- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Corporate Finance
- Corporate Debt

Assignment of Accounts Receivable: Meaning, Considerations
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/CharleneRhinehartHeadshot-CharleneRhinehart-ca4b769506e94a92bc29e4acc6f0f9a5.jpg)
Investopedia / Jiaqi Zhou
What Is Assignment of Accounts Receivable?
Assignment of accounts receivable is a lending agreement whereby the borrower assigns accounts receivable to the lending institution. In exchange for this assignment of accounts receivable, the borrower receives a loan for a percentage, which could be as high as 100%, of the accounts receivable.
The borrower pays interest, a service charge on the loan, and the assigned receivables serve as collateral. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the agreement allows the lender to collect the assigned receivables.
Key Takeaways
- Assignment of accounts receivable is a method of debt financing whereby the lender takes over the borrowing company's receivables.
- This form of alternative financing is often seen as less desirable, as it can be quite costly to the borrower, with APRs as high as 100% annualized.
- Usually, new and rapidly growing firms or those that cannot find traditional financing elsewhere will seek this method.
- Accounts receivable are considered to be liquid assets.
- If a borrower doesn't repay their loan, the assignment of accounts agreement protects the lender.
Understanding Assignment of Accounts Receivable
With an assignment of accounts receivable, the borrower retains ownership of the assigned receivables and therefore retains the risk that some accounts receivable will not be repaid. In this case, the lending institution may demand payment directly from the borrower. This arrangement is called an "assignment of accounts receivable with recourse." Assignment of accounts receivable should not be confused with pledging or with accounts receivable financing .
An assignment of accounts receivable has been typically more expensive than other forms of borrowing. Often, companies that use it are unable to obtain less costly options. Sometimes it is used by companies that are growing rapidly or otherwise have too little cash on hand to fund their operations.
New startups in Fintech, like C2FO, are addressing this segment of the supply chain finance by creating marketplaces for account receivables. Liduidx is another Fintech company providing solutions through digitization of this process and connecting funding providers.
Financiers may be willing to structure accounts receivable financing agreements in different ways with various potential provisions.
Special Considerations
Accounts receivable (AR, or simply "receivables") refer to a firm's outstanding balances of invoices billed to customers that haven't been paid yet. Accounts receivables are reported on a company’s balance sheet as an asset, usually a current asset with invoice payments due within one year.
Accounts receivable are considered to be a relatively liquid asset . As such, these funds due are of potential value for lenders and financiers. Some companies may see their accounts receivable as a burden since they are expected to be paid but require collections and cannot be converted to cash immediately. As such, accounts receivable assignment may be attractive to certain firms.
The process of assignment of accounts receivable, along with other forms of financing, is often known as factoring, and the companies that focus on it may be called factoring companies. Factoring companies will usually focus substantially on the business of accounts receivable financing, but factoring, in general, a product of any financier.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1970442766-9bc978054b4341f2b5e596f7c25129c6.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- What is SAP FICO?
- SAP FICO Training Tutorials for Beginners
- SAP FICO Define Account Group
- SAP FICO Reverse Clearing Document
- Foreign Currency Valuation Configuration
- SAP FICO User Exit for Vendor Master
- FICO Vendor Account Group Table
- SAP FICO Withholding Tax
- SAP FICO Dunning Area
- SAP FICO Cash Management Group
- Assessment Cycle vs Profit Center
- SAP FICO Asset Accounting
- SAP FICO Posting Key for Bank
- SAP FICO Document Type
- SAP FICO Document Number Ranges
- SAP FICO Parked Workflow Configuration
- SAP FICO Classic GL vs New GL
- SAP FICO GL Account for Cash Journal
- SAP FICO Accounts Receivable Process Cycle
- SAP FICO Accounts Receivable Configuration
- GR/IR Accounting Entries and Journal Entries
- SAP FICO Chart of Accounts
- SAP FICO Transaction Codes
- SAP AS11 Create Asset Sub-Number
- SAP Business Area and Profit Center
- SAP Inconsistent Withholding Tax Info
- SAP Active vs Passive Document Splitting
- Reverse MIRO Document in SAP
- SAP FICO Scope and Opportunity
- FICO Certification Cost in India
- SAP FICO Interview Questions
- SAP FICO Tree Menu
What is Account assignment in SAP FICO ?
Updated Apr 01, 2023
Account assignment is a critical aspect of financial accounting and management in any organization. It refers to the process of allocating financial transactions to specific cost or profit centers, projects, or business processes. By properly assigning financial transactions to the appropriate account, organizations can accurately track their expenses, revenues, and profitability. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about resource allocation, cost control, and overall financial management.
In SAP FICO, account assignment is a core module that offers various types of account assignment options, including cost center accounting, profit-center accounting, internal order accounting, and WBS element accounting. These options provide organizations with greater visibility into their financial performance, enabling them to optimize their operations and drive greater value for their stakeholders.
Types of Account Assignment
There are several types of account assignments in SAP FICO, including:
- Cost center accounting
- Profit center accounting
- Internal order accounting
- WBS element accounting
i) Cost center accounting
Cost center accounting is the process of tracking and analyzing costs associated with each department, function, or unit of an organization. SAP FICO provides a module that allows organizations to create and manage cost centers, allocate expenses, and generate reports to track performance.
By tracking expenses at a granular level, organizations can make informed decisions about resource allocation, identify areas of inefficiency, and make changes to improve overall performance, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
ii) Profit center accounting
Profit center accounting is a process that allows organizations to track revenues and expenses at a granular level, providing insights into the profitability of individual business units, product lines, or geographic regions. By allocating revenues and expenses to specific profit centers, organizations can generate reports that help identify areas of high profitability or inefficiency.
SAP FICO provides a comprehensive profit center accounting module that enables organizations to create and manage profit centers, allocate revenues and expenses, and generate reports to analyze profitability. This information can be used to make informed decisions about product lines, investments, and resource allocation, enabling organizations to optimize their profitability and drive growth.
iii) Internal order accounting
Internal order accounting is a process that allows organizations to track and control expenses associated with a specific project, event, or business process. By assigning costs to a specific internal order, organizations can monitor actual expenses versus budgeted expenses, and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.

iv) WBS element accounting
WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) element accounting is a process that allows organizations to track and control expenses associated with a specific project or work breakdown structure. It involves breaking down large projects into smaller, manageable tasks or work packages, each of which is assigned a WBS element.
Expenses are then allocated to each WBS element to track actual versus planned expenses and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
Advantages of Account Assignment
The advantages of account assignment in SAP FICO include:
Better visibility: Account assignment allows organizations to track expenses and revenues at a granular level, providing better visibility into financial performance.
Resource allocation: By tracking expenses and revenues, organizations can make informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Cost control: By identifying areas of inefficiency or waste, organizations can make changes to control costs and improve profitability.
Accurate reporting: Account assignment provides accurate reporting and analytics, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about their financial performance.
Compliance: Account assignment helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and accounting standards.
How to Define Account Assignment?
Please follow the steps below to define the account assignment:
Execute t-code OKB9 in the SAP command field as shown in the image below.
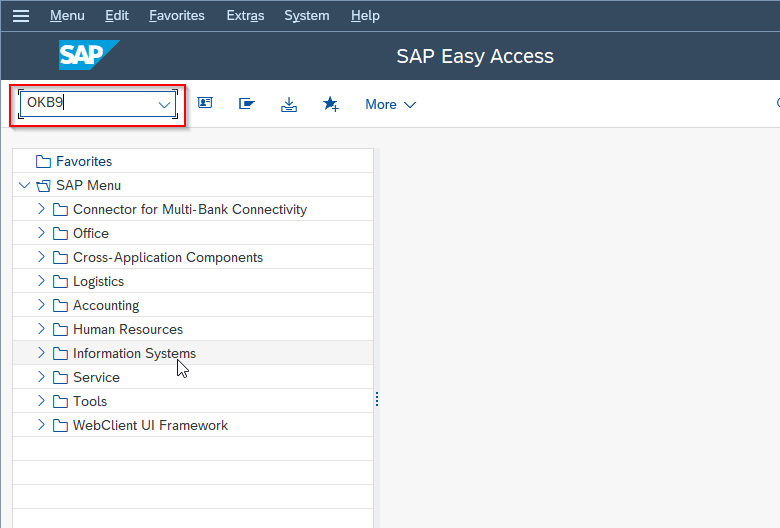
On Change View "Default account assignment": Overview you will see the list of default account assignments.
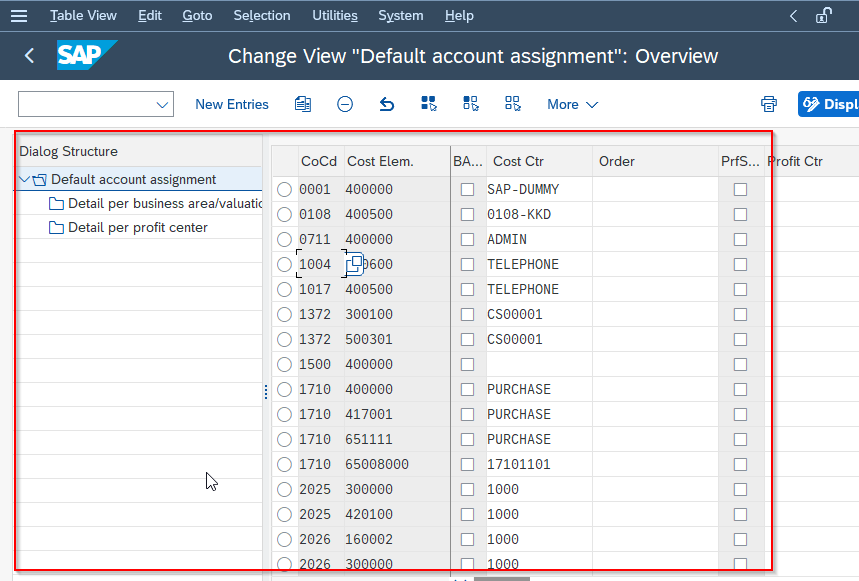
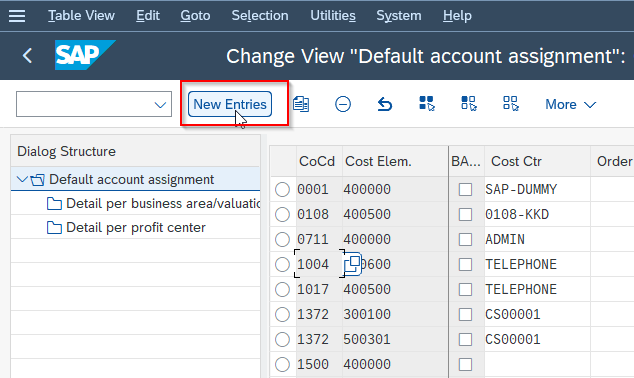
Next, click the New Entries button to create a new account assignment.
In the next window, enter the following fields:
- Cost Ctr
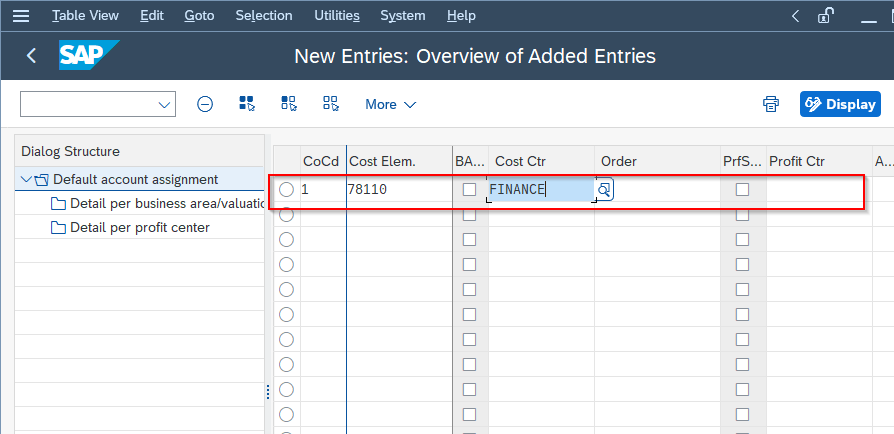
Now click on the Save button to save the new account assignment.
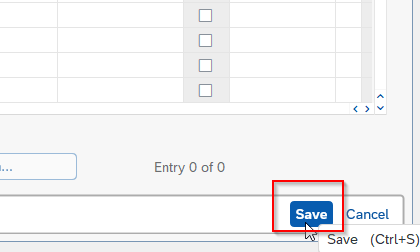
Now in order to post a test document to check that the account assignment works, execute t-code FB50 in the SAP command field.
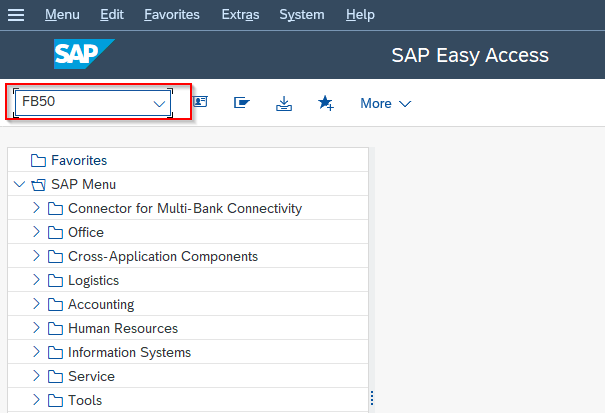
On the next popup enter Company Code as shown below.
.png)
Now on the next window, click Tree On button.
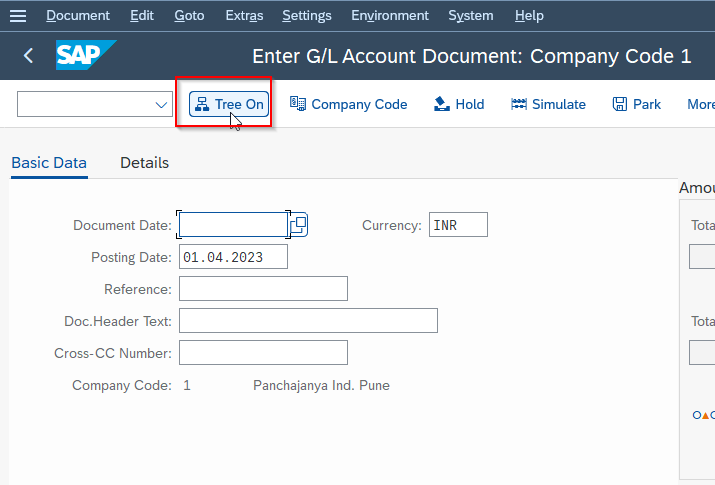
Next, select the Screen Variant in the next window and click Tree Off button.
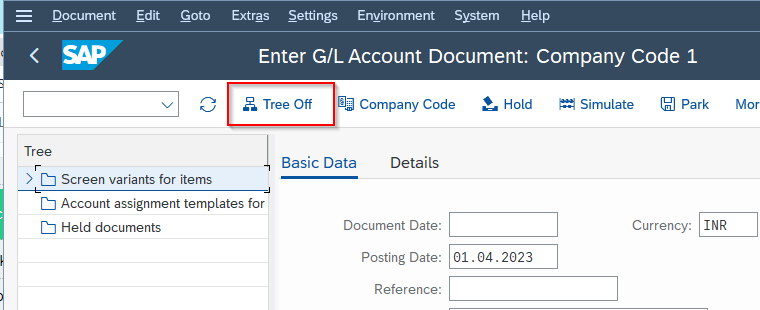
In the next window, enter the following fields according to your requirements:
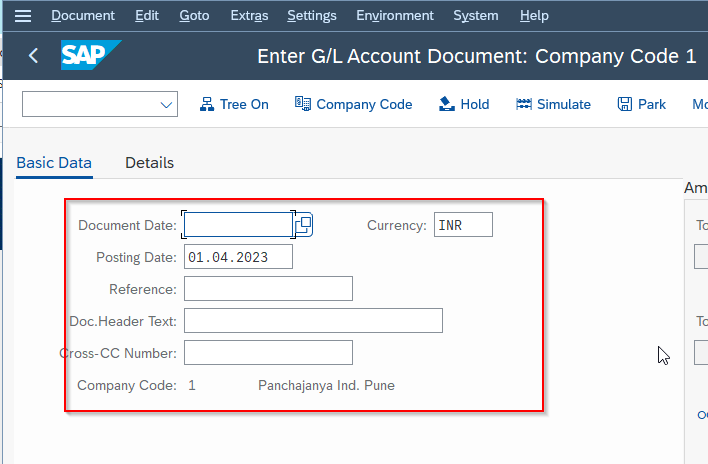
To make the document assignment, click the Post button.
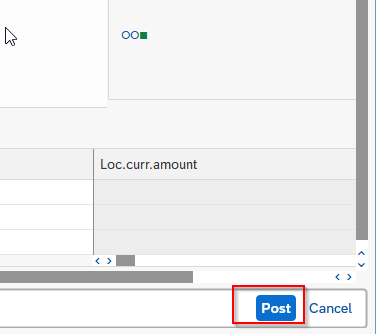
The account assignment is now defined and can be used for tracking expenses and revenues at a granular level in SAP FICO.
- 04 Dec 2013 7:51 am rekha Account assignment is used in Sap Fico if you frequently use the same broad account assignments, such as a distribution of amounts to several company codes, accounts, or cost centers, you can use the account assignment model method to save input time and avoid input errors. The use of account assignment models is limited to G/L account items. T-code OK17 is used in the account assignment. If you have CO-FI real-time integration active you need this account assignment.
Simple English definitions for legal terms
assigned account
Read a random definition: noncompetition agreement
A quick definition of assigned account:
A more thorough explanation:.
An assigned account is a pledge of an account receivable to a bank or factor as security for a loan. For example, if a business needs a loan, they may pledge their accounts receivable as collateral. This means that if they don't pay back the loan, the bank or factor can collect the money owed to the business from their customers.
One example of an assigned account is when a construction company pledges their accounts receivable to a bank in exchange for a loan. The bank can collect the money owed to the construction company from their customers if they don't pay back the loan.
assign dower | assigned counsel
- Data download
Help us make LSD better!
The Difference Between Assignment of Receivables & Factoring of Receivables
You can raise cash fast by assigning your business accounts receivables or factoring your receivables. Assigning and factoring accounts receivables are popular because they provide off-balance sheet financing. The transaction normally does not appear in your financial statements and your customers may never know their accounts were assigned or factored. However, the differences between assigning and factoring receivables can impact your future cash flows and profits.
How Receivables Assignment Works
Assigning your accounts receivables means that you use them as collateral for a secured loan. The financial institution, such as a bank or loan company, analyzes the accounts receivable aging report. For each invoice that qualifies, you will likely receive 70 to 90 percent of the outstanding balance in cash, according to All Business. Depending on the lender, you may have to assign all your receivables or specific receivables to secure the loan. Once you have repaid the loan, you can use the accounts as collateral for a new loan.
More For You
How to decrease bad debt expenses to increase income, what does "paid on account" in accounting mean, what is a financing receivable, what do liquidity ratios measure, what are some examples of installment & revolving accounts, assignment strengths and weaknesses.
Using your receivables as collateral lets you retain ownership of the accounts as long as you make your payments on time, says Accounting Coach. Since the lender deals directly with you, your customers never know that you have borrowed against their outstanding accounts. However, lenders charge high fees and interest on an assignment of accounts receivable loan. A loan made with recourse means that you still are responsible for repaying the loan if your customer defaults on their payments. You will lose ownership of your accounts if you do not repay the loan per the agreement terms.
Advertisement
Article continues below this ad
How Factoring Receivables Works
When you factor your accounts receivable, you sell them to a financial institution or a company that specializes in purchasing accounts receivables. The factor analyzes your accounts receivable aging report to see which accounts meet their purchase criteria. Some factors will not purchase receivables that are delinquent 45 days or longer. Factors pay anywhere from 65 percent to 90 percent of an invoice's value. Once you factor an account, the factor takes ownership of the invoices.
Factoring Strengths and Weaknesses
Factoring your accounts receivables gives you instant cash and puts the burden of collecting payment from slow or non-paying customers on the factor. If you sell the accounts without recourse, the factor cannot look to you for payment should your former customers default on the payments. On the other hand, factoring your receivables could result in your losing customers if they assume you sold their accounts because of financial problems. In addition, factoring receivables is expensive. Factors charge high fees and may retain recourse rights while paying you a fraction of your receivables' full value.
- All Business: The Difference Between Factoring and Accounts Receivable Financing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assignment of accounts receivable is a method of debt financing whereby the lender takes over the borrowing company's receivables. This form of alternative financing is often seen as less ...
Account assignment is a critical aspect of financial accounting and management in any organization. It refers to the process of allocating financial transactions to specific cost or profit centers, projects, or business processes.
Assigning accounts receivable is a fairly straightforward business financing option where a company receives a loan using its outstanding invoices as collateral. It is a form of asset-based financing. In general assignment, the company uses all accounts receivable as collateral. In specific assignment, the borrower only puts up select invoices ...
definition. assignment account means the current account to be notified to the Borrower by the Bank in the event that the Bank makes an assignment of rights. The amounts corresponding to the installments, including any taxes, fees, and any other amount to be paid by the Borrower, up to an amount equal to the percentage of the Agreement subject ...
An assigned account is a pledge of an account receivable to a bank or factor as security for a loan. For example, if a business needs a loan, they may pledge their accounts receivable as collateral. This means that if they don't pay back the loan, the bank or factor can collect the money owed to the business from their customers.
Account Assignment Model is a reference for document entry that provides default values for posting business transactions. An account assignment model can contain any number of G/L account items and can be changed or supplemented at any time. In contrast to sample documents, the G/L account items for account assignment models may be incomplete.
Under an assignment of arrangement, a pays a in exchange for the borrower assigning certain of its receivable accounts to the lender. If the borrower does not repay the , the lender has the right to collect the assigned receivables. The receivables are not actually sold to the lender, which means that the borrower retains the of not collecting ...
Account Modification - IT indicates what GL account it will be posted through the Account Determination; acct.assgt (Derive Account Assignment) - If this is configured for an account assignment category, then the GL account and Cost Center will be pulled automatically by the system. (Pre-requisite: In Acct Modification whatever value is ...
Assignment of Accounts means the first priority assignment of each Earnings Account by an Obligor (or Internal Charterer, as applicable), in favor of the Security Agent, substantially in the form of Exhibit A hereto, together with appropriate notices and acknowledgments thereof; Sample 1. Based on 1 documents.
Assigning your accounts receivables means that you use them as collateral for a secured loan. The financial institution, such as a bank or loan company, analyzes the accounts receivable aging report.