clarity and conciseness. Structuring your essay with a logical flow will allow your readers to effortlessly follow your thought process and grasp your central ideas. Employing strong transitions between paragraphs and employing cohesive language will ensure a seamless reading experience. Additionally, honing your analytical skills and supporting your claims with factual evidence will lend credibility to your work while fostering a deep understanding of the topic.
Furthermore, incorporating vivid examples and engaging anecdotes will breathe life into your expository essay, making your content relatable and memorable. By utilizing descriptive language and the art of storytelling, you will create a lasting impact in the minds of your readers. Whether it is a personal experience, a historical event, or a scientific study, weaving in these narratives will amplify the effectiveness and persuasiveness of your essay, leaving a lasting imprint on your audience.

Mastering the Art of Crafting a Compelling Expository Composition: Pointers and Illustrations

An in-depth exploration of the fundamentals behind composing an impactful expository essay can serve as an invaluable tool in your academic and professional endeavors. By harnessing the power of language, analysis, and evidence, you can construct a persuasive and enlightening piece of writing that will captivate your readers. Let us embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of crafting an exquisite expository essay.
1. Avoid monotony: Deliver your ideas in a fresh, stimulating manner to enthrall your audience. Strive to maintain a captivating narrative flow by skillfully employing synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and metaphors. This will invigorate your writing and make it truly memorable.
2. Be concise yet comprehensive: Accomplish the delicate balance of being succinct without sacrificing the clarity and depth of your exposition. Remember to select your words wisely, presenting each idea concisely while ensuring it is thorough and complete.
3. Provide evidence: Back up your statements with solid evidence and well-researched examples. Citing credible sources, such as reputable studies, expert opinions, and statistical data, will add credibility and weight to your arguments, making them more persuasive and powerful.
4. Organize your thoughts: Structure your essay in a logical and coherent manner, ensuring that each idea flows seamlessly into the next. Utilize transitional words and phrases to guide your readers through the different sections of your essay, enabling them to follow your line of reasoning effortlessly.
5. Cater to your audience: Tailor your language, tone, and examples to suit the preferences and background of your intended audience. Use relatable and engaging references to convey your message effectively and establish a connection with your readers.
6. Emphasize clarity: Clarity is key when it comes to expository writing. Avoid excessive jargon, convoluted sentences, and ambiguous expressions. Instead, strive for lucidity and precision, ensuring that your readers can easily grasp the main points of your essay.
7. Show don’t tell: Instead of merely stating information, aim to vividly illustrate your ideas through anecdotes, case studies, and real-life examples. This will make your essay more relatable and memorable, enabling your readers to form a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
8. Revise and refine: Do not underestimate the importance of the revision process. Review your essay meticulously, focusing on grammar, clarity, and coherence. Eliminate redundancies, enhance sentence structure, and refine your vocabulary to elevate the quality and impact of your writing.
By equipping yourself with these essential guidelines and examples, you are well-prepared to embark on your expository essay writing journey. Remember, mastering the art of crafting a compelling expository composition requires practice and perseverance. Let your ideas flow, embrace creativity, and allow your words to inspire, educate, and leave an indelible mark in the minds of your readers.
The Significance of an Expository Article
When it pertains to written compositions, the significance of an expository article cannot be underestimated. This type of writing piece serves a crucial purpose in communicating information, presenting facts, and explaining ideas in a clear and concise manner. By utilizing objective analysis, evidence-based reasoning, and logical arguments, an expository essay provides readers with a deeper understanding of a subject matter.
Unlike other forms of writing, an expository essay focuses on informing rather than persuading or entertaining. It acts as a reliable source of knowledge, offering readers an opportunity to broaden their horizons and gain new insights. Whether used in academic, professional, or personal settings, the expository essay serves as a valuable tool for conveying information accurately and objectively.
Furthermore, an expository essay aids in building critical thinking and analytical skills. Through the process of researching and organizing information, the writer develops the ability to evaluate sources, discern facts from opinions, and present arguments based on logical reasoning. This type of writing encourages readers to question assumptions, analyze evidence, and draw their own conclusions.
Moreover, mastering the art of composing an expository essay equips individuals with essential communication skills that are applicable in various aspects of life. By learning how to present complex ideas in a clear and coherent manner, one becomes an effective communicator across different fields and disciplines. Whether it be writing research papers, reports, or even delivering presentations, the skills acquired from writing an expository essay are invaluable in expressing ideas persuasively and engaging an audience.
In conclusion, the importance of an expository essay lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive and objective understanding of a subject matter. By offering factual information, logical arguments, and clear explanations, this type of writing contributes to the development of critical thinking skills and effective communication. Whether in academic, professional, or personal settings, the expository essay plays a vital role in disseminating knowledge and fostering intellectual growth.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience
In order to create a compelling and impactful expository essay, it is important to have a clear understanding of the purpose and audience of your writing.
The purpose of an expository essay is to explain or inform the reader about a specific topic or idea. Unlike other types of essays, the main goal is to provide a balanced analysis and present factual information in a clear and concise manner. The purpose may vary depending on the specific assignment or context, but it is important to always keep the purpose in mind when writing an expository essay.
Equally important is knowing your audience. Understanding who will be reading your essay will help you tailor your writing style, tone, and level of complexity to effectively communicate your ideas. Consider the background knowledge, interests, and beliefs of your audience to ensure that your essay is accessible and engaging.
- Start by identifying the demographic characteristics of your audience, such as age, education level, and background.
- Consider their prior knowledge on the topic. Are they familiar with the subject matter, or do you need to provide additional context?
- Think about their potential biases or preconceived notions. Are there any potential challenges or objections you need to address?
By understanding the purpose and audience of your expository essay, you can craft a well-written and relevant piece that effectively communicates your ideas and engages your readers.
Choosing the Right Topic and Gathering Information
One of the crucial steps in writing an outstanding expository essay is selecting a compelling topic and gathering relevant information. The topic should be interesting, relevant, and align with the purpose of your essay. It’s important to choose a topic that you are passionate about and have a good understanding of, as it will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and easier.
Start by brainstorming different ideas and concepts that you find intriguing. Consider your personal experiences, hobbies, or areas of expertise that you would like to explore further. You can also look for inspiration from current events, popular trends, or societal issues that grab your attention. Once you have a list of potential topics, narrow it down to the one that has enough depth and scope for exploration.
Once you have chosen a topic, it’s time to gather information to support your thesis statement and provide evidence for your claims. Start by conducting thorough research using various sources such as books, scholarly articles, reputable websites, and interviews with experts in the field. Take notes and keep track of the sources you use for referencing purposes.
| Tips for Gathering Information: |
|---|
| 1. Use reliable and credible sources to ensure the accuracy of the information. |
| 2. Take detailed notes and organize them based on different subtopics or arguments. |
| 3. Look for different perspectives and opinions on the topic to present a well-rounded view. |
| 4. Don’t rely solely on internet sources, but also explore books and academic journals. |
| 5. Use quotation marks or proper citation methods when including direct quotes or paraphrasing information from sources. |
| 6. Keep track of all the sources you use to avoid plagiarism and provide proper references in your essay. |
By choosing the right topic and gathering relevant information, you lay the foundation for a well-researched and compelling expository essay. Take the time to explore different ideas, conduct thorough research, and organize your findings effectively. Remember, a well-chosen topic and solid information will make your essay engaging and informative for your readers.
Structuring Your Expository Essay

When it comes to composing an expository essay, the way you structure your piece is crucial. Organizing your thoughts and ideas in a clear and logical manner will not only make your writing more coherent and easy to follow, but it will also help you effectively convey your message to the readers.
One effective way to structure your expository essay is to use the traditional five-paragraph format. This format consists of an introduction paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall development of your essay.
The introduction paragraph is where you grab the attention of your readers and provide them with a brief overview of what your essay will be about. It should include a strong thesis statement that clearly states your main argument or point of view.
The body paragraphs are where you present your evidence, provide supporting details, and analyze your topic. Each body paragraph should focus on one main idea or aspect of your topic. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main point, and then provide examples, facts, or explanations to support your argument.
In the conclusion paragraph, you should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. Avoid introducing new information or arguments in this section. Instead, focus on leaving a lasting impression on your readers and reinforcing the main ideas discussed throughout your essay.
Remember to use appropriate transition words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas. Examples of transitional phrases include “firstly,” “in addition, “finally,” and “on the other hand,” among others.
By following a well-structured approach, you can effectively organize your expository essay and make it engaging and informative for your readers. Take the time to plan your essay, identify your main points, and arrange them in a logical order. With a clear structure, your expository essay will be a powerful piece of writing that effectively conveys your ideas.
Enhancing Clarity and Coherence
Creating a clear and coherent expository essay requires skillful use of language and organization. By carefully selecting words and arranging ideas logically, you can ensure that your essay is easy to understand and follow.
Word Choice: One of the most effective ways to enhance clarity is through thoughtful word choice. Consider using precise and specific language to convey your ideas. Instead of using general terms, opt for more descriptive words that accurately depict the information you are presenting.
Logical Organization: Coherence in your essay can be achieved through proper organization. Present your ideas in a logical progression, ensuring that each paragraph flows smoothly into the next. Use transitional words and phrases to connect your thoughts and guide the reader through your essay.
Consistent Structure: To enhance clarity and coherence, maintain a consistent structure throughout your essay. Use a clear introduction to outline your main points and a strong conclusion to summarize your findings. Each body paragraph should focus on a single topic and provide sufficient evidence and examples to support your claims.
Effective Transitions: Transitions are essential in ensuring a cohesive flow between ideas and paragraphs. Use transitional words and phrases such as “however,” “in addition,” and “furthermore” to link your ideas and create a smooth transition between different sections of your essay.
Eliminating Ambiguity: To enhance clarity, it is crucial to eliminate any ambiguity or confusion from your writing. Be precise in your language and avoid using vague terms or jargon. Make sure your ideas are clearly articulated and leave no room for misinterpretation.
Proofreading: Finally, closely edit and proofread your essay for clarity and coherence. Look for any unclear sentences or confusing phrases and revise them for greater clarity. Ensure that your ideas are presented in a logical and coherent manner, leaving no room for confusion.
By enhancing clarity and coherence in your expository essay, you can effectively communicate your ideas and engage your readers. Thoughtful word choice, logical organization, consistent structure, effective transitions, and careful proofreading all play important roles in creating a clear and coherent essay that will leave a lasting impact.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services, expository essays | step-by-step manual with examples.

- Tags: Academic Writing , Essay , Essay Writing
The term “expository” refers to expounding on, or elaborating on a topic. Hence, the main goal of an expository essay is to provide factual information on a particular subject. Although writing an engaging essay is definitely a plus, it is secondary. The main goal of writing an expository essay is to educate.
An expository essay is a relatively unbiased piece of writing that explores a topic from all angles. In this article, we will explore the meaning of an expository essay and how to write one with the help of a few expository essay examples. Let’s take a look.
Elevate your essay with our expert essay editing services! Get started
What is an expository essay?
An expository essay is an unbiased, factual piece of writing that provides an in-depth explanation of a topic or set of ideas. It aims to explain a topic from all angles and takes no decisive stance on it.
Expository essays make no new arguments on a topic but rather explain preexisting information in a structured format. They are mainly used in assignments or exams to test the student’s knowledge of a subject.
However, the expository essay definition remains incomplete without understanding the different types of expository essays. An “expository essay” is an umbrella term used to describe different types of essays. These essays include classification essays, definition essays, process essays, compare and contrast essays, and cause-and-effect essays.
Now that we’ve understood what is an expository essay, let’s look at its types.
1. Classification essay
A classification essay aims to group objects into distinct categories. It also involves comparing objects within the same group and highlighting their similarities and differences. For example, if the essay topic is evergreen trees, it would explore different types like pine and fir and discuss the similarities and differences between them.
2. Definition essay
A definition essay aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of a particular topic. As the name implies, the main goal is to define the subject matter in detail. So if you were writing a definition essay on the Victorian era, you would begin by defining the historical period. Then, you would move on to describe the cultural aspects such as fashion styles, notable figures, and societal norms that characterized that period.
3. Process essay
A process essay is a step-by-step guide to performing a particular task. It follows a logical, chronological order of detailed steps on how to achieve a desired outcome. For instance, if you want to write a process essay on “how to make a paper airplane” you will provide a step-by-step chronological guide on how to fold the paper in different ways to create the airplane.
4. Compare and contrast essay
A compare and contrast essay aims to point out the subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two or more subjects. For instance, a compare and contrast essay about the types of ramen served in different parts of Japan may include the differences and similarities in the broth, ingredients used, types of noodles, and flavor profiles in each of them.
5. Cause and effect essay
A cause-and-effect essay seeks to explore the aftermath of a specific incident. So a cause-and-effect essay on the Himalayan mountain range may analyze the movement of the tectonic plates that led to the formation of the Himalayas.
Now that we’ve fully understood what’s an expository essay let’s understand its structure.
Expository essay structure
An expository essay is written in the third person and the expository essay format, like any other essay format, consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. There is no limit on the length of your essay unless instructed by your teacher or professor.
The expository essay format typically consists of one paragraph for the introduction and conclusion and three paragraphs for the body. But you can add additional body paragraphs depending on the scope of your topic. Here’s the expository essay paragraph structure:
1. Introduction
The purpose of an introduction is to acquaint your reader with your topic or thesis statement. It also involves using engaging information and a relevant context to captivate the reader.
The thesis statement for an expository essay should be unbiased and should aim to provide the reader with more information on a topic. Here’s an example of an introductory paragraph for an expository essay:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
The Victorian era, spanning from 1837 to 1901, left an indelible mark on English society. With its strict expectations governing everything from fashion to employment, it was known to be a conservative society. But amidst the rigidity, the period also saw remarkable progress in industry, technology, and science. It’s a time of paradox, where tradition and innovation coexisted. In this essay, we’ll delve into the fascinating complexities of the Victorian era and how they shaped English society for generations to come.
2. Body paragraph
After understanding how to start an expository essay the next step is to construct substantial body paragraphs. Each body paragraph in an expository essay consists of a topic sentence, its explanation, and a transition statement. A single idea should be introduced in each paragraph.
These ideas can be arranged chronologically, in the order of importance, or even in a random manner, depending on the purpose and the message of your essay. For instance, a step-by-step guide will always be written chronologically, from the first to the final step. Let’s take a look at an example of a body paragraph for an expository essay.
- Topic sentence
- Explanation
- Transition statement
During the Victorian era, the social hierarchy was rigid, with the aristocracy and landed gentry holding most of the power, wealth, and privilege . Shockingly, the upper class comprised only 0.7% of the population, yet dominated England’s resources and politics. Meanwhile, the working class, who made up the majority of society, faced harsh living and working conditions and had limited opportunities for upward mobility. Working-class men in industrial cities had an average life expectancy of just 16 years. Despite these challenges, the Victorian era also saw a growing movement towards social reform, such as the National Health Service and Factory Act, aimed at improving the working class’s quality of life. Although the oppressive social hierarchy was highly apparent, the Victorian era represented a time of progress and change in England for many.
3. Conclusion
The purpose of the conclusion is to tie up loose ends and to provide a short summary of your essay. End your essay with a strong, meaningful statement that leaves a lasting impression. This helps reinforce the significance of your thesis statement to the reader.
The conclusion should introduce no new information but rather focus on the broader impact and applications of your topic and central idea. Here’s an example of a concluding paragraph for an expository essay.
- Updated thesis statement
- Brief overview
- Concluding statement
The Victorian era brought about significant changes in society, culture, and technology, including the rise of the middle class, the expansion of the British Empire, the emergence of new literary and artistic movements, and the advancement of science and technology. Despite its flaws, it laid the foundation for modern society and continues to impact contemporary culture. This essay explored the Victorian era’s impact on literature, social norms, and technological advancements, providing a comprehensive overview of this era’s influence on society and culture. Overall, the Victorian era’s legacy continues to shape our world today.
Now that we’re familiar with the structure of an expository essay, let’s understand how to write it.
How to write an expository essay
Although an essay is a highly versatile piece of writing, it follows the same basic steps. This involves choosing a relevant topic, crafting a clear thesis statement, creating a structured outline, and writing and revising your essay. Here are some simple steps to write an expository essay.
1. Choose an appropriate topic
An expository essay is based on accurate facts and information, so it makes sense to choose a topic you’re already familiar with. This will not only make the research process much easier but will also help you approach your topic in depth.
2. Craft the thesis statement
Create an interesting and succinct thesis statement that you can expound on. A thesis statement that is both intriguing and clear creates a strong foundation for your essay.
3. Create an essay outline
You can better understand how to structure your expository essay by constructing an outline.
An outline not only provides flow to your essay but also serves as a base to fall back on when in doubt. It is created by constructing relevant topic sentences that support your thesis statement and arranging them in a logical order.
4. Write the first draft
Once you have created the outline, the next step is to flesh it out and start writing your essay. Make sure that you use reliable sources of information and accurately cite them during your writing process.
5. Revise and proofread
After the first draft of your essay is complete, make sure to proofread it and revise any structural, grammatical, or factual inconsistencies. If you have the option, it always helps to hire essay editing services that can handle this crucial task for you.
Expository essay outline
Before embarking on your essay writing journey, make sure that you have a solid base to fall back on. This can be done by creating a comprehensive expository essay outline with a detailed thesis statement, relevant topic sentences, and supporting bits of information.
Here’s an example of an expository essay outline on the impact of the wheel on modern-day technology:
The Impact of the Wheel on Modern-Day Technology
I. Introduction
A. Hook: An interesting fact or a historical anecdote about the invention of the wheel
B. Context: The significance of the wheel in ancient times
C. Thesis statement: The wheel has been a crucial invention that has influenced modern-day technology in various fields.
II. History and Evolution of the Wheel
A. Origin and early uses of the wheel
B. Development of the wheel and axle
C. Role of the wheel in ancient civilizations, such as Mesopotamia, China, and Egypt
D. The role of the wheel in the Industrial Revolution
III. The Influence of the Wheel on Transportation Technology
A. The invention of the modern-day car and its components
B. The development of airplanes and trains
C. The influence of the wheel on space exploration
IV. The Influence of the Wheel on Manufacturing Technology
A. The role of wheels and conveyors in modern factories
B. The use of wheels in heavy machinery and equipment
C. The influence of the wheel in assembly line production
V. The Influence of the Wheel on Everyday Technology
A. The role of the wheel in household appliances and gadgets
B. The use of wheels in sporting equipment and toys
C. The influence of the wheel on modern-day robotics
VI. Conclusion
A. Restate thesis statement
B. Summarize the main points of the essay
C. Final thoughts: The significance of the wheel on modern-day technology
D. Call to action or recommendation for further research or action
Expository essay example
To help you in your writing process, we’ve provided a comprehensive expository essay example. It discusses the impact of Shakespeare’s work on modern-day literature. This expository essay sample deviates from the original five-paragraph structure and consists of an introductory paragraph, four body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.
Influence of Shakespeare on Modern-Day Literature
William Shakespeare is widely regarded as one of the greatest playwrights in the history of English literature. His works have had a significant influence on modern-day literature, and his plays continue to be performed and adapted into various forms, including films, television shows, and novels. In this essay, we will explore the influence of Shakespeare on modern-day literature.
Shakespeare’s influence on the English language cannot be overstated. He is credited with the invention of over 1,700 words and phrases, including “eyeball,” “fashionable,” “addiction,” and “bedazzled,” to name a few. His writing style, characterized by poetic language, rich imagery, and powerful themes, has inspired countless writers and poets over the centuries. Many writers have attempted to imitate his style or use his works as a reference for their writing.
Moreover, Shakespeare’s plays, which were written over 400 years ago, still resonate with audiences today. His exploration of universal themes such as love, jealousy, power, and ambition, continues to captivate readers and audiences worldwide. The characters in his plays, such as Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , and Othello , are iconic and have become part of our cultural heritage.
As a result, today’s media and entertainment have been heavily influenced by Shakespeare’s works. Many writers have adapted his plays into modern settings, retelling the stories in contemporary contexts. For example, the musical West Side Story , which is based on Romeo and Juliet , is set in 1950s New York City, while the film 10 Things I Hate About You is a modern retelling of The Taming of the Shrew .
Shakespeare’s influence is not only evident in media but also in the language and themes used in modern literature. His exploration of human nature and the human condition has inspired many writers to delve deeper into the human psyche, exploring complex emotions and motivations. His use of metaphors, symbolism, and imagery has become a hallmark of literary writing, inspiring many writers to use similar techniques in their works.
In conclusion, William Shakespeare’s influence on modern-day literature cannot be overstated. His works continue to be read and performed, inspiring writers and artists around the world. His use of language, themes, and characters has become part of our cultural heritage and continues to shape how we view the world. Shakespeare’s impact on modern-day literature is a testament to his enduring legacy as one of the greatest writers of all time.
Now that you have clarity about expository essays, you can use this information to write expository essays. As providers of essay editing services , we realize that you may also have doubts about other types of essays like narrative essays, argumentative essays, and more.
Keep reading with more resources from your loyal editors and proofreaders:
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of an expository essay, how long is an expository essay, how are persuasive and expository essays different, how is an analytical essay different from an expository essay, is writing an expository essay easy, what is the structure of an expository essay.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Additional Resources
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Essay Writing Guide
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Citation and Referencing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Expository Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an expository essay?
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
Please note : This genre is commonly assigned as a tool for classroom evaluation and is often found in various exam formats.
The structure of the expository essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the exposition of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. What is more, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
Often times, students are required to write expository essays with little or no preparation; therefore, such essays do not typically allow for a great deal of statistical or factual evidence.
- A bit of creativity!
Though creativity and artfulness are not always associated with essay writing, it is an art form nonetheless. Try not to get stuck on the formulaic nature of expository writing at the expense of writing something interesting. Remember, though you may not be crafting the next great novel, you are attempting to leave a lasting impression on the people evaluating your essay.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students will inevitably begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize and come to a conclusion concerning the information presented in the body of the essay.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of the Great Depression and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the exposition in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the Depression. Therefore, the expository essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph Essay
A common method for writing an expository essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of:
- an introductory paragraph
- three evidentiary body paragraphs
- a conclusion
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Expository Writing: Definition and Examples

By Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is expository writing, what is an expository paragraph, expository writing examples, how prowritingaid can help you with expository composition.
One of the most common types of writing is expository writing. Whether you’re a student taking an English class or a professional trying to communicate to others in your field, you’ll need to use expository writing in your day-to-day work.
So, what exactly does this term mean?
The short answer is that expository writing refers to any writing designed primarily to explain or instruct.
Read on to learn the definition of expository writing as well as some examples of what this type of writing can look like.
Before we look at examples of expository writing, let’s start with a quick definition of what this term actually means.
Expository Writing Definition
The term expository writing refers to any writing that’s designed to explain something. We use the word expository to describe any passage of writing that’s supposed to present information and help you understand it in an objective way.
Some common examples of expository writing include academic essays, textbooks, instructional guides, and news reports. Good expository writing should be factual, objective, and clear.

To better understand what this term means, think about the difference between a scientific article, a short story, and an advertisement.
The scientific article is considered expository writing because its primary purpose is to explain a particular topic in more detail. It presents data, analyzes what that data means, and focuses on the facts.
On the other hand, the short story isn’t considered expository writing, because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s probably trying to entertain you or to take you on a journey. Short stories are narrative writing.
Similarly, an advertisement isn’t expository writing because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s trying to persuade you to buy what it’s selling. Advertisements are persuasive writing.
Here’s a quick rundown of what expository essays should and shouldn’t do.
An expository essay should:
Teach the reader about a particular topic
Focus on the facts
Follow a clearly organized structure
Present information and details from credible sources
An expository essay should not:
Try to change the reader’s mind about something
Present the author’s personal opinions
Include made-up narratives or stories
Follow experimental or nonlinear structures

An expository paragraph is exactly what it sounds like—a paragraph of expository writing.
A well-written expository paragraph should follow a specific format to make it as clear and easy to read as possible. Most expository paragraphs do the following things:
Start with a topic sentence, which explains what the paragraph will be about
Then, include 3 – 5 body sentences that provide supporting details for the topic sentence
Finally, wrap things up with a closing sentence that summarizes what the paragraph has said
Writing an expository paragraph is a great way to practice expository writing. That’s because the paragraph follows the same structure as a more complex expository essay, just on a smaller scale.
Most expository essays should follow this format:
Start with an introductory paragraph that includes the thesis statement, which tells the reader the core statement of the essay
Then, include 3 – 5 body paragraphs that provide factual evidence to support the thesis statement
Finally, wrap things up with a concluding paragraph that summarizes what the body paragraphs and thesis statement said
You can see the similarities between the two formats. If you can write a fantastic expository paragraph, you’ll be well-prepared to move on to writing a full expository essay.
Example of Expository Paragraph
Here’s an example of an expository paragraph that follows the structure described above.
The leading cause of death in the United States is heart disease, which can be fatal if it leads to heart attack or cardiac arrest. Heart attacks occur when a blockage in the coronary artery prevents oxygenated blood from reaching the heart. Cardiac arrests occur when the heart stops pumping entirely, which prevents the patient from breathing normally. Both of these problems can be deadly, even in seemingly healthy people who don’t have noticeable risk factors. As a result, heart disease is an important problem that many doctors and scientists are researching.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
There are many ways you can present information in an expository essay. Here are four of the most popular ways, along with examples of each one.
Problem and Solution Essay
A problem and solution essay presents the reader with a problem and then considers possible solutions to that problem.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a problem and solution essay:
Among the many proposed solutions to rising carbon emissions, one promising possibility is carbon trapping. Scientists are figuring out how to pull carbon emissions out of the atmosphere and trap it in less harmful forms, such as by injecting carbon dioxide underground so it will turn to stone.
Compare and Contrast Essay
This type of essay takes two subjects and compares and contrasts them. It focuses on highlighting the differences and similarities between those two things.
Here’s an example passage of this type of expository writing:
Though country music and R&B music have very different sounds, they also share many similarities. For one thing, both types of music embody a specific cultural identity. For another, both genres trace their roots back to the 1920s, when the Victor Talking Machine Company signed singers from the American South.
Classification Essay
In a classification essay, you describe the categories within a certain group of things.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a classification essay:
There are three ways in which artificial intelligence might become stronger than humans in the future: high speed, high collective intelligence, and high quality. A speed AI would be able to perform calculations and experience the world much faster than humans. A collective intelligence, like a hive mind, would be able to break down a complex task into several parts and pursue them simultaneously. Finally, a quality AI would simply be able to solve more complex problems than humans could.
Process Essay
In a process essay, you give the reader the steps for completing a specific process. This is similar to a how-to guide or an instruction manual.
Here’s an example passage you might find in this type of expository writing:
Caramelize the chopped onions in a frying pan. When the onions have caramelized, mix in the bell peppers, mushrooms, and tomatoes and stir for 4 – 6 minutes or until all the ingredients have softened. If you want to add meat, you can add ground beef and cook for another 4 – 6 minutes. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Good expository writing should be easy to read. After all, the purpose of exposition is to explain things to your readers, and you won’t be able to accomplish that if they have trouble understanding your writing.
That’s why ProWritingAid can help you write an expository essay. The grammar checker can help you ensure your sentences flow well, you’re not missing any necessary punctuation, and all your words are precise and clear.
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah Yang
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay
4-minute read
- 29th March 2020
An expository essay explains something. This means investigating an idea, looking at evidence, coming to a conclusion, and explaining your thinking. But how do you write a strong expository essay? Our top tips include:
- Read the essay prompt carefully and using it to guide your research.
- Come up with a thesis statement (i.e., a position that you’ll explain).
- Plan the structure of your essay before you start writing.
- Once you have a first draft, revise and proofread to make sure it is perfect.
For more advice on how this works, check out the guide below.
1. Read Your Essay Prompt
Most expository essay prompts will ask you to do one of the following:
- Define and explain a concept or theory.
- Compare and contrast two ideas.
- Examine a problem and propose a solution.
- Describe a cause and effect relationship.
- Explain a step-by-step process.
- Analyze a broad subject and classify examples into groups.
When you’ve been set an expository assignment, then, check the prompt or question carefully. You can use the phrasing to guide your research. You may also need to select a topic to write about. If so, try to think of something:
- You already know at least something about.
- You find interesting enough to research.
- That fits with the instructions in the essay prompt (e.g., if you’ve been asked to contrast two things, you’ll need a topic that allows for a comparison).
- That is narrow enough to discuss in one essay.
Start by brainstorming topics, then narrow it down to one or two ideas.
2. Come Up with a Thesis Statement
Once you have a topic, you’ll need to do some research and develop a thesis statement. This is the proposition or position that you’ll explain in your essay.
Your thesis statement should be something you can back up with evidence and facts, as well as something that answers the question in your essay prompt. Keep in mind, too, that an expository essay should present a balanced account of the facts available, not personal opinions. For instance, we’ve come up with thesis statements for a few example essay prompts:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When you’ve selected a thesis, make sure you’ve got evidence to back it up! This may mean doing a little more research before you start writing.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Structuring an Expository Essay
The exact length and content of your essay will depend on the topic and prompt. However, most expository essays follow a similar basic structure:
- Introduction – A paragraph where you introduce the essay topic and your thesis statement (i.e., the issue or idea you will explain in the essay).
- Main Body – A series of short paragraphs in which you explain your thesis statement, providing evidence and arguments to support each point.
- Conclusion – A final paragraph where you restate your thesis and how your evidence supports this. Try not to introduce any new information here (if it’s important, it should go in the main body).
- References – If required, include a bibliography of sources you’ve used.
Before you start writing, then, create an essay outline with the structure above in mind and plan what each paragraph will say.
4. Editing and Proofreading
When you have a first draft, take a break and re-read it. Now comes the redrafting ! This is where you go back over your essay and look for areas to improve. Do you provide enough evidence? Is your argument clear? Even a few tweaks may increase your mark, so make sure to redraft at least once!
Finally, make sure to have your essay proofread before you submit it for marking. This will ensure your writing is error free and easy to read, giving you an even better chance of getting the grades you deserve.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- How it works

How to Write an Expository Essay
Published by Grace Graffin at August 17th, 2021 , Revised On July 26, 2023
Expository means “to describe or explain something” . It is related to the words ‘exposition’, ‘expound’, and ‘expose’ – to explain or reveal the meaning, to lay open, speak one’s mind.
Whenever there is a need to gather research and describe an idea, a topic , or a process clearly and logically, it is done in the form of an expository essay .
An expository essay requires the writer to take a balanced approach to the subject matter rather than justifying a particular point of view.
Expository essays are assigned to students to evaluate their subject knowledge and composition skills. When compared with argumentative essays , they involve a lot less research.
Definition of Expository Essay
“The expository essay is the type of essay that involves an investigation of an idea or topic, appraises relevant supporting evidence material, and presents an argument in a clear and concise manner. ”
When to Write an Expository Essay
Your school or university could assign an expository essay to you as coursework or as part of an online exam.
However, the guidelines may or may not clearly state that your assignment is an expository essay. If that is the case, then look for keywords like ‘explain’, ‘describe’, ‘define’, etc., to be sure that what has been asked for is an expository essay.
You might even be asked to explain and emphasise a particular concept or term. Writing a simple definition will not be enough because you will be expected to explore the ideas in detail.
Writing an Expository Essay
An expository essay should not be based on your personal experiences and opinions. It rather takes an objective approach. You will be expected to explain the topic in a balanced way without any personal bias.
Make sure to avoid the first and second person (“I” and “You”) when writing an expository essay.
How to Structure an Expository Essay
The structure and format of your expository essay assignment will depend on your school’s guidelines and the topic you are investigating. However, it is always a good idea to develop an outline for your essay before starting to work.
The Five-Paragraph Essay Writing Approach
An expository essay will require you to take the five-paragraph essay approach: an introductory paragraph , a main body paragraph , and a concluding paragraph . This is often referred to as the hamburger style of the essay because, like a hamburger, it contains five main parts: the introduction and conclusion being the bun that encapsulates everything.
Rationale and Thesis Statement
Start your essay with a rationale and thesis, also known as the thesis statement , so your readers know what you set out to achieve in your expository essay assignment. Ensure the thesis statement is narrow enough to follow the guidelines in the assignment brief. If the thesis statement is weak and too broad, you will struggle to produce a flawless expository essay.
The Framework
Construct a framework, so you know what elements will constitute the basis of your essay.
Expository Essay Introduction
Like other essay types , an expository essay begins with an introduction , including a hook, background to the topic, and a thesis statement. Once you have grabbed the readers’ interest, it will be easier to get them to read the remaining essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will i need the skill of expository writing after i finish my studies.
It depends on what you are studying for. While you might or might not write any more expository essays after your formal education has ended, the skill will be very useful in certain careers, such as business reports, journalism, and in scientific and technical writing.
How does an expository essay differ from an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is usually longer and requires more research. It starts with a claim about something that will need supporting evidence. And both sides of the argument need to be discussed. In an expository essay, there is no requirement to make an original argument and defend/support it.
What is the purpose of expository essays?
This style of essay is necessary when you have to showcase your knowledge on a given subject, or your ability to gather research on one and present your findings.
How long is an expository essay?
There is no fixed length but an expository essay could be part of an exam, in which case it might only be 1,000 words or less. They are usually shorter than argumentative essays . It can depend on the subject under discussion. You will likely be given instructions on the required word count.
Are there different types of expository essay?
There are six different types of expository essay, each with a different purpose.
The six types are:
Process essay – describing a task, a method, how to complete something Cause and effect essay – why something happened and its effects Problem-solution essay – provide analysis of problems and their solutions Compare and contrast essay – describe the similarities and differences between two subjects Definition essay – define the topic in detail and explain the how, what, and why Classification essay – separate the topic’s categories and define them in detail
When you are assigned your essay, you should be able to distinguish which of these approaches you are required to take.
You May Also Like
What are topic sentences? In academic writing they briefly describe what a paragprah will explore. Here is all you need to know about topic sentences.
Here are some tips on writing the main body paragraphs of an essay to help you correctly plan and organize the most critical part of your academic essay.
Narrative essays let the authors provide an account of their personal experience in the form of a story. In a narrative essay, you can let your creativity and ideas flow freely.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
5 Expository Essay Examples (Full Text with Citations)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
- Video Overview
- Quick Example
- Formatting Guide
An expository essay attempts to explain a topic in-depth, demonstrating expert knowledge and understanding.
This form of essay is structured around the clear, factual presentation of information, devoid of the writer’s personal opinions or arguments.
The primary goal is to inform or explain rather than persuade.
Unlike an argumentative essay, which is built around defending a particular point of view with evidence and persuasion, an expository essay maintains a neutral stance, focusing on delivering straightforward facts and explanations.
An example of expository writing could be an article explaining the process of photosynthesis.
The article would systematically describe each stage of how plants convert sunlight into energy, detailing the role of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
It would explain the sequence of reactions – first, second, third, fourth, fifth – that occur and the importance of each step in supporting the life of the plant.
An expository essay generally follows this essay format:

- A) To persuade the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint
- B) To inform or explain a topic clearly
- C) To present the writer’s personal opinions and arguments
- D) To entertain the reader with creative writing
- A) An expository essay uses creative storytelling techniques
- B) An expository essay remains neutral and avoids personal opinions
- C) An expository essay focuses on persuading the reader with evidence
- D) An expository essay prioritizes the writer’s personal experiences
Expository Essay Examples
#1 impacts of technology on education.
955 words | 4 Pages | 15 References

Thesis Statement: “The integration of technology in education represents a complex and critical area of study crucial for understanding and shaping the future of educational practices.”
#2 Impacts of Globalization on Education
1450 words | 5 Pages | 9 References

Thesis Statement: “This essay examines the profound and multifaceted effects of globalization on education, exploring how technological advancements and policy reforms have transformed access to, delivery of, and perceptions of education.”
#3 The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Interpersonal Relationships
1211 Words | 5 Pages | 22 References

Thesis Statement: “The central thesis is that EI, defined as the ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions, is a crucial determinant of success and well-being.”
#4 The Future of Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact
870 words | 4 Pages | 20 References

Thesis Statement: “The essay posits that although renewable energy sources hold immense promise for a sustainable future, their full integration into the global energy grid presents significant challenges that must be addressed through technological innovation, economic investment, and policy initiatives.”
#5 The Psychology Behind Consumer Behavior
1053 words | 4 Pages | 17 References

Thesis Statement: “The thesis of this essay is that consumer behavior is not merely a product of rational decision-making; it is deeply rooted in psychological processes, both conscious and subconscious, that drive consumers’ choices and actions.”
How to Write an Expository Essay

Unlike argumentative or persuasive essays, expository essays do not aim to convince the reader of a particular point of view.
Instead, they focus on providing a balanced and thorough explanation of a subject.
Key characteristics of an expository essay include:
- Clarity and Conciseness
- Structured Organization (Introduction, Body, Conclusion)
- Objective Tone
- Evidence-Based (Cite academic sources in every body paragraph)
- Objective thesis statement (see below)
- Informative purpose (Not argumentative)
You can follow my expository essay templates with AI prompts to help guide you through the expository essay writing process:

How to write a Thesis Statement for an Expository Essay
An expository thesis statement doesn’t make an argument or try to persuade. It uses ‘is’ rather than ‘ought’ statements.
Take these comparisons below. Note how the expository thesis statements don’t prosecute an argument or attempt to persuade, while the argumentative thesis statements clearly take a side on an issue:
| (Ought Statements) | |
|---|---|
| “Governments should prioritize the adoption of electric vehicles over traditional gasoline-powered cars to combat climate change and reduce environmental pollution.” | “Electric vehicles contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.” |
| “Online education should be widely adopted as it offers more inclusive and adaptable learning solutions compared to traditional classroom-based education.” | “Online education provides accessible and flexible learning opportunities, utilizing digital platforms for course delivery and student-teacher interaction.” |
💡 AI Prompt for Generating Sample Expository Thesis Statements An expository essay’s thesis statement should be objective rather than argumentative. Write me five broad expository thesis statement ideas on the topic “[TOPIC]”.
Go Deeper: 101 Thesis Statement Examples

Differences Between Expository and Argumentative Essays
Expository and argumentative essays are both common writing styles in academic and professional contexts, but they serve different purposes and follow different structures.
Here are the key differences between them:
- Expository Essay : The primary purpose is to explain, describe, or inform about a topic. It focuses on clarifying a subject or process, providing understanding and insight.
- Argumentative Essay : The goal is to persuade the reader to accept a particular point of view or to take a specific action. It’s about presenting a stance and supporting it with evidence and logic.
- Expository Essay : It maintains a neutral and objective tone. The writer presents information factually and impartially, without expressing personal opinions or biases.
- Argumentative Essay : It often adopts a more assertive, persuasive, and subjective tone. The writer takes a clear position and argues in favor of it, using persuasive language.
- Expository Essay : The reader is expected to gain knowledge, understand a process, or become informed about a topic. There’s no expectation for the reader to agree or disagree.
- Argumentative Essay : The reader is encouraged to consider the writer’s viewpoint, evaluate arguments, and possibly be persuaded to adopt a new perspective or take action.
Go Deeper: Expository vs Argumentative Essays
Ready to Write your Essay?

Take action! Choose one of the following options to start writing your expository essay now:
Read Next: Process Essay Examples

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 26 Dorm Room Decoration Ideas (for Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Study Desk Aesthetic Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Thoughtful Ways to Greet your Students
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Pre-School Decor Ideas (Inspiring & Beautiful!)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expository Essays Made Simple: The Guide With Examples
What is an expository essay?
How to write, structure, and format it to reach its purpose?
This article is here to answer all your questions on expository writing. I’ll share the meaning and provide a few templates and examples for extra clarity.
Expository Essay Definition
Examples of such explanatory texts are:
- Scholarly articles
- Instructional or technical guides
- Unbiased journalistic investigations
- A news report
- Business writing
It’s an expository text definition for us to understand the nature of this paper type. For more info, let’s learn the characteristics and elements of an expository essay.
What are the characteristics of expository essay?
Expository papers are factual and objective. They have a clear purpose, and their structure is linear and logical. In such essays, writers don’t share their opinions and don’t try to persuade readers.
Expository essays:
- Teach readers about the topic.
- Provide detailed information.
- Describe and explain facts.
- Clear, concise, and written with formal language.
- Organized, in the 3rd person, with precise word choice.
What are the elements of an expository essay?
- Strong thesis statement
- Evidence and examples
- Specific supporting details to explain the topic for a better understanding
- Logical structure and transitions between paragraphs
- Compelling conclusion to help readers remember the information better
What Is the Purpose of an Expository Essay?
The purpose of an expository essay is to present information and explain a topic. No personal opinions or biased statements are here, just facts with evidence.
The main focus is logic and coherence.
I’ve found the method for you to remember expository essays’ organization. It’s POET:
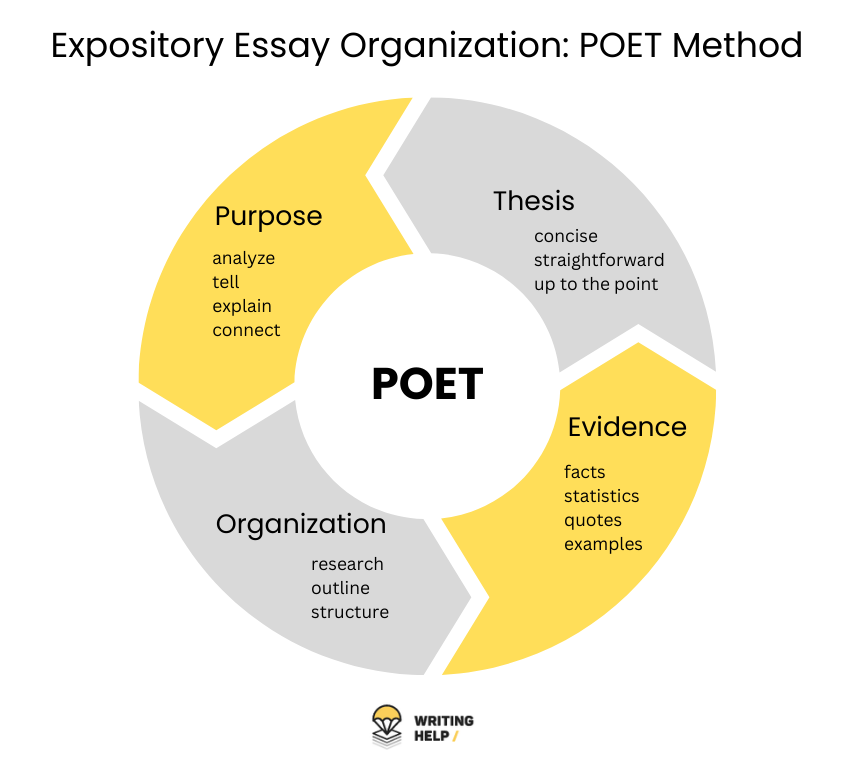
- P — Purpose: analyze, tell, explain, and connect the information.
- O — Organization: do research, outline, and structure your paper.
- E — Evidence: use facts, statistics, expert quotes, and examples.
- T — Thesis: be concise and straightforward.
Expository vs. Argumentative
| Objective | Subjective |
| Thesis statement is a topic presentation | Thesis statement is an argument |
| Explore a topic, only give facts and reasons; neutral | Choose a position about a topic (for or against) |
| Write in the 3rd person (he, she, it, they) | Possible to write in the 1st person (I, we) unless otherwise stated in the prompt |
An easy way to understand the meaning and purpose of explanatory papers is to compare them with other text types. Students most often confuse expository essays with argumentative (persuasive) ones. The above table demonstrates the differences for you to remember.
Types of Expository Writing
As a rule, teachers mention the type of expository essay in the assigned prompt. It helps you understand how to structure and present the information in your paper.
The five types of expository writing are:
- Definition. These papers describe and explain concepts. You just tell readers about something: a person, a place, a situation, etc.
- Classification. Here you need to break a broad concept into subcategories. Start with a general topic, and then tell about each subgroup. (Example: an essay about movie genres, cat breeds, book styles, etc.)
- Process (how-to). These texts explain to readers how to create or do something. Give instructions, steps, and practical tips. We also know process essays as problem-solution papers. A writer introduces and describes a problem and then tells the audience how to solve it.
- Compare-and-Contrast. Here you tell about the similarities and differences between at least two subjects. Or, you can describe the pros and cons of something. (Example: compare two novels of the same author; pros and cons of living in a village; etc.)
- Cause-and-Effect. These essays explain why something happened and what the outcome was. (Example: why Executed Renaissance (1) happened in Ukraine in the 1930s and what effects it has now.)
Expository Essay Structure
In academia, expository essays are standard 5-paragraph papers. You write an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Below is more information on what to include in every paragraph.
Introduction
The introduction of expository essays includes the topic and the main idea. Three elements to write here:
- A writing hook to grab the reader’s interest
- A topic’s background (introducing the topic)
- A thesis statement summarizing the main idea (what you’ll tell about the subject)
Here’s an example:

Body Paragraphs
Expository papers have at least three body paragraphs, each exposing one idea. It’s critical to craft logical transitions between paragraphs and include evidential support.
Each paragraph should have a logical connection to the thesis statement. As for evidence, use statistics, citations, and other info you’ve got when researching. (2)
Here go your four E’s to consider:
- Explanations
- Elaboration
That’s what a body paragraph of your expository paper might look like:

Three elements to include:
- Topic sentence (to state what this paragraph will be about)
- Explanation of the topic in detail
- Concluding sentences with a logical transition to the next paragraph
The final paragraph restates the thesis, given the evidence you provided in the essay. Summarize the topic, but don’t introduce any new information. Leave readers with a positive impression of your work.
Three elements of expository essay conclusions:
- Readdressing the thesis in light of the provided information
- A brief overview of the essay’s key points
- The key takeaway for readers to remember from your essay

Expository Essay Format
| No paragraph/section headers | |
| Standard five-paragraph paper | |
| 12-point Times New Roman | |
| Left | |
| Double-spaced, standard-size paper | |
| 1-inch on all sides | |
| MLA | |
| +/- 800 words |
Example of Expository Essay
Below is your example of expository writing to see the structure and format. It’s a standard five-paragraph essay students write in college. The number of words and paragraphs may differ depending on the prompt you get from teachers.
Feel free to use it for inspiration and a better understanding of how to write:

What is the primary purpose of an expository text?
The primary purpose of an expository text is to inform readers about the topic. Such texts describe and explain concepts to educate the audience. They are objective. A writer shouldn’t express personal opinions or attempt to persuade readers. Expository essays are descriptive, not argumentative or persuasive.
How to write an expository essay?
First, review the prompt; it will tell you all the instructions. You’ll know a topic, a word count, a format, etc. Then, do research and gather all the information about your subject. What will you tell the readers? What evidence you’ll use to support your points? Once ready, create an outline. You’ll need to specify the thesis statement and think about how you structure an essay. Finally, write a draft and proofread and edit it before submitting it to a teacher’s review.
What is typically included in the introductory section of an expository essay?
An introductory paragraph starts with a hook to grab readers’ attention to the topic. Then, provide a topic’s background for readers to understand what you write about. Finally, finish your introduction with a thesis statement. In the thesis, summarize the main idea of your paper.
How long is an expository essay?
Target about 800 words for expository writing. It includes five paragraphs: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Check your prompt carefully: It often mentions the number of words to write.
Over to You
I hope this article has answered your “What is an expository essay” question. Remember about the purpose: inform and educate readers. Imagine yourself as a lecturer who needs to tell the audience about the subject — and voila !
Follow the logical structure, write in the 3rd person, and use evidence to prove your information. The above tips and examples are here to help you.
References:
- https://www.husj.harvard.edu/articles/the-executed-renaissance-paradigm-revisited
- https://www.nhcc.edu/academics/library/doing-library-research/basic-steps-research-process
- Essay samples
- Essay writing
- Writing tips
Recent Posts
- Writing the “Why Should Abortion Be Made Legal” Essay: Sample and Tips
- 3 Examples of Enduring Issue Essays to Write Yours Like a Pro
- Writing Essay on Friendship: 3 Samples to Get Inspired
- How to Structure a Leadership Essay (Samples to Consider)
- What Is Nursing Essay, and How to Write It Like a Pro
How to Write an Expository Essay Better, Faster, and In a More Satisfying Manner

Mark Bradford
What Is an Expository Essay?
If you find yourself here, it's likely because you've recently received an assignment for an expository essay, or perhaps you're drawn to exploring ideas beyond the surface level. Whatever the reason, we're here to guide you through the expository essay definition, its outline, and examples.
Let's start by understanding what an expository essay is and its purpose. In simple terms, an expository essay provides information on a particular topic, elucidating aspects of a situation, person, idea, or event and conveying knowledge to the reader. Unlike persuasive writing, it doesn't seek to sway the audience's opinion but relies on facts to inform and educate about the subject.
From sharing personal experiences to outlining work assignments, expository writing covers a broad spectrum of questions, making it arguably the most prevalent form of writing worldwide. If at any point you feel overburdened with assignments, use our essay writing services to relax and wrap up your homework faster.

Why Students Have to Write Expository Essays?
Expository writing serves a distinct purpose – to impart knowledge to the reader. While it may offer entertainment or persuasion as secondary benefits, these are not the primary objectives of the author. A well-crafted piece of expository writing showcases the author's expertise on the subject and often reveals their journey of acquiring knowledge.
For instance, consider the task of crafting an essay about a mock trial your class conducted. In an expository essay, you would begin by introducing the assignment and detailing the case your class tackled during the trial. Subsequent body sections would systematically elaborate on each stage of the mock trial process – covering discovery, opening statements, cross-examination, closing statements, jury deliberation, and the final verdict – illustrating how your class navigated through each phase. Concluding the essay, you would present the verdict reached by your class and the judge's ruling.
Crucially, your expository essay on the mock trial does not take a stance on whether the ruling was right or wrong. Instead, it elucidates the procedural intricacies your class followed, offering a comprehensive understanding of how real court cases progress through the legal system. In essence, your essay is a presentation of facts and processes rather than expressing personal opinion or commentary.
Types of Expository Essays
As previously noted, expository essays manifest in various forms. These encompass the following types:
Classification
In the realm of classification essays, you delve into various subjects within a single category, examining the distinctive characteristics of each subject while highlighting the traits that connect them to others in the same category. For instance, a classification essay on herding dogs could commence with a thesis statement elucidating the differences between herding breeds from other dog categories. Subsequent paragraphs would then delve into specific herding breeds, such as corgis, collies, heelers, and more.
A definition essay elucidates its subject by presenting factual data. To illustrate, your definition essay might challenge prevalent myths surrounding a historical event by offering firsthand accounts from primary sources. It would also delve into relevant social, political, and economic trends that influenced the event, shaping perceptions of it. We’d also like to recommend you read our guide on how to write a descriptive essay .
A process essay guides the reviewer through the steps required to complete a task akin to a recipe. The opening passage of a process essay outlines the covered process and the anticipated result. Each body chapter corresponds to a step in the process, leading to a conclusion that explains what the reader should have accomplished by following each step.
Compare and Contrast
In a compare-and-contrast essay, your key statement is substantiated by examining the differences and similarities between cited sources. For instance, an essay comparing and contrasting school dress codes might scrutinize variations in allowed clothing items and the precision of language in each policy. It could also explore the degree of ambiguity present in the rules of each dress code.
Cause and Effect
True to its name, a cause-and-effect essay delves into how specific events or actions trigger subsequent occurrences. These essays often trace chains of events to comprehend the reasons behind current circumstances. An example could be a cause-and-effect essay tracking the influence of shifting market trends on regional industries over the past few decades, ultimately shaping the present local economy. Our guide on writing a narrative essay could also help increase your knowledge and skills.
Expository Essay Structure
Structuring an expository essay follows the familiar format applicable to any essay assignment: an introduction, a main body for elaboration and support, and a concluding section that reinforces your thesis and restates key points. While there's no strict word count requirement unless specified by your instructor, your essay should comprehensively express your ideas, maintaining a logical and accurate flow. Adhering to the following format, with the flexibility to adjust the number of sections based on supporting points, will effectively guide your expository essay:

Introduction
In this opening section, you introduce your essay topic, present your thesis statement, and aim to engage the reader with captivating facts. Providing the necessary context and introducing supporting evidence help your audience grasp the essence of your focal sentence.
First Body Paragraph
Dedicate a separate passage for each supporting point you make. While the traditional five-paragraph structure is often considered standard, you may require more subsections to convey your thesis statement thoroughly.
Second Body Paragraph
Write smooth transitions between verses using appropriate transition words and sentences. These transitional elements convey the relationships between subparagraphs, clarifying the purpose of each point and its contribution to your overall argument.
Third Body Paragraph
As you approach the final writing clause, focus on transitioning to your conclusion. Avoid premature summarization; instead, offer insightful details comparable to your earlier items.
In the concluding section, restate your thesis statement and succinctly recap the key points covered in your body. Ensure a cohesive closure, addressing any remaining questions your professor might have and tying up loose ends neatly.
Expository Essay Writing Tips
While you now have a solid understanding of the expository essay format, there are additional considerations to bear in mind. This section will guide you through specific steps to take when tackling the task of writing an expository essay.

Do Your Research
Start by thoroughly reviewing the assignment guidelines to ensure a clear understanding of requirements, including potential topic restrictions and word counts. Consider writing down different concepts aligned with the types of expository essays and gauge which type best suits your chosen theme. Reflect on class discussions, teacher expectations, and personal interests to generate a list of potential questions. Conduct preliminary research on each topic to evaluate the availability of reputable sources and deepen your understanding, leading to a well-informed and engaging expository essay subject.
Create an Outline
Once you've selected a topic, initiate research with a focus on developing body paragraphs, considering three main ways to explain the topic. While researching, contemplate potential thesis statements, allowing them to evolve organically with the accumulation of evidence. Develop an expository essay outline, organizing information under the relevant chapters to streamline the writing process. Writing a preliminary thesis statement by the end of the planning stage provides a clear direction for your research and writing.
Prepare the First Draft
Now is the time to translate your outline into full sentences. It is often useful to leave the introduction till the end because after writing the central paragraphs, you will have a better idea of what to say in an introduction, but make sure that you write down your thesis statement. Use the information you have found to create a cohesive analysis of the topic in each paragraph. Make sure that the information you present is on point and connects to the other facts around it. Think about what the purpose of each body section is and question whether the info you are presenting fits that purpose or not. Make sure to use transition words within the paragraph and transition sentences between paragraphs to improve overall comprehensibility and flow.
Finish the Draft
Go over the first draft of the expository essay and focus on whether the different paragraphs make sense or not. Don't be afraid of writing sections over or completely getting rid of some pieces of information. As you write your draft, new ways of expressing the testimony that will make the overall text more powerful can come to mind. Make sure that you are not trying to make a persuasive argument and that you are using facts rather than opinions as evidence.
Check each sentence to make sure that it is clear and that it fits the purpose of the paragraph it is in. Look at the details you have included and ensure they are useful and enhance your understanding of the topic. It is better to have less information than more if the supporting data is distracting or does not add anything to the expository essay. Try to read the paper as if it is the first time you are coming across the subject matter to see if it makes sense or not. Congratulations, you are just one step away from writing and submitting an A-grade expository paper!
Revise the Document
As the writing stage is over, scan through the final draft of your expository essay to check for formatting errors, grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, etc., and make sure that it complies with all the guidelines of the assignment. Finally, ask a friend or relative to go over the paper to do the last check. If you feel like you still need to make a lot of changes, don't be disheartened, spend the extra time to consult our persuasive essay guide for more insights.
Expository Essay Example
In this section, we’d like to present an example of an expository essay written by one of our writers. Check it out, get inspired, and you’ll be able to write a composition of your own!

FAQs About Expository Essays
What is the purpose of an expository essay, how to start an expository essay, how to write a thesis for an expository essay, how to write a conclusion for an expository essay, how are a persuasive essay and an expository essay different.
Mark Bradford , a passionate and talented artist, utilizes his innovative spirit to support academic pursuits. In partnering with EssayHub, he leverages his artistic insights to assist students as a professional essay writer, helping them navigate and complete their academic assignments at every level of difficulty.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
How to Write an Expository Essay: Definition, Outline, Writing Tips, and Examples

In the realm of academic writing, this type of essay stands as a beacon of clarity, demanding writers to illuminate a subject with precision and objectivity. Whether you're a seasoned essayist or a student embarking on your first exploration of this genre, mastering the art of expository writing is a valuable skill that transcends disciplines. This form of essay invites you to delve into expository essay topics, dissect their intricacies, and present your findings in a straightforward manner.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the terrain of expository writing, unraveling the techniques and strategies that transform a mere composition into a beacon of insight. From understanding the fundamental principles to honing your ability to craft a compelling thesis, join us on a journey that promises to demystify the process of writing, empowering you to articulate ideas with clarity and purpose. Or, you can get our essay writing help and take care of other important tasks set for today.
What Is an Expository Essay
An expository essay is a form of academic writing that aims to elucidate, clarify, and present a balanced analysis of a particular topic or idea. Unlike other essay types that may delve into personal opinions or narratives, the expository essay emphasizes objectivity and factual accuracy. The primary objective is to provide a clear and comprehensive explanation of the chosen subject, exploring its various facets, presenting evidence, and ensuring a logical progression of ideas.
.webp)
According to an expository essay definition, this genre requires the writer to delve into research, organize information systematically, and deliver a coherent and informative piece that educates the reader on the chosen topic. Whether investigating a scientific concept, historical event, or literary work, it serves as a vehicle for conveying knowledge in a concise, lucid manner.
Expository Essay Examples
An expository essay example serves as a valuable tool for students, offering a concrete illustration of the structure, style, and depth expected in this genre of writing. By studying examples, students gain insights into effective thesis formulation, organizing ideas within paragraphs, and integrating supporting evidence to bolster arguments.
Additionally, examples showcase how to balance factual accuracy and engaging prose, providing a model for clear and concise communication. Students can draw inspiration from the content and presentation of well-crafted expository essays, honing their own skills in research, analysis, and effective expression. By the way, we have an interesting autobiography example , so check it out!
Example 1: “The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence”
This expository essay explores the multifaceted evolution of artificial intelligence (AI), examining its historical roots, contemporary applications across various industries, and the consequential societal impact. It provides a comprehensive overview of AI's journey from philosophical debates and early computational developments to its current role as a transformative force in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and entertainment. Additionally, the essay addresses ethical considerations surrounding the widespread adoption of AI, including concerns related to job displacement, privacy, and responsible development. Ultimately, it navigates the complex landscape of artificial intelligence, shedding light on its remarkable advancements and its challenges to our ever-changing society.
Example 2: “The Benefits of Outdoor Education for Children”
This essay highlights the advantages of outdoor education for children, emphasizing its positive impacts on their physical, mental, and social development. It argues that outdoor activities like hiking, camping, and team sports not only promote physical health by encouraging movement and reducing sedentary behavior but also contribute to mental well-being by providing a respite from everyday stressors and fostering a connection with nature. Furthermore, it suggests that exposure to outdoor environments cultivates environmental awareness and a sense of stewardship among children.
Need some help with your homework?
Get help from our expository essay writing service ! Leave us a notice and we'll make your tasks asap.
Types of Expository Essay
Expository essays come in several distinct types, each serving a unique purpose and requiring specific approaches to convey information effectively. One common categorization includes:
- Descriptive Expository Essay. This type focuses on painting a vivid picture of a subject, using sensory details to engage the reader's imagination. It aims to create a clear and sensory-rich portrayal of a person, place, object, or experience.
- Process Expository Essay. Here, the writer breaks down a complex process or procedure into manageable steps, providing a detailed and sequential explanation. This type of essay is instructional, guiding readers through a series of actions to achieve a specific outcome.
- Comparison and Contrast Expository Essay. This form involves analyzing similarities and differences between two or more subjects, offering insights into their shared characteristics or divergent qualities. It requires a careful examination of the chosen elements to highlight their relationships.
- Cause and Effect Expository Essay. Focused on exploring the reasons behind an occurrence and its subsequent consequences, this type delves into the cause-and-effect relationships within a given topic. Writers elucidate the connections between actions and outcomes, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Problem and Solution Expository Essay. Addressing real-world issues, this essay type identifies a specific problem, analyzes its root causes, and proposes viable solutions. It encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, compelling readers to consider alternative approaches to challenges.
- Definition Expository Essay. This essay seeks to clarify and explain the meaning of a particular term, concept, or idea. Writers provide a comprehensive definition, often including examples and illustrations to ensure readers grasp the essence of the subject.
- Cause and Effect Expository Essay. This type of essay examines the reasons behind a particular phenomenon or event and explores its subsequent effects. It aims to establish a clear cause-and-effect relationship, allowing readers to comprehend the interconnected elements of the topic.
Understanding these diverse types of essays empowers writers to choose the most suitable approach for effectively conveying information and achieving their communicative goals. Our experts can rewrite essay that you already did according to any of the above-mentioned types.
Expository Essay Topics
Selecting compelling expository essay topics requires thoughtful consideration of both personal interest and the potential engagement of the intended audience. Start by identifying subjects that genuinely captivate your curiosity or align with your expertise, as this enthusiasm will naturally infuse vigor into your writing. Additionally, assess the topic's relevance in the broader context, ensuring it addresses contemporary issues or timeless themes.
Consider the audience's interests, aiming for subjects that resonate with their experiences or evoke a sense of shared relevance. Striking a balance between uniqueness and accessibility is key—opt for topics that allow you to offer fresh perspectives while ensuring there is ample research material available. Ultimately, the best topics seamlessly blend your passion, the audience's interests, and the broader significance of the chosen subject, ensuring a captivating and informative exploration for both writer and reader alike. Here are expository essay ideas from our writers for your inspiration:
.webp)
- The influence of art on human emotions.
- Exploring the life cycle of a star.
- Tips for sustainable living in urban areas.
- The impact of social media on political awareness.
- How to cultivate a positive mindset in challenging times.
- The history and cultural significance of tattoos.
- The process of recycling electronic waste.
- Benefits of incorporating meditation into daily routines.
- The role of laughter in maintaining mental health.
- Understanding the psychology of decision-making.
- The impact of fashion on individual expression.
- Tips for effective conflict resolution in relationships.
- The science behind the sense of taste.
- The significance of biodiversity in ecosystems.
- Exploring the history of traditional folk music.
- How to foster a sense of community in a neighborhood.
- The benefits of learning a musical instrument.
- The evolution of communication technologies.
- The process of seed germination in plants.
- Tips for creating a productive home office space.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on job markets.
- Understanding the concept of emotional intelligence.
- The benefits of practicing gratitude daily.
- The history and cultural importance of tea.
- How to develop effective public speaking skills.
- Exploring the world of virtual reality technology.
- The significance of water purification methods.
- Tips for maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
- The process of making sustainable food choices.
- The role of literature in shaping societal norms.
Expository Essay Outline
An outline for expository essay is a structured plan that serves as a roadmap for organizing the main ideas and supporting details of the essay in a logical and coherent manner. While the specific structure may vary based on the assignment or preferences, a typical outline generally includes the following components, beginning with how to start an expository essay:
.webp)
Expository Essay Introduction
- Hook or attention-grabbing statement.
- Background information on the topic.
- Clear thesis statement that presents the main idea.
Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Topic sentence for each paragraph, presenting a main point or supporting idea.
- Supporting evidence, facts, or examples to illustrate and explain the topic sentence.
- Analysis or interpretation of the evidence to connect it back to the thesis.
Expository Essay Conclusion
- Restatement of the thesis in different words.
- Summary of the main points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Concluding thoughts or insights, possibly suggesting implications or future considerations.
Transitions
- Smooth transitions between paragraphs to ensure a cohesive flow of ideas.
- Clear connections between sentences and paragraphs to guide the reader through the essay.
Revising and Editing
- Space for notes on areas that may need revision or improvement.
- Consideration of clarity, coherence, and overall effectiveness.
By creating an expository essay outline, a college essay writer can organize their thoughts, ensure a logical progression of ideas, and maintain a clear and concise structure. This framework helps writers stay focused on the main purpose of the essay – to inform, explain, or analyze a particular subject – while providing a roadmap for readers to follow and comprehend the information presented.
How to Write an Expository Essay Step by Step
Writing an expository essay involves a systematic process that ensures clarity, coherence, and effectiveness in conveying information. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft an expository essay:
Choose a Topic
- Select a topic that interests you and aligns with the purpose of an expository essay – to inform, explain, or analyze a subject.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant and credible information to support your chosen topic.
- Utilize reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and reliable websites.
Create an Outline
- Develop a clear and organized outline that includes the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Each section should have a specific purpose and contribute to the overall coherence of the essay.
Write the Introduction
- Start with an attention-grabbing hook that relates to your topic.
- Provide background information and context, leading to a concise and focused thesis statement that outlines the main idea.
Develop Body Paragraphs
- Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point.
- Support the topic sentence with evidence, facts, or examples.
- Ensure a logical flow between paragraphs, using transitions to guide the reader.
Provide Evidence
- Support your points with credible evidence and examples.
- Ensure that each piece of evidence directly relates to the topic sentence and supports the overall thesis of the essay.
Analyze and Interpret
- After presenting evidence, analyze and interpret it.
- Explain the significance of the evidence and how it relates to your thesis.
- This step helps to ensure that your audience understands the relevance of the information presented.
Write the Conclusion
- Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs without introducing new information.
- Restate the thesis in different words and offer concluding insights or implications related to the topic.
Revise and Edit
- Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency.
- Check for grammatical errors and awkward phrasing, ensuring a smooth flow of ideas.
- Consider feedback from others or take a break before revising to gain a fresh perspective.
- Carefully proofread your essay to catch any remaining errors, typos, or issues.
- Pay attention to grammar and punctuation.
By following these steps, you can systematically approach the writing process and create a well-organized and informative expository essay. Remember to stay focused on the purpose of informing, explaining, or analyzing the chosen topic throughout the entire writing process.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to write an expository essay offers students several important advantages. First off, it helps them express their thoughts clearly and organize ideas effectively, skills that are useful not only in academics but also in various professional situations where clear communication is key.
Moreover, writing expository essays improves critical thinking as students practice analyzing information, connecting ideas, and presenting well-supported arguments. This skill is valuable in everyday decision-making and problem-solving scenarios.
Additionally, the process of crafting such essays enhances research abilities, teaching students how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively. Overall, mastering expository writing equips students with practical, transferable skills that can positively impact their academic and professional pursuits. You can use our research paper service to cope with assignments better and faster.
Want to Ace Your Expository Writing?
Your wish is our command - order now and experience the excellence of our expert writers!
What are the Different Types of Expository Essays?
What is the most important part of the expository essay structure, what is the main idea in expository writing.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
- How to Order
Expository Essay
Complete Guide to Expository Essays: Writing Help and Topics
12 min read
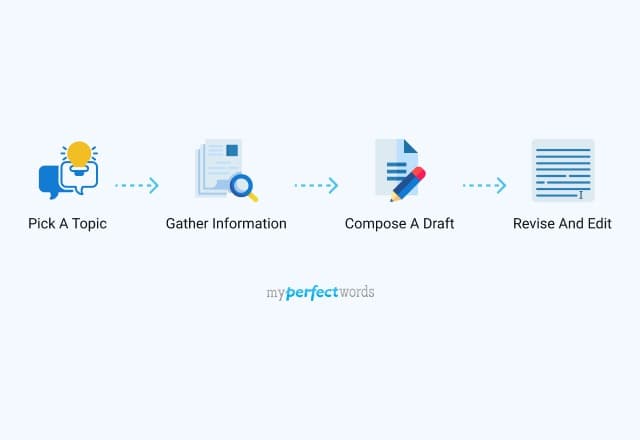
People also read
Interesting Expository Essay Topics For Your Next Paper
How to Write an Expository Essay Outline Like a Pro
Types of Expository Writing - Definition and Examples
Free Expository Essay Examples For Students
Ultimate Guide to Writing an Expository Essay About a Person
Learn to Write an Expository Essay About Yourself
Learn the Basics of Crafting an Expository Essay about a Book
Learn to Write Expository Essay About Mental Health - Examples & Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay about Bullying: A Guide
Expository Essay About Dogs: Steps, Examples & Topics
A Guide to Writing an Expository Essay about Education
Expository Essay About Friendship: A Writing Guide
Discover How to Write Expository Essays About Music – A Step-by-Step Guide
Writing essays can be a real challenge for many students. They often struggle to organize their thoughts and convey them clearly in expository essays.
This struggle leads to essays that lack clarity and fail to captivate the reader’s interest.
But worry not! This guide is your go-to helper. We're going to break down the ins and outs of expository writing using simple steps. Plus, we’ve included some tips and topic ideas, so you can craft essays that are both clear and engaging!
So, keep reading!
- 1. What is an Expository Essay?
- 2. Types of Expository Essay
- 3. Structure of an Expository Essay
- 4. How to Write an Expository Essay?
- 5. Expository Essay Example
- 6. Expository Essay Topics
- 7. Tips for Writing a Good Expository Essay
What is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is a type of essay that aims to inform, describe, or explain a particular subject or topic.
It's different in its approach as it focuses on presenting facts and analyzing information. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding without adding personal opinions or biases.
Why Write an Expository Essay?
The purpose of writing an expository essay is to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a specific topic in a clear and straightforward manner.
This type of essay aims to present facts, provide explanations, and offer insights. It avoids the writer's personal opinions, enabling readers to understand the subject thoroughly.
Types of Expository Essay
Expository essays come in various forms, each designed to explain or inform in different ways.
Here are the main types of expository essays:
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays aim to create a detailed image or sensory experience in the reader's mind by vividly describing a particular place, object, person, or event.
They use rich language and sensory details to paint a clear picture and evoke emotions, making the reader feel like they're experiencing what's being described.
Process Analysis Essays
In a process analysis essay , the writer breaks down a series of steps needed to achieve a specific task or goal.
They provide a clear, step-by-step guide, making complex tasks easy to understand. For example, they might explain how to bake a cake, fix a bicycle, or perform a scientific experiment.
Compare and Contrast Essays
Compare and contrast essays focus on exploring the similarities and differences between two or more subjects.
They present a balanced view, showing how things are alike and how they're different. Whether it's comparing different cultures, products, historical events, or ideas, these essays aim to offer insights into relationships and contrasts.
Cause and Effect Essays
Cause and effect essays delve into examining the causes that lead to specific effects or the effects that arise from certain causes.
They analyze the relationship between events, explaining why things happen and what outcomes result from those actions or occurrences. They aim to provide a clear understanding of the connections between different elements.
Problem and Solution Essays
Focused on a specific issue, problem and solution essays identify a problem, its causes, and effects, and propose solutions to address and resolve the problem.
They aim to offer practical, effective solutions to real-life issues, providing a roadmap for solving problems or improving situations.
Structure of an Expository Essay
An expository essay typically has three main components: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Here's what the general structure of an expository essay looks like:
Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay is where the writer presents the topic, provides background information, and ends with a clear thesis statement .
This section aims to grab the reader's attention and set the stage for the discussion that follows.
Body Paragraphs
The body of the essay contains a series of paragraphs that delve deeper into the topic.
Each paragraph should begin with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea or argument.
These body paragraphs present evidence, examples, or explanations supporting the thesis statement. Smooth transitions between paragraphs ensure a coherent flow of information.
The conclusion of an expository essay restates the thesis statement using different wording. It summarizes the key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
Finally, it offers a sense of closure, wrapping up the essay's main ideas. It's not just a repetition of earlier information but rather a synthesis of the key points to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Here’s a standard expository essay format:
|
How to Write an Expository Essay?
Writing an expository essay involves a step-by-step process to effectively communicate information. Here's a guide to crafting an expository essay:
Select a Topic
When selecting a topic for an expository essay, it's crucial to choose something that's not only interesting but also suitable for an informative discussion.
Consider the following pointers while choosing an expository essay topic:
- Select a topic that personally interests you.
- Choose a topic that can be explained within the essay's scope
- Choose subjects allowing for an objective, fact-based analysis.
- Consider prevalent issues or areas of curiosity for discussion.
Conduct Research
When researching for your expository essay, explore diverse and credible sources like books, scholarly articles, and reputable websites.
Ensure the information gathered directly relates to your topic and is from reliable sources. Verify the credibility by checking the author's credentials and publication dates.
Consider various perspectives to present a well-rounded view. Organize your findings systematically, keeping detailed notes for citation. This approach helps in crafting a well-informed and supported expository essay.
Create an Outline
Develop a structured outline for your essay. Organize your thoughts, decide on the main points, and arrange them logically.
An engaging opening statement or question to capture the reader’s attention. Brief context or background information on the topic. A clear, concise statement outlining the main point or argument of the essay.
Introduce the main idea of the paragraph. Provide supporting details or examples. Explain how the evidence supports the topic sentence. Smoothly lead to the next paragraph. Introduce the main idea of the paragraph. Provide supporting details or examples. Explain how the evidence supports the topic sentence. Smoothly lead to the next paragraph. Introduce the main idea of the paragraph. Provide supporting details or examples. Explain how the evidence supports the topic sentence. Smoothly lead to the conclusion. Summarize the main argument using different wording. Recap the main points from the body paragraphs. Offer a final thought or call to action to leave a lasting impression on the reader. |
This outline template provides a clear structure, allowing for a well-organized and coherent expository essay.
View this in-depth guide on creating an expository essay outline for a structured essay!
Write The Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay plays a pivotal role in engaging the reader and setting the stage for the discussion. Here are the essential components:
- Engaging Hook : Begin your essay with a captivating fact, question, quote, or story related to the topic to captivate the reader's attention and encourage them to continue reading.
- Background Context: Offer essential background information about the topic, providing the necessary context for the reader to understand its relevance and importance.
- Clear Thesis Statement: End the introduction with a clear thesis statement. It should express the main idea or argument of your essay. This statement helps guide the reader, indicating the purpose and direction of your essay.
Compose Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs serve as the essay's core.
Each paragraph starts with a topic sentence introducing the main idea. Back up this idea with evidence or examples to support your point.
Make sure each paragraph smoothly connects to the next for a logical flow of ideas. This structured approach ensures a coherent and well-supported discussion throughout your expository essay.
Write the Conclusion
In the conclusion of your expository essay, recap the main points without introducing new information.
Restate the thesis in different words to reinforce the main argument. Additionally, offer closing thoughts or discuss the broader implications related to the topic. This section serves as a summary, emphasizing the significance of the essay's ideas and their broader relevance.
Revise and Edit
Revision and editing are crucial steps in the essay writing process.
Review the content for coherence and logical flow, ensure the essay structure is smooth and well-organized, and focus on clear, concise language.
Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, verify citations, and seek feedback for improvements. Finally, perform a final proofread to ensure the essay is error-free and polished for submission.
Expository Essay Example
Below is an example illustrating the concept of climate change and its effects, exploring the causes, impacts, and potential solutions.
|
Here is another expository essay sample:
Expository Essay PDF
Need more examples? Check out these expertly crafted expository essay examples on multiple topics and themes!
Expository Essay Topics
Expository essay topics typically revolve around subjects that can be explained, clarified, or described without personal opinions.
You can pretty much write an expository essay about anything, including a person, any piece of music , a book or themes like education , bullying , mental health or friendship . These topics should allow for in-depth exploration.
Here are some essay topics for students:
Expository Essay Topics for High School Students
- The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers
- Benefits of Exercise and Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Exploring Climate Change: Causes and Effects
- The Importance of Education in Today's Society
- Understanding Cyberbullying and its Impact
- Analyzing a Historical Event: The Civil Rights Movement
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of E-Learning
- Explaining the Process of Photosynthesis
- The Effects of Video Games on Adolescents
- The Role of Leadership in Problem Solving
Expository Essay Topics for University Students
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence and its Ethical Implications
- Analyzing the Impact of Globalization on World Economies
- Climate Change: Policy Interventions and Global Strategies
- The Psychology Behind Procrastination and Ways to Overcome It
- Exploring Renewable Energy Sources and Their Viability
- The Evolution of Social Media and its Societal Impact
- Gender Disparities in the Workplace: Causes and Solutions
- The Effects of Stress on Mental Health in Modern Society
- Analyzing the Influence of Cultural Diversity in Global Business
- Understanding Quantum Mechanics: Principles and Applications
Can’t pick a topic? Have a look at these extensive expository essay topics and get more ideas!
Tips for Writing a Good Expository Essay
Here are some tips for writing a good expository essay:
- Ensure the essay has a clear and narrowly defined topic for effective exploration.
- Present facts, statistics, and evidence without incorporating personal opinions or biases.
- Utilize a well-structured format with logical sequencing of ideas and paragraphs.
- Provide detailed and comprehensive explanations to support each point or idea.
- Use diverse and relevant examples to illustrate and reinforce key points.
- Present information in a concise and easily understandable manner, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Use transitional words and phrases for seamless connections between paragraphs and ideas.
- Make sure that all information presented is relevant and sourced from credible, reputable materials.
With our steps, tips, and topics, you have all you need to get started on your expository essay.
If you're still encountering challenges in composing your expository essay, our essay writing service is here to offer custom essay help .
Our proficient writers specialize in creating well-structured, informative expository essays. With our expert support, you can be sure you’ll receive a top-quality, plagiarism-free essay.
Reach out to our expository essay writing service today to get the help you need. Place your order today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Free Al Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
- Articles of Word
How to Write an Introduction Paragraph: Examples and Guide
There are times when an introduction predicts what your entire essay will say—it’s essentially a reflection. If done successfully, it grabs the reader’s attention and entices them to read further into the essay. As a writer, I know the importance of a strong and engaging introduction, and with practice, I have excelled in the art of writing a good intro. Here’s how you can write a compelling introduction with examples.
The Purpose of the Introduction Paragraph
A good introduction serves as a roadmap for your essay, setting the stage for what is to come. Its primary purpose is to grab the reader’s attention, provide necessary background information, and clearly state the main argument or thesis of the essay. By doing so, it helps the reader transition from their own world into the context of your analysis, making them interested in reading further. A well-written introduction also outlines the structure of the essay, ensuring that the reader knows what to expect in the body paragraphs. This initial section is crucial for making a strong first impression, establishing the tone, and demonstrating the quality and direction of your work. A good introduction paragraph should be able to:
Engage the Reader: Capture interest with an intriguing opening sentence or a compelling story.
Provide Context: Offer background information needed to understand the topic.
State the Thesis: Clearly present your main argument or thesis statement.
Outline the Structure: Briefly mention the main points or sections covered in the essay.
Establish Relevance: Explain why the topic is important and worth discussing.
Set the Tone: Establish the style and tone of your writing.
Write an Introduction Paragraph
An introduction paragraph sets the tone for your entire essay, shaping your reader's expectations and mood. It's like the gateway to your ideas - a good one hooks the reader, compelling them to continue, while a weak introduction might make them lose interest before they've even begun. That's why learning how to start an introduction paragraph for an essay is crucial for students and writers alike.
With tools like WPS Office at your fingertips, you're not just getting a word processor, but an AI assistant to guide you through the entire journey of crafting that perfect opening. In fact, I'll be using WPS Office for this tutorial to demonstrate its features. So, let's dive in and explore how to write an essay introduction step by step:
The hook is the opening sentence or a few sentences of an essay designed to grab the reader's attention and entice them to keep reading. It serves to engage the reader by presenting something intriguing, surprising, or relevant to the essay's topic.
The main purpose of the hook is to spark the reader's interest and make them want to read more. It's the first impression the reader gets, so it needs to be compelling and relevant to the essay's subject.
1.Start with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: Begin with an interesting or shocking fact that relates to your topic. This immediately grabs the reader's attention.
Bad Example: "Drunk driving is a serious issue."
Good Example: "Every year, over 1.25 million people die in car accidents, many of which are caused by drunk driving."
2.Use a Quote: Introduce your essay with a relevant quote that encapsulates your main point.
Bad Example: "Drunk driving is defined as driving while impaired by alcohol."
Good Example: “At eighteen, Michelle had a lifetime of promise in front of her. Attending college on a track scholarship, she was earning good grades and making lots of friends. Then one night her life was forever altered…”
3.Pose a Rhetorical Question: Ask a question that provokes thought and engages the reader.
Bad Example: "Have you ever driven a car?"
Good Example: "What if every time you got behind the wheel, you risked not only your life but the lives of others?"
4.Tell an Anecdote or Story: Share a brief, compelling story that relates to your topic.
Bad Example: "I once heard a story about a drunk driver."
Good Example: "At eighteen, Michelle had a lifetime of promise in front of her. Attending college on a track scholarship, she was earning good grades and making lots of friends. Then one night her life was forever altered..."
If you need ideas to help you improve on the hook for your introduction, consider providing WPS AI with a prompt such as:
"Write an introduction on the topic 'Risks of Driving Intoxicated' and provide four individual hooks: one with a surprising fact, one using a quote, one with rhetorical questions, and one through telling an anecdote."
WPS AI will produce a catchy hook statement that you can use for your introduction, such as:
Background Information
Background information provides the reader with the necessary context to understand the essay's topic. This may include historical, geographical, or social context, definitions of key terms, or an outline of the debate surrounding the topic.
The background helps to bridge the gap between the hook and the thesis statement. It gives the reader the context they need to understand the main argument of the essay and why it's important.
1.Provide Context: Explain the broader context of your topic to show its significance.
Bad Example: "Drunk driving is bad."
Good Example: "Michelle's story is not isolated. Each year, over 1.25 million people die in car accidents, many of which are caused by drunk driving."
2.Introduce Key Terms and Concepts: Define any terms or concepts that are crucial to understanding your thesis.
Bad Example: "Drunk driving is when you drink alcohol and drive."
Good Example: "Drunk driving, legally defined as operating a vehicle with a blood alcohol content (BAC) of 0.08% or higher, is a preventable cause of many fatalities."
3.Set Up the Problem: Briefly discuss the scope of the issue or debate you will be addressing.
Bad Example: "People drive drunk sometimes."
Good Example: "Despite strict laws, drunk driving continues to be a significant problem worldwide, leading to devastating consequences for victims and their families."
To give an effective and detailed background information in your introduction consider proving WPS AI with a prompt like this:
“This serves as the background to my introduction: 'People frequently choose to drive under the influence of alcohol.' Please enhance it to address the problem and discuss its scope."
WPS AI will produce a detailed background passage for your introduction, give as:
Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of the essay. It usually appears at the end of the introduction and states the essay's central argument or position.
The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay by informing the reader what the essay will argue or discuss. It sets the tone and focus of the entire paper.
1.Be Clear and Specific: Clearly state your main point and how you will support it.
Bad Example: "This essay will talk about drunk driving."
Good Example: "Drunk driving laws need to include stricter penalties for those convicted of driving under the influence of alcohol to reduce accidents and save lives."
2.Make an Argument: Present a claim that requires evidence and can be debated.
Bad Example: "Drunk driving is bad and should be stopped."
Good Example: "Implementing harsher penalties for drunk driving will deter offenders and significantly decrease the number of alcohol-related accidents."
3.Outline Your Main Points: Indicate the main points you will cover in your essay to support your thesis.
Bad Example: "I will discuss the problems with drunk driving."
Good Example: "Stricter penalties are necessary because they act as a deterrent, they can prevent repeat offenses, and they provide justice for victims."
You can take help from WPS AI to extract the thesis statement of your essay using the WPS AI chat box.
Step 1: Click on the WPS AI widget at the top corner of the WPS Writer interface.
Step 2: The WPS AI pane will open on the right side of the screen. Type in your prompt to extract the thesis statement of your essay and then paste the essay.
Here is a prompt example that you can use:
"Extract the thesis statement from the following essay:"
Step 3: WPS AI will provide the thesis statement. To refine it further, engage with the WPS AI chatbot by asking more questions or queries.
The summary or road map briefly outlines how the essay will be structured. It provides a preview of the main points that will be covered, giving the reader a sense of the direction of the argument.
1.Summarize Main Points: Briefly mention the key arguments or points you will discuss in your essay.
Bad Example: "I will talk about drunk driving laws, penalties, and justice."
Good Example: "This essay will first examine the current state of drunk driving laws, then explore the impact of stricter penalties on reducing incidents, and finally discuss how these penalties can bring justice to victims."
2.Be Concise: Keep it short and to the point, providing a clear outline without going into too much detail.
Bad Example: "I will write about drunk driving and why it is bad."
Good Example: "By examining the effectiveness of current laws, the potential benefits of stricter penalties, and the importance of justice for victims, this essay argues that harsher punishments for drunk driving are essential."
“Write a concise summary for the introduction of an essay on the topic "Risks of Driving Intoxicated." The summary should briefly mention the key points that will be covered in the essay, without going into too much detail."
The summary should briefly outline the main points covered in the essay, emphasizing the societal impact, legal ramifications, and personal consequences of driving under the influence. Ensure clarity and coherence, setting the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the topic in the subsequent sections.
Examples of Different Essays
Essays come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose and following specific structures. Understanding these different types can help you write an essay introduction more effectively. Let's explore three common types of essays: Argumentative, Expository, and Literary. Each example below demonstrates the key elements of its respective essay type, including the hook, background information, and thesis statement.
Argumentary
An argumentative essay aims to present a position on a topic and support it with evidence.
An expository essay explains a topic in a clear and concise manner without arguing a specific position.
A literary essay analyzes and interprets a work of literature, focusing on elements such as theme, character, or style.
More Examples of Different Topics
Let's take a look at some sample introductions of essays in different disciplines. This will further help you in writing an effective essay introduction.
Example #1 Medicine
Example #2 literature, example #3 social sciences, example #4 engineering, example #5 business & marketing, using wps ai to perfect your introduction.
With WPS Office, you have access to a comprehensive suite of tools designed to support your academic writing needs. Its AI-powered features enhance your writing process, from initial drafting to final proofreading. Specifically, WPS Office AI will help perfect your introduction, ensuring it captures attention and sets the stage for your paper. Plus, WPS Office is available for free, making it an accessible and indispensable resource for students and academics alike.
1.Check the Grammar and Syntax
Your introduction sets the tone for your entire essay, so it's crucial that it's grammatically correct and free from syntax errors. WPS AI careful checks for any grammatical mistakes and syntax issues, ensuring that your introduction is polished and professional. It provides suggestions for corrections, helping you present a clear and error-free first impression.
2.Rewrite Your Statement for Clarity
WPS AI can improve the clarity and coherence of your introduction by rewriting complex or awkwardly phrased sentences. It identifies areas where your writing may be ambiguous or convoluted and offers alternative phrasing that enhances readability. This feature ensures that your introduction is clear, concise, and compelling.
3.Automatically Expand Content
When you need to elaborate on a point or expand your introduction, WPS AI can automatically generate additional content. This feature helps you add relevant information that aligns with your essay's theme and tone. It’s particularly useful for developing a strong hook, providing context, or setting up your thesis statement.
4.Give an Outline for Your Paper
Writing a strong introduction often involves giving your readers a brief outline of what to expect in your essay. WPS AI can assist in structuring your introduction to include a concise overview of your main points, providing a roadmap for your readers. This feature ensures that your introduction effectively sets the stage for the rest of your essay. Here is an example of an outline generated using WPS AI Writer for an essay:
If you find this outline suitable for your essay, simply scroll down and click on "Insert" to use the outline for your essay.
1. What is the structure of an essay?
An essay is divided into three main parts:
Introduction: This section introduces the topic and presents the main idea (thesis). It provides some background information and outlines what the essay will discuss.
Body: The body forms the essay's core, where you develop arguments to support your thesis. It is organized into several paragraphs, each presenting a distinct point backed by evidence.
Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points covered in the essay and strengthens the thesis statement. It wraps up the discussion and may offer final insights or suggestions.
2. Why do I need a thesis statement?
A thesis statement plays a crucial role in academic essays and research papers by presenting the central argument or idea to be explored and developed. Here are several key reasons why a thesis statement is essential:
It provides clear direction and focus for your writing.
It summarizes your main argument for the reader.
It maintains clarity and coherence throughout the essay.
It serves as the foundational basis for structuring the entire essay.
3. How long should the introduction paragraph be?
The introduction paragraph for a research paper typically spans one to two paragraphs. As a general rule, the entire introduction section—which includes the opening paragraph, literature review, and research questions—should constitute approximately 10% to 15% of the paper's total length. This structure allows for a comprehensive yet concise setup of your research topic, providing readers with the necessary context before delving into the main body of your work.
Beyond the Hook: Building a Strong Introduction Paragraph
Writing an introduction is perhaps the most thought-provoking and critical task in crafting any assignment. With the myriad features offered by WPS Office, you can effortlessly create a phenomenal essay introduction. WPS AI enhances this process with tools that ensure clarity, coherence, and creativity. Whether it's organizing your thoughts or refining your language, WPS Office empowers you to craft introductions that captivate readers from the start. Download WPS Office today and experience firsthand how it transforms your writing process into a seamless and impactful journey.
- 1. Free AI Paragraph Writing Tool Generator - No Sign Up
- 2. How to Use Transitions to Start a Paragraph [Tips with Examples]
- 3. Microsoft Word 365 Product Review: Introduction & Alternatives
- 4. Microsoft 365 Copilot: Introduction and tips for using it
- 5. What is PowerPoint: Introduction, Guide and Tips
- 6. HWP Viewers Review: Introduction, Features, How to Use [2024]

15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This format consists of an introduction paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall development of your essay. The introduction paragraph is where you grab the attention of your readers and provide them with a brief overview of what your essay will be about.
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Sections of an Expository Essay. Expository essays are structured in the following manner. Introduction: The introduction, which is the first paragraph, is meant to provide a brief background presenting a global context to the essay as well as the thesis statement. The writer could choose to incorporate a hook in the very first sentence ...
An expository essay is a genre of writing that explores and explains a specific topic in a logical and straightforward manner. The main goals of expository writing are to inform the reader, explain a subject, or describe a topic in a way that is accessible and comprehensible. You're not trying to confuse or overwhelm a reader with all of your ...
The thesis statement for an expository essay should be unbiased and should aim to provide the reader with more information on a topic. Here's an example of an introductory paragraph for an expository essay: Hook; Background information; Thesis statement; The Victorian era, spanning from 1837 to 1901, left an indelible mark on English society.
An expository essay is an essay that communicates factual information. Broadly, this type of writing is known as expository writing. Expository essays rely on different structures to communicate their positions, like compare and contrast, process essays, and analyzing cause and effect. Expository writing is one of the four main types of writing ...
The five-paragraph Essay. A common method for writing an expository essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of: an introductory paragraph; three evidentiary body paragraphs; a conclusion; Resources
That's because the paragraph follows the same structure as a more complex expository essay, just on a smaller scale. Most expository essays should follow this format: Start with an introductory paragraph that includes the thesis statement, which tells the reader the core statement of the essay
3. Structuring an Expository Essay. The exact length and content of your essay will depend on the topic and prompt. However, most expository essays follow a similar basic structure: Introduction - A paragraph where you introduce the essay topic and your thesis statement (i.e., the issue or idea you will explain in the essay).
Suppose you use the five-paragraph model for your expository essay. In that case, the five parts of the paper are the introduction, body paragraph 1, body paragraph 2, body paragraph 3, and the conclusion. What is a good expository essay topic? Picking the right topic depends on what type of expository essay you are writing. Expository essays ...
The Five-Paragraph Essay Writing Approach. An expository essay will require you to take the five-paragraph essay approach: an introductory paragraph, a main body paragraph, and a concluding paragraph. This is often referred to as the hamburger style of the essay because, like a hamburger, it contains five main parts: the introduction and ...
Unlike argumentative or persuasive essays, expository essays do not aim to convince the reader of a particular point of view. Instead, they focus on providing a balanced and thorough explanation of a subject. Key characteristics of an expository essay include: Clarity and Conciseness; Structured Organization (Introduction, Body, Conclusion)
The body of your essay can be anywhere from 2-3 paragraphs to several paragraphs long. As you compose your outline, write down the different headings for your paragraphs so you can see exactly how each one transitions into the next. 4. Write your first draft. Start with an introduction, where you include your thesis statement.
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Learning how to write a good expository essay is an academic writing skill that lays the foundation for the type of expository writing that's necessary for numerous professions.
paragraph is an introduction; the second, third, and fourth paragraphs form the body of the essay; and the fi fth paragraph is a conclusion (see diagram on page 4). This book will focus exclusively on the fi ve-paragraph essay. Although essays may vary in length, the fi ve-paragraph essay structure can be adapted for longer or shorter essays ...
An expository essay is a type of essay that involves explaining an idea or theme within a given subject or topic. We guide you through writing one with examples. Dictionary ... An introduction paragraph that provides a hook, background information, and a thesis statement;
Expository Essay Structure. In academia, expository essays are standard 5-paragraph papers. You write an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below is more information on what to include in every paragraph. Introduction. The introduction of expository essays includes the topic and the main idea. Three elements to write here:
Begin writing an expository essay with a strong introduction that grabs the reader's attention. This can be achieved through a compelling anecdote, a relevant quote, or a thought-provoking question. Clearly state the thesis or main idea of the essay, providing a roadmap for what the reader can expect in the subsequent paragraphs.
Since expository writing may take various forms, understanding the different sorts of essays will help you pick a topic and organize the essay's general trajectory and framework. Process Essays - In a typical process essay, the introduction presents what you will learn, the body paragraphs offer step-by-step instructions, and the conclusion ...
An expository essay asks for a critical explanation of a specific idea, theory, or topic. Our expert tips can help you write a well-structured and informative piece. ... There's certainly some overlap between expository essays and argumentative essays, and some people suggest it comes down to being objective or subjective. ... An introductory ...
An expository essay has three parts: an introduction (with a thesis statement or argument), body paragraphs, and a conclusion that ties the main ideas of what has been said in the essay together.
An expository essay typically has three main components: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Here's what the general structure of an expository essay looks like: Introduction. The introduction of an expository essay is where the writer presents the topic, provides background information, and ends with a clear thesis statement.
Write an Introduction Paragraph. An introduction paragraph sets the tone for your entire essay, shaping your reader's expectations and mood. It's like the gateway to your ideas - a good one hooks the reader, compelling them to continue, while a weak introduction might make them lose interest before they've even begun.