myCBSEguide
- Class 11 Physics Case...

Class 11 Physics Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2024-25, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Looking for complete and comprehensive case study questions for class 11 Physics? myCBSEguide is just a click away! With extensive study materials, sample papers, case study questions and mock tests, myCBSEguide is your one-stop solution for class 11 Physics exam preparation needs. So, what are you waiting for? Log on to myCBSEguide and get started today!
What is the purpose of physics?
Physics is the study of the fundamental principles governing the natural world. It is a vital part of the scientific enterprise, providing the foundation on which other sciences are built. Physics is essential for understanding how the world works, from the smallest particles to the largest structures in the Universe. In class 11 Physics, students are introduced to the basic concepts of physics and learn about the fundamental principles governing the natural world. Class 11 Physics concepts are essential for understanding the world around us and for further study in physics and other sciences.
What are case study questions in physics?
In physics, case study questions are intended to evaluate a student’s ability to apply theoretical principles to real-life situations. These questions usually ask the student to assess data from a specific experiment or setting in order to discover what physical principles are at play. Problem-solving and critical-thinking skills are developed through case study questions, which are an important aspect of physics education.
CBSE Case Study Questions in Class 11 Physics
CBSE Class 11 Physics question paper pattern includes case study questions. Class 11 Physics case study questions assess a student’s ability to apply physics principles to real-world environments. The questions are usually focused on a situation provided in the Class 11 Physics question paper, and they demand the student to answer the problem using their physics knowledge. Class 11 Physics case study questions are an important aspect of the CBSE physics curriculum. Class 11 Physics case study questions are a useful way to assess a student’s expertise in the subject.
Sample Class 11 Physics Case Study Questions
Expert educators at myCBSEguide have created a collection of Class 11 physics case study questions. The samples of Class 11 physics case study questions are given below. Class 11 physics case study questions are designed to test your understanding of the concepts and principles of physics. They are not meant to be easy, but they should be done if you have a good grasp of the subject. So, take a look at the questions and see how you fare. Good luck!
Class 11 Physics Case Study Question 1
Read the case study given below and answer any four subparts: Potential energy is the energy stored within an object, due to the object’s position, arrangement or state. Potential energy is one of the two main forms of energy, along with kinetic energy. Potential energy depends on the force acting on the two objects.
- kinetic energy
- potential energy
- mechanical energy
- none of these
- potential energy decreases
- potential energy increases
- kinetic energy decreases
- kinetic energy increases
- only when spring is stretched
- only when spring is compressed
- both a and b
- 5 × 10 4 J
- 5 × 10 5 J
Answer Key:
Class 11 Physics Case Study Question 2
- distance between body
- source of heat
- all of the above
- convection and radiation
- (b) convection
- (d) all of the above
- (a) convection
- (a) increase
- (c) radiation
Class 11 Physics Case Study Question 3
- internal energy.
- 1 +(T 2 /T 1 )
- (T 1 /T 2 )+1
- (T 1 /T 2 )- 1
- 1 – (T 2 / T 1 )
- increase or decrease depending upon temperature ratio
- first increase and then decrease
- (d) 1- (T 2 / T 1 )
- (b) increase
- (c) constant
Class 11 Physics Case Study Question 4
- It is far away from the surface of the earth
- Its surface temperature is 10°C
- The r.m.s. velocity of all the gas molecules is more than the escape velocity of the moon’s surface
- The escape velocity of the moon’s surface is more than the r.m.s velocity of all molecules
- T(H 2 ) = T(N 2 )
- T(H 2 ) < T(N 2 )
- T(H 2 ) > T(N 2 )
The given samples of Class 11 Physics case study questions will help Class 11 Physics students to get an idea on how to solve it. These Class 11 Physics case study questions are based on the topics covered in the Class 11 Physics syllabus and are designed to test the student’s conceptual understanding. The questions are of varying difficulty levels and cover a wide range of topics. By solving these Class 11 Physics case study questions, students will be able to develop their problem-solving skills and improve their understanding of the concepts.
Examining Class 11 Physics syllabus
Senior Secondary school education is a transitional step from general education to a discipline-based curriculum concentration. The current curriculum of Class 11 Physics takes into account the rigour and complexity of the disciplinary approach, as well as the learners’ comprehension level. Class 11 Physics syllabus has also been carefully crafted to be similar to international norms.
The following are some of the Class 11 Physics syllabus’s most notable features:
- Emphasis is placed on gaining a fundamental conceptual knowledge of the material.
- Use of SI units, symbols, naming of physical quantities, and formulations in accordance with international standards are emphasised.
- For enhanced learning, provide logical sequencing of subject matter units and suitable placement of concepts with their links.
- Eliminating overlapping concepts/content within the field and between disciplines to reduce the curricular load.
- Process skills, problem-solving ability, and the application of Physics principles are all encouraged.
CBSE Class 11 Physics (Code No. 042)
myCBSEguide: A true saviour for many students
myCBSEguide has been a true saviour for many students who struggle to find resources elsewhere. It is a reliable source of information and provides students with everything they need to excel in their academics. myCBSEguide has helped many students score high marks in their exams and has been a valuable resource for their studies. Teachers recommend myCBSEguide to all CBSE students. And best of all, it’s available 24/7, so you can study at your own pace, anytime, anywhere. So why wait? Get started today and see the difference myCBSEguide can make to your studies.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships
Class 11th Physics - Kinetic Theory Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Physics Subject - Kinetic Theory, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

QB365 - Question Bank Software
Kinetic theory case study questions with answer key.
11th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
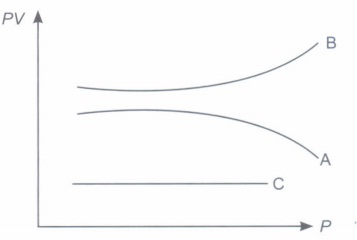
The molecules of a gas move in all directions with various speeds. The speeds of the molecules of a gas increase with rise in temperature. During its random motion, a fast molecule of ten strikes against the walls of the container of the gas. The collisions are assumed to be prefectly elastic i.e., the molecule bounces back with the same speed with which it strikes the wall. Since the number of molecules is very large, billions of molecules strike against the walls of the container every second. These molecules exert force on the wall. The force exerted per unit area is the pressure exerted by the gas on the walls. According to the kinetic theory, the pressure of a gas of density p at absolute temperature T is given by \(P=\frac{1}{3} \rho\) \(v_{r m s}^{2}, \) where v rms is the root mean square speed of the gas molecule and is given by \(v_{r m s}=\sqrt{\frac{3 K_{B} T}{M}}\) where M is the mass of a molecule and KB is Boltzmann constant. (i) State the relation between pressure and kinetic energy of the gas. (ii) On what factors does the average kinetic energy of translation per molecule of the gas depends? (iii) State absolute zero temperature in terms of root mean square velocity of gas. (iv) Define root mean square speed and establish its relation with temperature. (v) The absolute temperature of a gas is made four times. How many times will its total kinetic energy pressure and r.m.s velocity become? (vi) Two different gases have exactly the same temperature. Does this mean that their molecules have the same r.ms. speed? (vii) On reducing the volume of the gas at constant temperature, the pressure of the gas increases. Explain on the basis of kinetic theory.
The number of degrees of freedom of a dynamical system is the total number of co-ordinates or independent quantites required to describe completely the position and configuration of the system. For a dynamical system, the number of degrees of freedom is obtained by subtracting the number of independent relations from the total number of co-ordinates required to specify the position of constituebnt particles of the system. N = 3A - R, where N - number of degrees of freedom of the system. A - number of particles in the system R - number of independent relations among the particles. Each degree of freedom contributes equally In the distribution of the energy associated with each molecule. In thermal equilibrium the energy associated with each molecule per degree of freedom is \(\frac{1}{2} K_{B} T\) . (i) Determine the number of degrees of freedom of a non-linear triatomic molecule. (ii) State law of equipartition of energy. (iii) If a gas has n degrees of freedom, determine the ratio of principal specific heat of the gas. (iv) Determine the energy contributed by a vibrational mode in total energy. (v) Determine the ratio of specific heat for monoatomic gas molecule.
During their random motion, the molecules of a gas often come close to each other. Molecules are perfect elastic spheres and their size is very small compared to the distance between them. Gas molecules undergo elastic collision. Therefore, they cannot move straight unhindered. The paths of molecules keep on getting deflected incessantly. Path of a single gas molecule consists of a series of short zig zag paths of different lengths. These paths of different lengths are called free paths of the molecules and their mean is called mean free path. Mean free path of gas molecules depends on diameter (d) of gas molecule and molecular density (n) as follows \(\lambda=\frac{1}{n \pi d^{2}}\) (i) Define mean free path of gas molecules. (ii) On what factors do the mean free path of gas molecules depends? (iii) What is significance of mean free path? (iv) How many collisions per second does each molecule of a gas make, when the average speed of a molecule is 500 ms -1 and mean free path is 2.66 x 10 - 7 m? (v) Calculate the mean free path of molecules, if number of molecules per cm 3 is 3 x 10 19 and diameter of each molecule is 2A.
*****************************************
Kinetic theory case study questions with answer key answer keys.
(i) In ideal gas 1. the size of the molecule of a gas is zero. 2. there is no force of attraction or repulsion amongst the molecules of the gas. Real gases behave as ideal gas at extremely low pressure and high temperature. (ii) It states that equal volumes of all gases under identical conditions of pressure and temperature would contain equal number of molecules. Avogadro number N A is equal to 6.02 x 10 23 number of molecules which any gas of amount 22.4 litre contains at N.T.P (iii) Boyle's law: States that when temperature of a given mass of a gas is kept constant, its pressure varies inversely as the volume of the gas i.e., PV = constant. Charles's law: When pressure of a given mass of a gas is kept constant, volume of gas varies directly as the temperature of the gas i.e \(\frac{V}{T}\) = constant from Boyle and Charles's law perfect gas equation is PV = nRT, where n-no. of moles of gas. R- Universal gas constant. (iv) Boltzmann constant \(K_{B}=\frac{R}{N_{A}}\) Where R is universal gas constant and N A -Avogadro's constant. \(K_{B}=\frac{8.31 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mole}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}}{6.023 \times 10^{23} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}\) = 1.38 x 10 - 23 JK -1 (v) Gas C is ideal, because PV is constant for this gas. It means the gas C obeys Boyle's law at all pressures.
(i) The pressure exerted by an ideal gas is numerically equal to two third of the mean kinetic energy of translation per unit volume of gas. \(P=\frac{2}{3} E\) (ii) The average kinetic energy of a molecule is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas. It is independent of pressure, volume or nature of the ideal gas. (iii) Absolute zero temperature is that at which the root mean square velocity of the gas molecule reduces to zero i.e., molecular motion ceases at absolute zero. (iv) It is defined as the square root of the mean of the squares of the random velocities of the individual molecules of a gas \(v_{r m s} \text { or } C_{r m s}=\sqrt{\frac{C_{1}^{2}+C_{2}^{2}+\ldots C_{n}^{2}}{n}}=\sqrt{\frac{3 K_{B} T}{M}}\) where K B - Boltz-mann constant, M - Mass of each molecule. (v) Since K.E \(\propto\) Temperature, hence K.E will become four times \(v_{r m s} \propto \sqrt{T}\) hence v rms becomes twice and \(P \propto\left(v_{m s}\right)^{2}\) therefore pressure becomes 4 times. (vi) When the two gases have exactly the same temperature, the average K.E per molecule for each gas is the same. But as the different gases may have molecules of different masses, the r.m.s speed (C) of molecules of different gases shall be different. (vii) On reducing the volume, the number of molecules per unit volume increases. As a result of which more molecules collide with the walls of the vessel per second and hence a larger momentum is transferred to walls per second. Due to which the pressure of the gas increases.
(i) In a non-linear triatomic molecule, the three atoms are present at the three vertices of a triangle, N = 3A - R, Since A = 3, and R = 3 Number of degrees of freedom N = 3 x 3 x 3 = 6 (ii) Law of equipartition of energy states that in thermal equilibrium, at temperature T each mode of energy: translational, rotational, and vibrational, contributes an average energy equal to \(\frac{1}{2} K_{B} T\) . (iii) Ratio of C p and C v of the gas having n degrees of freedom \(\gamma=\frac{C_{P}}{C_{V}}=1+\frac{2}{n}\) . (iv) Each vibrational mode contributes \(2 \times \frac{1}{2} K_{B} T\) total energy, because a vibrational mode has both kinetic and potential energy mode. (v) \(\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{V}}=\frac{3}{2} R, C_{P}=\frac{5}{2} R, \gamma=\frac{C_{P}}{C_{V}}=\frac{5}{3}=1.67\)
(i) Mean free path of gas molecules is the average distance travelled by a molecule between two successive collisions. \(\lambda=\frac{\lambda_{1}+\lambda_{2}+\lambda_{3} \ldots \lambda_{n}}{n}=\frac{\overline{c t}}{n}\) Where c is mean speed of the molecules. (ii) Mean free path of gas molecules depends on number density (n) and area of molecules (d 2 ) as follow \(\lambda=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2} n \pi d^{2}}\) (iii) The concept of mean free path is of great significance in understanding transport phenomena like diffusion, viscosity and thermal conduction. (iv) Here \(\bar{\lambda}\) = 2.66 x 10 - 7 m; v = 500 ms -1 , Number of collision made per second by each molecule of the gas i.e., collision frequency, \(f=\frac{v}{\bar{\lambda}}=\frac{500}{2.66 \times 10^{-7}}=1.88 \times 10^{9} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}\) (v) Here n = 3 x 10 19 cm -3 = 3 x 10 25 m -3 d = 2A = 2 x 10 - 10 m \(\bar{\lambda}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2} \pi d^{2} n}\) \(=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2} \pi \times\left(2 \times 10^{-10}\right)^{2} \times 3 \times 10^{25}}\) = 1.876 x 10 - 7 m
Related 11th Standard CBSE Physics Materials
11th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 11th chemistry structure of atom chapter case study question with answers, cbse 11th chemistry some basic concept of chemistry chapter case study questions with answers, 11th biology biological classification chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th biology the living world chapter case study question with answers cbse, class 11th business studies - internal trade case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th business studies - social responsibilities of business and business ethics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th business studies - emerging modes of business case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th business studies - business service case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th business studies - private, public and global enterprises case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th business studies - business, trade and commerce case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Class 11th Applied Mathematics - Coordinate Geometry Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Class 11th applied mathematics - basics of financial mathematics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - descriptive statistics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - calculus case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

11th Standard CBSE Study Materials

11th Standard CBSE Subjects


Class 11 Physics Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Physics
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Class 11 Physics Case Study Questions are available here. You can read these Case Study questions by chapter for your final physics exam. Subject matter specialists and seasoned teachers created these quizzes. You can verify the right response to each question by referring to the answer key, which is also provided. To achieve high marks on your Board exams, practice these questions.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

We are providing Case Study questions for Class 11 Physics based on the Latest syllabus. There is a total of 14 chapters included in the CBSE Class 11 physics exams. Students can practice these questions for concept clarity and score better marks in their exams.
Table of Contents
Class 11th PHYSICS: Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions play a crucial role in the Class 11 Physics curriculum. They are designed to assess your understanding of various concepts and principles in real-life scenarios. These questions help you apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, enhancing your problem-solving skills.
Case Study-Based Questions for Class 11 Physics
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and Measurements
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 Motion in a Straight Line
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Laws of Motion
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 7 System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 8 Gravitation
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 Thermal Properties of Matter
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 13 Kinetic Theory
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Waves
- Case Study Based Questions on Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Oscillations
Class 11 Physics MCQ Questions
Before the exams, students in class 11 should review crucial Physics Case Study issues. They will gain a better understanding of the kinds of Case Study questions that may be offered in Physics exams for Grade 11. These questions were created by our highly qualified faculty for standard 11 Physics based on the questions that appeared most frequently in last year’s exams. The solutions have been written in a way that will make them simple to grasp and will aid students in grade 11 in understanding the topics.
Class 11 Books for Boards

Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2024
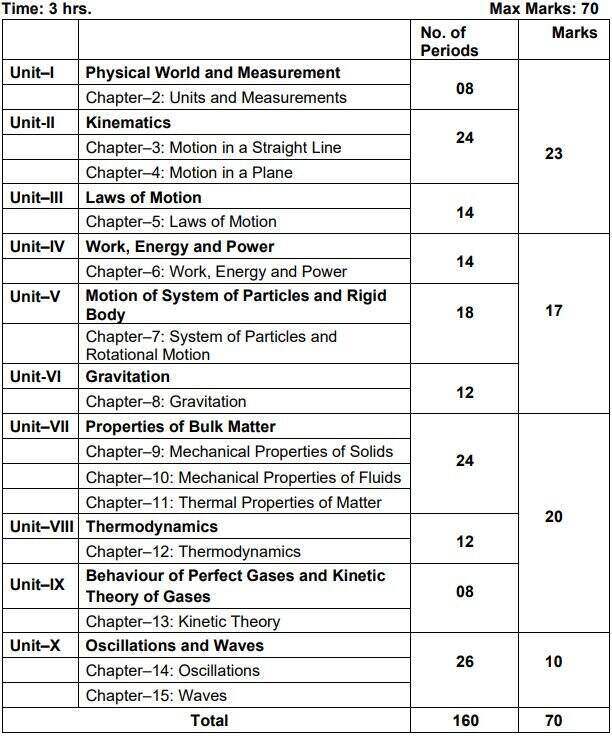
Unit I: Physical World and Measurement 08 Periods
Chapter–2: Units and Measurements
Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental and derived units. significant figures. Dimensions of physical quantities, dimensional analysis and its applications.
Unit II: Kinematics 24 Periods
Chapter–3: Motion in a Straight Line
The frame of reference, Motion in a straight line, Elementary concepts of differentiation and integration for describing motion, uniform and non-uniform motion, and instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated motion, velocity-time and position-time graphs. Relations for uniformly accelerated motion (graphical treatment).
Chapter–4: Motion in a Plane
Scalar and vector quantities; position and displacement vectors, general vectors and their notations; equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; addition and subtraction of vectors, Unit vector; resolution of a vector in a plane, rectangular components, Scalar and Vector product of vectors. Motion in a plane, cases of uniform velocity and uniform acceleration projectile motion, uniform circular motion.
Unit III: Laws of Motion 14 Periods
Chapter–5: Laws of Motion
Intuitive concept of force, Inertia, Newton’s first law of motion; momentum and Newton’s second law of motion; impulse; Newton’s third law of motion. Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications. Equilibrium of concurrent forces, Static and kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction, lubrication.
Dynamics of uniform circular motion: Centripetal force, examples of circular motion (vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a banked road).
Unit IV: Work, Energy and Power 14 Periods
Chapter–6: Work, Energy and Power
Work done by a constant force and a variable force; kinetic energy, workenergy theorem, power. Notion of potential energy, potential energy of a spring, conservative forces: non- conservative forces, motion in a vertical circle; elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
Unit V: Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body 18 Periods
Chapter–7: System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Centre of mass of a two-particle system, momentum conservation and Centre of mass motion. Centre of mass of a rigid body; centre of mass of a uniform rod. Moment of a force, torque, angular momentum, law of conservation of angular momentum and its applications. Equilibrium of rigid bodies, rigid body rotation and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions. Moment of inertia, radius of gyration, values of moments of inertia for simple geometrical objects (no derivation).
Unit VI: Gravitation 12 Periods
Chapter–8: Gravitation
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth. Gravitational potential energy and gravitational potential, escape velocity, orbital velocity of a satellite.
Unit VII: Properties of Bulk Matter 24 Periods
Chapter–9: Mechanical Properties of Solids
Elasticity, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke’s law, Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, shear modulus of rigidity (qualitative idea only), Poisson’s ratio; elastic energy.
Chapter–10: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal’s law and its applications (hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes), effect of gravity on fluid pressure. Viscosity, Stokes’ law, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, critical velocity, Bernoulli’s theorem and its simple applications. Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary rise.
Chapter–11: Thermal Properties of Matter
Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases, anomalous expansion of water; specific heat capacity; Cp, Cv – calorimetry; change of state – latent heat capacity. Heat transfer-conduction, convection and radiation, thermal conductivity, qualitative ideas of Blackbody radiation, Wein’s displacement Law, Stefan’s law .
Unit VIII: Thermodynamics 12 Periods
Chapter–12: Thermodynamics
Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature zeroth law of thermodynamics, heat, work and internal energy. First law of thermodynamics, Second law of thermodynamics: gaseous state of matter, change of condition of gaseous state -isothermal, adiabatic, reversible, irreversible, and cyclic processes.
Unit IX: Behavior of Perfect Gases and Kinetic Theory of Gases 08 Periods
Chapter–13: Kinetic Theory
Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done in compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases – assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic interpretation of temperature; rms speed of gas molecules; degrees of freedom, law of equi-partition of energy (statement only) and application to specific heat capacities of gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro’s number.
Unit X: Oscillations and Waves 26 Periods
Chapter–14: Oscillations
Periodic motion – time period, frequency, displacement as a function of time, periodic functions and their application. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M) and its equations of motion; phase; oscillations of a loaded spring- restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M. Kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum derivation of expression for its time period.
Chapter–15: Waves
Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal waves, speed of traveling wave, displacement relation for a progressive wave, principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats.
FAQs about Class 11 Physics Case Studies
What is the best website for a case study of physics class 11 .
studyrate.in is the best website for Class 11 Physics Case Study Questions for Board Exams. Here you can find various types of Study Materials, Ebooks, Notes, and much more free of cost.
How do you write a case study question for Class 11?
The CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE Class 11th Maths Question Paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 will be case-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph.
Are the case study questions based on the latest syllabus?
Yes, the case study questions are curated to align with the latest Class 11 Physics syllabus.

You Might Also Like
50+ neet mcq questions kinetic theory with solutions, download dc pandey objective physics pdf for neet, summary, important formula – physics notes for jee main and neet class 12 physics, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!

IMAGES
VIDEO