Solomon Asch Conformity Line Experiment Study
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Solomon Asch experimented with investigating the extent to which social pressure from a majority group could affect a person to conform .
He believed the main problem with Sherif’s (1935) conformity experiment was that there was no correct answer to the ambiguous autokinetic experiment. How could we be sure that a person conformed when there was no correct answer?
Asch (1951) devised what is now regarded as a classic experiment in social psychology, whereby there was an obvious answer to a line judgment task.
If the participant gave an incorrect answer, it would be clear that this was due to group pressure.
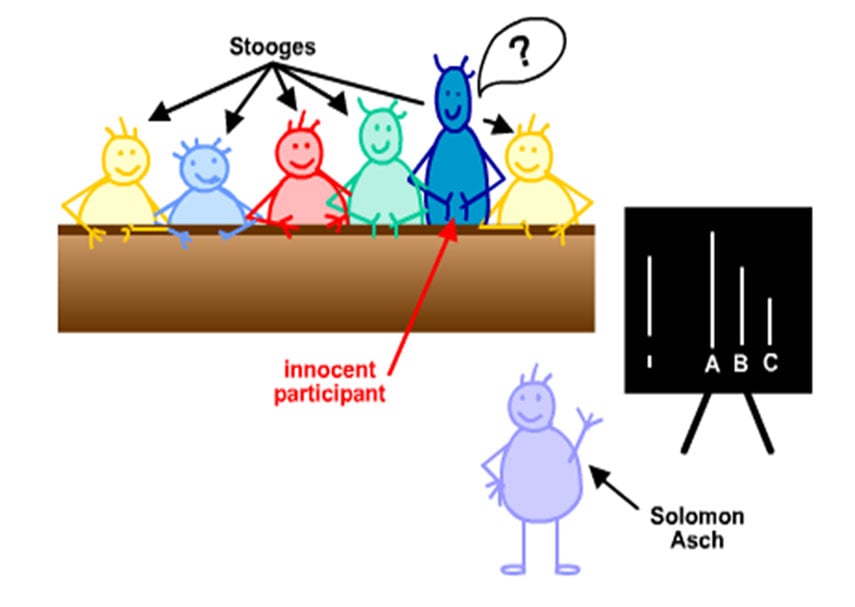

Experimental Procedure
Asch used a lab experiment to study conformity, whereby 50 male students from Swarthmore College in the USA participated in a ‘vision test.’
Using a line judgment task, Asch put a naive participant in a room with seven confederates/stooges. The confederates had agreed in advance what their responses would be when presented with the line task.
The real participant did not know this and was led to believe that the other seven confederates/stooges were also real participants like themselves.

Each person in the room had to state aloud which comparison line (A, B or C) was most like the target line. The answer was always obvious. The real participant sat at the end of the row and gave his or her answer last.
At the start, all participants (including the confederates) gave the correct answers. However, after a few rounds, the confederates started to provide unanimously incorrect answers.
There were 18 trials in total, and the confederates gave the wrong answer on 12 trials (called the critical trials). Asch was interested to see if the real participant would conform to the majority view.
Asch’s experiment also had a control condition where there were no confederates, only a “real participant.”
Asch measured the number of times each participant conformed to the majority view. On average, about one third (32%) of the participants who were placed in this situation went along and conformed with the clearly incorrect majority on the critical trials.
Over the 12 critical trials, about 75% of participants conformed at least once, and 25% of participants never conformed.
In the control group , with no pressure to conform to confederates, less than 1% of participants gave the wrong answer.
Why did the participants conform so readily? When they were interviewed after the experiment, most of them said that they did not really believe their conforming answers, but had gone along with the group for fear of being ridiculed or thought “peculiar.
A few of them said that they did believe the group’s answers were correct.
Apparently, people conform for two main reasons: because they want to fit in with the group ( normative influence ) and because they believe the group is better informed than they are ( informational influence ).
Critical Evaluation
One limitation of the study is that is used a biased sample. All the participants were male students who all belonged to the same age group. This means that the study lacks population validity and that the results cannot be generalized to females or older groups of people.
Another problem is that the experiment used an artificial task to measure conformity – judging line lengths. How often are we faced with making a judgment like the one Asch used, where the answer is plain to see?
This means that the study has low ecological validity and the results cannot be generalized to other real-life situations of conformity. Asch replied that he wanted to investigate a situation where the participants could be in no doubt what the correct answer was. In so doing he could explore the true limits of social influence.
Some critics thought the high levels of conformity found by Asch were a reflection of American, 1950’s culture and told us more about the historical and cultural climate of the USA in the 1950s than then they did about the phenomena of conformity.
In the 1950s America was very conservative, involved in an anti-communist witch-hunt (which became known as McCarthyism) against anyone who was thought to hold sympathetic left-wing views.
Perrin and Spencer
Conformity to American values was expected. Support for this comes from studies in the 1970s and 1980s that show lower conformity rates (e.g., Perrin & Spencer, 1980).
Perrin and Spencer (1980) suggested that the Asch effect was a “child of its time.” They carried out an exact replication of the original Asch experiment using engineering, mathematics, and chemistry students as subjects. They found that in only one out of 396 trials did an observer join the erroneous majority.
Perrin and Spencer argue that a cultural change has taken place in the value placed on conformity and obedience and in the position of students.
In America in the 1950s, students were unobtrusive members of society, whereas now, they occupy a free questioning role.
However, one problem in comparing this study with Asch is that very different types of participants are used. Perrin and Spencer used science and engineering students who might be expected to be more independent by training when it came to making perceptual judgments.
Finally, there are ethical issues : participants were not protected from psychological stress which may occur if they disagreed with the majority.
Evidence that participants in Asch-type situations are highly emotional was obtained by Back et al. (1963) who found that participants in the Asch situation had greatly increased levels of autonomic arousal.
This finding also suggests that they were in a conflict situation, finding it hard to decide whether to report what they saw or to conform to the opinion of others.
Asch also deceived the student volunteers claiming they were taking part in a “vision” test; the real purpose was to see how the “naive” participant would react to the behavior of the confederates. However, deception was necessary to produce valid results.
The clip below is not from the original experiment in 1951, but an acted version for television from the 1970s.
Factors Affecting Conformity
In further trials, Asch (1952, 1956) changed the procedure (i.e., independent variables) to investigate which situational factors influenced the level of conformity (dependent variable).
His results and conclusions are given below:
Asch (1956) found that group size influenced whether subjects conformed. The bigger the majority group (no of confederates), the more people conformed, but only up to a certain point.
With one other person (i.e., confederate) in the group conformity was 3%, with two others it increased to 13%, and with three or more it was 32% (or 1/3).
Optimum conformity effects (32%) were found with a majority of 3. Increasing the size of the majority beyond three did not increase the levels of conformity found. Brown and Byrne (1997) suggest that people might suspect collusion if the majority rises beyond three or four.
According to Hogg & Vaughan (1995), the most robust finding is that conformity reaches its full extent with 3-5 person majority, with additional members having little effect.
Lack of Group Unanimity / Presence of an Ally
The study also found that when any one individual differed from the majority, the power of conformity significantly decreased.
This showed that even a small dissent can reduce the power of a larger group, providing an important insight into how individuals can resist social pressure.
As conformity drops off with five members or more, it may be that it’s the unanimity of the group (the confederates all agree with each other) which is more important than the size of the group.
In another variation of the original experiment, Asch broke up the unanimity (total agreement) of the group by introducing a dissenting confederate.
Asch (1956) found that even the presence of just one confederate that goes against the majority choice can reduce conformity by as much as 80%.
For example, in the original experiment, 32% of participants conformed on the critical trials, whereas when one confederate gave the correct answer on all the critical trials conformity dropped to 5%.
This was supported in a study by Allen and Levine (1968). In their version of the experiment, they introduced a dissenting (disagreeing) confederate wearing thick-rimmed glasses – thus suggesting he was slightly visually impaired.
Even with this seemingly incompetent dissenter, conformity dropped from 97% to 64%. Clearly, the presence of an ally decreases conformity.
The absence of group unanimity lowers overall conformity as participants feel less need for social approval of the group (re: normative conformity).
Difficulty of Task
When the (comparison) lines (e.g., A, B, C) were made more similar in length it was harder to judge the correct answer and conformity increased.
When we are uncertain, it seems we look to others for confirmation. The more difficult the task, the greater the conformity.
Answer in Private
When participants were allowed to answer in private (so the rest of the group does not know their response), conformity decreased.
This is because there are fewer group pressures and normative influence is not as powerful, as there is no fear of rejection from the group.
Frequently Asked Questions
How has the asch conformity line experiment influenced our understanding of conformity.
The Asch conformity line experiment has shown that people are susceptible to conforming to group norms even when those norms are clearly incorrect. This experiment has significantly impacted our understanding of social influence and conformity, highlighting the powerful influence of group pressure on individual behavior.
It has helped researchers to understand the importance of social norms and group dynamics in shaping our beliefs and behaviors and has had a significant impact on the study of social psychology.
What are some real-world examples of conformity?
Examples of conformity in everyday life include following fashion trends, conforming to workplace norms, and adopting the beliefs and values of a particular social group. Other examples include conforming to peer pressure, following cultural traditions and customs, and conforming to societal expectations regarding gender roles and behavior.
Conformity can have both positive and negative effects on individuals and society, depending on the behavior’s context and consequences.
What are some of the negative effects of conformity?
Conformity can have negative effects on individuals and society. It can limit creativity and independent thinking, promote harmful social norms and practices, and prevent personal growth and self-expression.
Conforming to a group can also lead to “groupthink,” where the group prioritizes conformity over critical thinking and decision-making, which can result in poor choices.
Moreover, conformity can spread false information and harmful behavior within a group, as individuals may be afraid to challenge the group’s beliefs or actions.
How does conformity differ from obedience?
Conformity involves adjusting one’s behavior or beliefs to align with the norms of a group, even if those beliefs or behaviors are not consistent with one’s personal views. Obedience , on the other hand, involves following the orders or commands of an authority figure, often without question or critical thinking.
While conformity and obedience involve social influence, obedience is usually a response to an explicit request or demand from an authority figure, whereas conformity is a response to implicit social pressure from a group.

What is the Asch effect?
The Asch Effect is a term coined from the Asch Conformity Experiments conducted by Solomon Asch. It refers to the influence of a group majority on an individual’s judgment or behavior, such that the individual may conform to perceived group norms even when those norms are obviously incorrect or counter to the individual’s initial judgment.
This effect underscores the power of social pressure and the strong human tendency towards conformity in group settings.
What is Solomon Asch’s contribution to psychology?
Solomon Asch significantly contributed to psychology through his studies on social pressure and conformity.
His famous conformity experiments in the 1950s demonstrated how individuals often conform to the majority view, even when clearly incorrect.
His work has been fundamental to understanding social influence and group dynamics’ power in shaping individual behaviors and perceptions.
Allen, V. L., & Levine, J. M. (1968). Social support, dissent and conformity. Sociometry , 138-149.
Asch, S. E. (1951). Effects of group pressure upon the modification and distortion of judgment. In H. Guetzkow (ed.) Groups, leadership and men . Pittsburgh, PA: Carnegie Press.
Asch, S. E. (1952). Group forces in the modification and distortion of judgments.
Asch, S. E. (1956). Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority. Psychological monographs: General and applied, 70(9) , 1-70.
Back, K. W., Bogdonoff, M. D., Shaw, D. M., & Klein, R. F. (1963). An interpretation of experimental conformity through physiological measures. Behavioral Science, 8(1) , 34.
Bond, R., & Smith, P. B. (1996). Culture and conformity : A meta-analysis of studies using Asch’s (1952b, 1956) line judgment task. Psychological bulletin , 119 (1), 111.
Longman, W., Vaughan, G., & Hogg, M. (1995). Introduction to social psychology .
Perrin, S., & Spencer, C. (1980). The Asch effect: a child of its time? Bulletin of the British Psychological Society, 32, 405-406.
Sherif, M., & Sherif, C. W. (1953). Groups in harmony and tension . New York: Harper & Row.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Test Conformity With Your Own Psychology Experiment
Plus, Questions to Spark Conformity Experiment Ideas
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
skynesher / Getty Images
- Famous Experiments
- Example Experiment
- Experiment Ideas
- Additional Tips
Conformity involves adopting certain attitudes or behaviors to fit in with a particular group of people. Conformity experiments can be interesting project ideas for a psychology class, in addition to just being fun to perform.
Here we share some conformity experiments that have sought to better understand how people conform . These can be used as inspiration when developing our own experiments. We also provide a few questions that can help us come up with even more conformity experiment ideas.
Famous Conformity Experiments
One of the most well-known series of conformity experiments was conducted by psychologist Solomon Asch in the 1950s. Known as the Asch conformity experiments , these studies demonstrated the impact of social pressure on individual behavior.
Participants in these studies were told that they were in a vision experiment and asked to look at three lines of different lengths to determine which was the longest. They were then placed with a group that they thought included others in the study. In reality, the others were actually in on the experiment.
After a few trials where everyone stated the correct answer, the subjects who were in on the experiment began choosing an incorrect response. When surrounded by people citing an incorrect answer, 75% of the true study subjects also gave an incorrect response to at least one of the line-length questions.
Other Conformity Experiments
Another popular conformity experiment was performed on the TV show Candid Camera. It involved a group of people on an elevator who all stood facing the rear of the elevator. Inevitably, everyone else who got on ended up also facing the rear so as not to stand out from the rest.
One young man even turned repeatedly to every side, along with the rest of the group, and took off his hat when the others did.
Other conformity experiments that have been performed include:
- Having a group of people stare up at a building
- Picketing with blank signs and pamphlets for no specific cause
- When one student leaves a classroom, the teacher has everyone else stand up when the student returns and sits down
A Conformity Experiment Example
Imagine that a student is in a math class and the instructor asks a basic math question. What is 8 x 4? The student knows that the correct answer is 32. However, when the teacher begins asking other students in the room for the answer, each one says that it is 27. How does the student respond?
This is a classic example of a conformity experiment in action. When the teacher finally gets to the student, does the student trust their own math skills and provide the correct answer or do they go along with the rest of the group and say that the answer is 27—even when they know that this is an incorrect response?
For some, the desire to fit in and belong is so strong that they will provide an answer that they know is incorrect. This helps them avoid being considered an "outsider" to others in the group.
Conformity Experiment Ideas
One way to envision our own experiment is to consider some of the conformity experiments that have been performed in the past. It can also be helpful to consider a few questions we could answer in our own psychology experiment.
Here are some questions that may spark a few conformity experiment ideas:
- How does group size impact conformity? Try the experiment with different numbers of helpers to see how many other people must be present before a person starts conforming to the group.
- What effect does age have on conformity? Try the experiment with participants in different age groups to see if the results differ.
- What's the impact of gender on conformity ? Experiment to see if a participant is more likely to conform if other participants are of the same gender. What are the results if no other participants share their gender?
- How does the situation influence conformity? Are people more likely to conform in certain settings, such as a classroom, than they are in more natural, everyday settings? Run trials in various settings to see if there is a difference.
Additional Conformity Experiment Tips
Performing a psychology experiment for class can be a bit intimidating. Before beginning, we should always talk with the instructor about our experiment ideas to be sure that we have permission to carry out our project. In some cases, we may have to submit our idea for review beforehand to receive permission to experiment with human participants.
Conducting conformity experiments is a great way to learn more about the impacts that groups can have on individuals. Playing around with certain variables can widen our understanding of how far people will go to fit in, making them good conformity experiment ideas to try.
Kim D, Hommel B. Social cognition 2.0: Toward mechanistic theorizing . Front Psychol . 2019;10:2643. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02643
Sowden S, Koletsi S, Lymberopoulos E, Militaru E, Catmur C, Bird G. Quantifying compliance and acceptance through public and private social conformity . Conscious Cogn . 2018;65:359-367. doi:10.1016/j.concog.2018.08.009
Howard J. Bandwagon effect and authority bias . In: Cognitive Errors and Diagnostic Mistakes . 2018:21-56. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93224-8_3
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Elevator Groupthink: An Ingenious 1962 Psychology Experiment in Conformity
By maria popova.
The psychology of conformity is something we’ve previously explored, but its study dates back to the 1950s, when Gestalt scholar and social psychology pioneer Solomon Asch , known today as the Asch conformity experiments . Among them is this famous elevator experiment, originally conducted as a part of a 1962 Candid Camera episode titled “Face the Rear.”

Ultimately, diversity contributes not just by adding different perspectives to the group but also by making it easier for individuals to say what they really think. […] Independence of opinion is both a crucial ingredient in collectively wise decisions and one of the hardest things to keep intact. Because diversity helps preserve that independence, it’s hard to have a collectively wise group without it.”
Perhaps the role of the global Occupy movement and other expressions of contemporary civic activism is that of a cultural confederate, spurring others — citizens, politicians, CEOs — to face the front of the elevator at last.
Complement with How To Be a Nonconformist , a satirical masterpiece from the same era, written and illustrated by a teenage girl.
HT Not Exactly Rocket Science
— Published January 13, 2012 — https://www.themarginalian.org/2012/01/13/asch-elevator-experiment/ —

www.themarginalian.org

PRINT ARTICLE
Email article, filed under, activism history knowledge politics psychology vintage, view full site.
The Marginalian participates in the Bookshop.org and Amazon.com affiliate programs, designed to provide a means for sites to earn commissions by linking to books. In more human terms, this means that whenever you buy a book from a link here, I receive a small percentage of its price, which goes straight back into my own colossal biblioexpenses. Privacy policy . (TLDR: You're safe — there are no nefarious "third parties" lurking on my watch or shedding crumbs of the "cookies" the rest of the internet uses.)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Asch paradigm was a series of conformity experiments by Solomon Asch designed to investigate how social pressure from a majority group could influence an individual to conform.
The Asch conformity experiments are among the most famous in psychology's history and have inspired a wealth of additional research on conformity and group behavior. This research has provided important insight into how, why, and when people conform and the effects of social pressure on behavior.
One of these studies is known as the “Asch Line Experiment”, where he found evidence supporting the idea that humans will conform to and accept the ideas of others around them, even if those ideas are obviously false. This study is one of the most influential studies in social psychology.
Learn how to conduct your own conformity experiments for a psychology class with these examples. We also provide questions to spark conformity experiment ideas.
The topics of conformity, social influence, obedience, and group processes demonstrate the power of the social situation to change our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We begin this section with a discussion of a famous social psychology experiment that demonstrated how susceptible humans are to outside social pressures.
The psychology of conformity is something we’ve previously explored, but its study dates back to the 1950s, when Gestalt scholar and social psychology pioneer Solomon Asch, known today as the Asch conformity experiments.
In psychology, the Asch conformity experiments or the Asch paradigm were a series of studies directed by Solomon Asch studying if and how individuals yielded to or defied a majority group and the effect of such influences on beliefs and opinions.