
- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions

Starbucks International Strategy - A Case Study for Global Success

Ever since Starbucks opened its first store outside North America in Tokyo in 1996, the coffee giant has relentlessly pursued global expansion . Today, Starbucks has over 32,000 stores spanning more than 80 countries worldwide, successfully spreading its coffee culture on a global scale. At the heart of Starbucks' phenomenal international business success lies a strategic multi-domestic approach that balances maintaining a consistent global brand with adeptly adapting to local cultures.
Through rigorous market research, cultural sensitivity, strategic partnerships, and premium positioning, Starbucks has seamlessly integrated into diverse international markets while retaining its core identity. This case study examines the key components of Starbucks international strategy, including cultural adaptation, strategic expansion phases, partnership models, and lessons that can be drawn from its international success. The systematic and thoughtful approach demonstrates how consistent brand execution combined with local customization can pave the way for global triumph.
Starbucks' Multidomestic Strategy
The framework that best describes Starbucks' internationalization approach is the multi-domestic strategy. As per this strategy, companies focus on individual foreign markets, treating each market as a separately competitive arena. It emphasizes low integration and high responsiveness.
For Starbucks, this has meant tailoring its products, marketing campaigns, store designs and operations to suit the unique preferences and customs of each local market. While maintaining consistency in quality, branding and customer experience core, it delegates decision-making powers to local franchisees. This allows them to adapt menus, aesthetic elements and promotional activities to match the local customer psyche.
Market Entry Strategies
When entering new markets, Starbucks uses three broad strategies - wholly-owned subsidiaries, joint ventures and licensing. Wholly owned stores give it full control in developed markets with sufficient market understanding like the US, and Canada.
Joint ventures allow leveraging local partner's networks and expertise to establish a foothold in relatively new markets. A prominent case is its joint venture with a Chinese company for China operations.
Licensing is used for quick expansion by granting local partners rights to use the Starbucks brand and set up stores as franchisees. Royalty and fee-based models require low investment while increasing footprint. These tailored entry modes have supported Starbucks' phased globalization process.
Cultural Sensitivity and Customization
Upon entering new markets, Starbucks conducts extensive research to gain cultural insights before store operations even begin. The brand meticulously analyzes local coffee drinking habits, social norms, and economic conditions to understand nuanced preferences. This data-driven approach informs strategic decisions on store layouts, menu customization, and marketing tactics tailored to the host country.
For example, in Japan, Starbucks offers matcha-infused beverages and traditional Japanese decor derived from research revealing local tea-drinking traditions. In China, Starbucks embraces the "ganbei" culture by creating a welcoming environment for social gatherings aligned with drinking customs. Regional preferences are also respected through customized food items—China sees xiaolongbao dumplings while India indulges in masala chai lattes.
By thoughtfully integrating localized flavors, Starbucks seamlessly blends into diverse coffee cultures while maintaining the consistent quality expected of the premium brand. This cultural sensitivity enables the establishment of an authentic local presence, resonating deeply with consumers and expediting market penetration. International success is founded upon such adaptive strategies embracing rather than confronting local identities.
Strategic Partnerships and Co-Owned Stores
Strategic partnerships with local enterprises are another cornerstone of Starbucks' international growth model. Such alliances confer several advantages—joint ventures leverage local expertise, gain government approvals rapidly, and share risks associated with new markets.
Notable examples include the 1998 partnership with Sazaby Café in Japan granting entry into a market protective of domestic firms. In China, collaborations with Kong Group and Maxim's Caterers facilitated swift expansion capitalizing on local supply chains. Most recently, Starbucks joined hands with Tata Group to spearhead robust growth across India leveraging the conglomerate's operational experience.
Co-owned stores following the joint venture model account for one-third of Starbucks' international presence. Local partners provide in-depth cultural understanding while Starbucks delivers consistent brand qualities. Such symbiotic relationships accelerate internationalization by overcoming regulatory hurdles through political familiarity and minimizing liability in uncertain environments. Successful partnerships exemplify mutual growth stemming from shared knowledge and aspirations.
Premium Positioning and Consistent Quality
Despite localized adaptations, Starbucks retains a notable premium positioning worldwide through the consistent execution of its brand. Stores exude sleek minimalism broadcast globally through meticulous design standards. Barista training manuals impart uniform customer service skills across borders to complement the quality drinking experience.
Most distinctively, product sourcing ensures coffee excellence irrespective of location. Green coffee beans are sourced sustainably from over 30 countries and then roasted in seven global processing plants to an identical profile. This commitment to quality justifies slightly higher prices while differentiating the Starbucks experience. Loyal patrons trust consistent flavors upon each international visit, reinforced by a premium brand image.
Globally standardized processes streamline operations for multinational firms yet risk cultural insensitivity. Starbucks balances such trade-offs through its multi-domestic approach—autonomous subsidiaries complement centralized quality controls yielding localization without compromising integrity. Premium branding and attention to detail regardless of borders bolster brand equity on a global scale .
Strategic Expansion Stages
Starbucks' international growth has unfolded strategically in stages, continually adapting its model to diverse conditions in new frontiers. Initial steps focused on contiguous expansion throughout North America and Europe utilizing company-operated stores. Entry into more complex Asian markets saw the rise of adaptive joint ventures and strategic local partnerships.
Most recently, emerging economies present immense opportunities alongside challenges requiring inventive solutions. India saw customized training programs while China leveraged mobile and delivery services to accommodate urbanization. Lessons from each phase cultivate more sophisticated strategies, preserving Starbucks' competitive advantage amidst disruptive global dynamics.
The multi-phased journey reflects an evolutionary approach, not passive diffusion. Careful strategic planning and experimentation have accelerated learning curves, solving problems before widespread proliferation. Cohesive long-term visions balance short-term wins, prioritizing sustainable partnerships over rapid numbers. Starbucks embraces diverse conditions rather than imposing standard blueprints, catalyzing tailored prosperity in every market.
Keys to International Success
Starbucks' case provides valuable insights for brands venturing overseas. Internationalization demands considering local markets as unique rather than homogeneous replicas—deep cultural understanding precedes standardized systems. Strategic alliances confer benefits unavailable to independent operations such as local relationships increasing trust from skeptical markets.
Consistency distinguishes premium brands yet risks cultural detachment—the delicate balance respects local identities amid consistent qualities. Thoughtful long-term visions navigate complexity better than imitations focusing on short-term gains. Success stems from integrating rather than confronting foreign environments by capitalizing on diverse contributions. International growth necessitates agility, learning evolving alongside expanding frontiers.
Current Positioning and Future Outlook
Today Starbucks is a globally recognized brand with a respected image of consistent quality and feel-good customer experience across 80+ nations. However, constantly shifting competitive dynamics and evolving consumer preferences pose new tests.
While Starbucks is well-poised to capture opportunities in still untapped developing geographies leveraging its learnings, local economic volatilities and rising indie cafe trends can impede future plans. Developing new service formats like drive-thrus, mobile ordering, and expanded delivery also becomes critical.
Sustaining differentiation through the premiumization of beverages, newer format stores, innovative loyalty programs and deeper forays in coffee education will determine Starbucks' longevity. Overall, its consistent strategy of blending global vision with local insights wields it an advantage for continued worldwide growth.
In conclusion, Starbucks provides an exemplary case study on designing and implementing a successful international strategy. The keys to its global dominance have been its multi-domestic approach balancing standardization with localisation, research-backed cultural sensitivity, strategic partnerships , consistent branding and marketing effectiveness.
Most significantly, its ability to thoughtfully adapt products, menus, designs, and communications as per every unique market setting while staying true to quality and experience mantras, earned it loyal customer communities worldwide. If replicated judiciously, such well-rounded strategies can become globally replicable models for other aspiring brands.

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password

Starbucks Competitor Analysis

Before we get into the specifics of Starbucks, let’s understand competitor analysis. Competitor analysis is a strategic research method companies use to identify, evaluate, and understand their current and potential competitors within the market. It’s an essential business strategy component and instrumental in understanding the industry landscape.
The process usually involves the following steps:
- Identifying Key Competitors : The first step is to identify who your competitors are. These may be direct competitors (those who offer the same or similar products or services as you) or indirect competitors (those who provide different products or services but compete for the same consumer dollar).
- Analyzing Competitors’ Strategies and Objectives : Once competitors are identified, the next step is to understand their business strategies and objectives. This may involve analyzing their marketing materials, financial performance, customer reviews, or any public information available about the company.
- Assessing Competitors’ Strengths and Weaknesses : This step involves evaluating the identified competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Strengths include unique products or services, strong brand recognition, and superior customer service. Weaknesses include poor product quality, weak customer service, or high prices.
- Understanding Competitors’ Products/Services : Understanding what your competitors offer and how your products or services compare is important. This could involve looking at features, quality, pricing, customer service, and marketing strategies.
- Observing Competitors’ Reaction Patterns : Some companies react more aggressively than others when faced with competition. Understanding these patterns lets you predict how these companies might respond to your business strategies.
- Drawing Conclusions and Formulating Strategy : The final step is to take all the information gathered from the analysis, draw meaningful conclusions, and use those to formulate or adjust your business strategies.
The main goal of a competitor analysis is to understand the competitive landscape, spot opportunities and threats, and position your company most advantageously. It helps to inform strategic decisions, from product development to marketing and sales efforts. Now, let’s do a competitor analysis of Starbucks.

Starbucks SWOT Analysis
Starbucks Marketing Mix (4Ps)
Starbucks PESTEL Analysis
Here is the competitor analysis of Starbucks
Dunkin’ donuts.
Starbucks competes with Dunkin’ Donuts through several strategies, highlighting the differences in their business models, target audiences, and product offerings:
- Product Quality and Variety : Starbucks positions itself as a premium coffee brand, offering a wide variety of high-quality coffee beverages, teas, and food items. The focus is on the coffee experience and the quality of the brew. Dunkin’ Donuts, while offering a range of coffee drinks, is more known for its donuts and other baked goods, focusing on providing quick, convenient, and affordable options.
- Store Ambiance and Experience : Starbucks stores are designed to offer a comfortable and inviting ambiance, encouraging customers to stay longer. This “third place” concept – a place between home and work – is a key differentiator. On the other hand, Dunkin’ Donuts typically focuses on speed and convenience, catering to customers on the go.
- Pricing Strategy : Starbucks often has higher prices, reflecting its premium positioning. Dunkin’ Donuts competes by offering more budget-friendly options, appealing to cost-conscious consumers.
- Brand Positioning and Marketing : Starbucks emphasizes its ethical sourcing, environmental stewardship, and community involvement, aiming to create a strong brand identity around social responsibility and high-quality products. Dunkin’ Donuts often markets itself as a down-to-earth, everyday coffee place, emphasizing speed and efficiency.
- Loyalty Programs and Digital Engagement : Starbucks has a robust digital presence with its mobile app and rewards program, which is highly popular and encourages repeat business through incentives and convenience. Dunkin’ Donuts also has a rewards program and app, but Starbucks is often seen as a leader in digital customer engagement.
- Global Presence : While both brands are international, Starbucks has a more extensive global footprint, with a strong presence in numerous countries outside of the U.S. Dunkin’ Donuts also has international locations, but its focus has been more on domestic expansion in the U.S.
- Product Innovation : Starbucks frequently introduces new and seasonal products, which helps to keep the brand fresh and exciting. Dunkin’ Donuts also innovates, but its new offerings often focus on variations of its existing bakery items and traditional coffee options.
Costa Coffee
Starbucks and Costa Coffee, both major players in the global coffee industry, compete through distinct strategies and brand positioning:
- Market Presence and Expansion : Starbucks has a broader global presence than Costa Coffee. While Costa is a dominant player in the U.K. and has a significant presence in Europe, Starbucks operates in more countries worldwide. This extensive international footprint allows Starbucks to reach a diverse customer base and establish a strong global brand identity.
- Brand Image and Customer Experience : Starbucks positions itself as a premium coffee brand, offering a wide range of high-quality coffee beverages and a unique customer experience. Their stores are designed to provide a comfortable and welcoming environment, promoting the concept of a “third place” between home and work. Costa Coffee also focuses on quality but tends to have a more traditional and cozy British coffeehouse feel, which appeals to different customer preferences.
- Product Offerings and Innovation : Both brands offer a variety of coffee beverages, teas, and food items, but Starbucks is known for its extensive menu and frequent introduction of new and seasonal items. This constant innovation helps keep the brand fresh and exciting. Costa Coffee, while also innovative, often focuses more on classic coffeehouse fare and traditional British items.
- Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility : Starbucks has significantly promoted ethical sourcing, environmental stewardship, and community involvement. These initiatives are a key part of their brand identity. Costa Coffee also engages in sustainability practices, including reducing waste and promoting recycling, but Starbucks often receives more global recognition for its sustainability initiatives.
- Pricing Strategy : Starbucks typically operates with a premium pricing strategy, reflecting its position as a high-end coffee brand. Costa Coffee, while not necessarily low-cost, often has slightly more competitive pricing, which appeals to a different market segment.
- Digital Engagement and Loyalty Programs : Starbucks is a leader in digital engagement, with a highly successful mobile app and rewards program that enhances customer convenience and loyalty. Costa Coffee also has a loyalty program and digital offerings, but Starbucks is often recognized for its innovation in digital customer engagement and technology integration.
- Customer Demographics : While there is some overlap, the typical customer demographics for the two brands can differ. Starbucks often appeals to a younger, more tech-savvy crowd attracted to the brand’s image, digital presence, and trendy offerings. Costa Coffee’s customer base may skew slightly older and more traditional, appreciating the classic coffeehouse experience.
Tim Hortons
Starbucks and Tim Hortons, both significant players in the coffee industry, adopt different strategies to appeal to their respective customer bases:
- Brand Positioning and Image : Starbucks positions itself as a premium coffee brand, focusing on the quality of its coffee and the customer experience in its stores. It’s known for its trendy, upscale ambiance and is often seen as a status symbol. On the other hand, Tim Hortons has a more down-to-earth image, popular as a quick and reliable stop for coffee and baked goods, particularly famous for its donuts.
- Product Offerings : Starbucks offers various coffee beverages, teas, and food items, including healthy and gourmet options. They are known for their seasonal and specialty drinks. Tim Hortons, while also offering a range of coffee drinks, emphasizes its baked goods, breakfast sandwiches, and more traditional, comfort food-oriented menu.
- Pricing Strategy : Starbucks typically operates with a premium pricing strategy, reflecting its high-end positioning. Tim Hortons offers more budget-friendly options, appealing to cost-conscious consumers looking for good quality at a reasonable price.
- Customer Experience and Store Design : Starbucks stores are designed to provide a comfortable, inviting ambiance, encouraging customers to linger. The concept of Starbucks as a “third place” between home and work is central to its brand. Tim Hortons, conversely, focuses more on speed and convenience, catering to customers who are often on the go.
- Market Presence : While both brands are international, Starbucks has a more extensive global footprint. Tim Hortons is a Canadian icon with a strong presence in Canada and growing visibility in the United States and other countries.
- Loyalty Programs and Digital Engagement : Starbucks has a strong digital presence with its mobile app and rewards program, encouraging repeat business through convenience and incentives. Tim Hortons has also developed digital initiatives, including a loyalty program, but Starbucks is often seen as more innovative in digital customer engagement.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility : Starbucks emphasizes its commitment to ethical sourcing, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility, a significant part of its brand identity. Tim Hortons also engages in community and sustainability initiatives, though Starbucks tends to be more vocal and globally recognized in this area.
- Cultural Resonance : Tim Hortons holds a special place in Canadian culture and is often seen as a quintessential Canadian brand. While globally recognized, Starbucks doesn’t have the same cultural symbolism in any specific country but is known worldwide as a symbol of American coffee culture.
Local coffee shops
Starbucks competes with local coffee shops through a multifaceted strategy that leverages its global brand, extensive resources, and standardized customer experience. Here’s how Starbucks maintains its competitive edge:
- Consistent Quality and Standardization : Starbucks offers a consistent product and experience across all its locations. This consistency is a significant draw for customers who prefer knowing exactly what to expect, whether in their hometown or traveling. Local coffee shops, while offering unique experiences, may not have the same level of consistency.
- Brand Recognition and Marketing : Starbucks, as a global brand, benefits from strong brand recognition and marketing capabilities. They have the resources to engage in extensive advertising campaigns, seasonal promotions, and new product launches. Local coffee shops often rely on word-of-mouth and local community engagement for marketing.
- Location and Convenience : Starbucks has a significant advantage in terms of its numerous locations, often strategically placed in high-traffic areas, making it highly accessible to a wide range of customers. Local coffee shops typically have fewer locations and may not be as conveniently located for some customers.
- Variety of Offerings : Starbucks offers various beverages, food items, and seasonal specials. This variety can appeal to a broad customer base with different preferences. Local coffee shops might have a more limited menu, although often more specialized or locally sourced.
- Loyalty Programs and Digital Engagement : Starbucks has a highly successful digital app and loyalty program, which enhances customer convenience and encourages repeat business. Local coffee shops may not have the resources to develop similar technology but can offer personalized service and local loyalty programs.
- Economies of Scale : Starbucks can leverage economies of scale to manage costs effectively. This capability allows them to offer competitive pricing, a wide variety of products, and continual innovation. Local coffee shops may have higher relative costs due to lower volumes.
- Ambiance and Experience : While Starbucks provides a standardized, comfortable environment suited for casual meetings or work, local coffee shops often offer a unique, community-focused atmosphere. They can attract customers who prefer supporting local businesses and enjoy a more personal touch.
- Sustainability and Ethical Practices : Starbucks has made strides in ethical sourcing, environmental practices, and social responsibility initiatives. While local coffee shops may also engage in sustainable practices, Starbucks’s global reach allows it to impact broader sustainability and ethical sourcing initiatives.
Check out the competitor analysis of global businesses
Related posts.

How to Write a Competitive Market Analysis for Your Business

Fiserv Competitor Analysis


Rent the Runway Competitor Analysis

Cloudflare Competitor Analysis
Okta Competitor Analysis

CrowdStrike Competitor Analysis

Workday Competitor Analysis

Sofi Competitor Analysis
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Digital Innovation and Transformation
Mba student perspectives.
- Assignments
- Assignment: Competing with Data
The Perfect Blend: Starbucks and Data Analytics

Every day, Starbucks grinds through mounds of coffee beans to serve its customers. In doing so, the company has also been collecting mounds of data that could be used to improve customer experience and business performance. In this article, we will investigate how this 26 Billion USD company captures value through data analytics.
An opportunity brewing
Through its network of over 30,000 stores worldwide, Starbucks has been gathering over 100 million transactions a week. To make use of these data, the company set up a dedicated team of data scientists, led by Jon Francis, Starbucks’ Senior Vice President of enterprise analytics, data science, research data, and analytics. Since then, the team and the company have been able to tap into the power of data analytics to enhance its business performance.
Using data collected at the store and through its mobile apps with over 17M members, the company has been able to drive business improvements in 3 significant ways.
(1) Personalized experiences and promotions
Pathways to a Just Digital Future
When Starbucks launched its rewards program and mobile app, they dramatically increased the data they collected and could use to get to know their customers and extract info about purchasing habits. Through its mobile app, Starbucks has been collecting data about what, where, and when members buy coffee. To do so, Starbucks leverages the Digital flywheel program, a cloud-based artificial intelligence engine that’s able to recommend food and drink items in a precise manner. As such, even when people visit a new Starbucks location, the store’s point-of-sale system can identify the customer through their phone and give the barista their preferred order.
Based on customers’ purchase history, Starbucks could also suggest new products a consumer might enjoy and provides unique discounts and rewards on certain items based on customers’ unique preferences. Taking it a step further, Starbucks has also been collecting data on weather patterns and their relationship with customer order patterns. Doing so allows the company to provide even more personalized experiences and promotions such as targeting a customer with cold drinks on hot days.
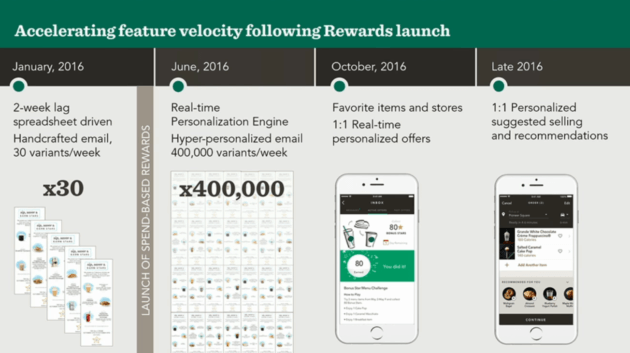
(2) New product introduction
When launching new products, Starbucks also turned to the data collected to determine what products they should offer. Specifically, when expanding its product lines into grocery stores, the company relies heavily on the data collected. For example, data collected has shown that 43 percent of tea-drinking customers tend to skip the sugar. To cater to this segment, Starbucks created its lines of unsweetened ice tea. When data has shown that 25 percent of consumers don’t add milk to their coffee, the company launched a new line of black iced coffee without milk.

(3) Location selection
Selecting the right location is critical to winning in retail. Using location-based analytics powered by Atlas, a mapping and business intelligence tool developed by Esri, the company can select the most strategic location to open up its new stores. The tool enables Starbucks to evaluate massive amounts of data including variables such as population, income levels, traffic, competitor presence, and proximity to other Starbucks locations before recommending a new store location. Using these data, the company can also predict revenues, profits, and other aspects of economic performance associated with that location.

While Starbucks was not born in the digital era, it has successfully integrated new technologies into its core business like a digitally native company. Over the years, data analytics has undeniably become the backbone of Starbucks’s continuous improvement. Looking ahead, I have no doubt that Starbucks will continue to gather more data and make even more innovative use of those data to create an even more personalized customer experience and achieve business excellence.
“Starbucks Isn’t a Coffee Business – It’s a Data Tech Company,” Marker, Jan 16, 2020
“Big Data: The Secret to Starbucks’ Supply Chain Success,” Sisense, Jun 25, 2020
“Starbucks: Using Big Data, Analytics And Artificial Intelligence To Boost Performance,” Forbes, May 28, 2018
“6 Ways in Which Starbucks Uses Big Data,” Analyticsteps, Nov 17, 2020
“How data empowers human connection at Starbucks,” Tableau, Jan 15, 2021
“Starbucks knows how you like your coffee,” CNBC, Apr 6, 2016
Student comments on The Perfect Blend: Starbucks and Data Analytics
Thanks, Max, for the very interesting article! I am just wondering how successfully Starbucks was able to attract new customers with their initiatives with big data. It definitely added a lot of value to existing customers but was it enough to pull customers who like other coffee shops? Also, I wonder what would happen (or maybe is already happening) if competitors start to do the same things with big data. In a such setting, what would be the real competitive advantage? Would it go back to the basic things such as the quality of the coffee?
Great post Max! Very informative. I did not know that Starbucks is actively monitoring the weather information to make product decisions. I would like to know if you think that data is giving Starbucks any sustained competitive advantage?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Starbucks is an American coffee company and coffeehouse chain. It has over 30,000 locations in more than 75 countries and a brand portfolio extending beyond Starbucks coffee to include Teavana and Ethos Water, among others. Starbucks is known for its hot and iced coffee beverages and espressos. The company purchases its coffee beans from 65 countries around the world, sourcing mainly from Brazil, Colombia, El Salvador, Guatemala and other Latin American countries.
Segment ranking summary
Starbucks outperforms most of its peers in the food service segment. Apart from its commitments to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction, Starbucks also shows its responsibility towards sourcing its most relevant commodities, coffee and cocoa, achieving close to 100% sustainable sourcing practices – although it has an opportunity to improve in its palm oil and soya purchases. Given its position in the food system, the company lags behind in terms of nutrition and has an opportunity to improve the nutritional characteristics of its portfolio. In terms of social inclusion, the company has the power to improve the livelihoods of raw material suppliers and can improve its performance by tracking the impact of its various initiatives in this area. Overall, and like most of its peers in the food service segment, the company has an opportunity to improve disclosure across all benchmark measurement areas.
Leading practices
Governance and strategy.
No leading practices were identified for the company in the governance and strategy measurement area.
Environment
Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions Starbucks has set a reduction target for 2030, pledging to cut its carbon footprint by half. Its target has been approved by the Science Based Targets Initiative. The company also discloses information on its activities to reach this target and reports on progress. As of 2021, the company had achieved an 11% reduction.
No leading practices were identified for the company in the nutrition measurement area.
Social inclusion
No leading practices were identified for the company in the social inclusion measurement area.
Risks and opportunities
Sustainable development strategy Starbucks reports on the development of its sustainable development strategy. It conducted an environmental baseline study in 2018, which led to a multi-decade plan to transform its business into a resource-positive one. However, while the company has conducted materiality assessments in the past, these are outdated, and no similar process to identify and prioritise its most relevant issues was found. The company can improve its performance by being more transparent about how it chooses the topics it focuses on.
Governance and accountability for sustainable development The company reports having an independent board that provides oversight of its sustainability management. In terms of remuneration tied to its sustainable development strategy, the company discloses that executive members of the company have non-financial performance goals based on environmental, social and governance metrics. Furthermore, the company has an incentive bonus based on performance on the same topics. The company can improve by adding nutritional metrics to its performance evaluations and by making information easily available.
Stakeholder engagement The company does not disclose stakeholder engagement activities, including how it selects the stakeholders, nor an overview of the topics discussed or their outcomes.
Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions Unlike its scope 1 and 2 GHG emission targets, the company’s GHG reduction target for scope 3 has not yet been approved by the Science Based Targets Initiative. The company is encouraged to continue working towards its scope 3 target validation and continuing to report on progress.
Protection of terrestrial natural ecosystems The company discloses in its Environmental Baseline Report that beef, soya, palm oil, cocoa and coffee are its main food commodities. It also explains how these commodities affect its environmental risks. The company has set various sourcing targets for its commodities and reports having achieved 98% and 100% of ethically sourced coffee and cocoa beans, respectively, through its C.A.F.E programme. The company can strengthen its efforts by being more transparent about its targets and progress regarding palm oil, beef and soy.
Food loss and waste While the company is addressing food loss and waste in its own operations through a food waste reduction programme, it has an opportunity to disclose a commitment by setting targets to reduce food loss and waste across its own operations and supply chain and reporting progress against these targets.
Plastic use and packaging waste While the company discloses that it is reducing its plastic use and transitioning to sustainable forms of packaging, it has an opportunity to strengthen its commitment by setting targets to reduce plastic use and transition to more sustainable forms of packaging and reporting progress against these targets.
Animal welfare While the company has a commitment on animal welfare that addresses animal welfare issues in its supply chain, this does not apply to all key species, geographies or products that are relevant to the company.
Availability of healthy foods While the company discloses that it introduces reformulated products, it has an opportunity to disclose quantitative evidence of its reformulation activities to reduce the level of salt and sugar in its products. The company discloses targets for both sodium and added sugar. However, its sodium target dates from 2015, and no reports on progress or quantitative data were found for any of the targets. Furthermore, its targets do not cover all of its operations.
Accessibility and affordability of healthy foods The company does not disclose a commitment and activities to improve the accessibility and affordability of healthy foods for vulnerable groups.
Clear and transparent labelling While the company discloses a commitment of compliance with national regulations regarding labelling and commits to making nutritional information available for all consumers, it has an opportunity to make nutritional information more visible to consumers through the adoption of front-of-pack labels and/or any other consumer-facing nutrition label.
Food safety While Starbucks is part of the Steering Committee of the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) and has disclosed some information on this matter in its Standards for Food Suppliers, it can commit to food safety in its operations by disclosing more relevant metrics and by achieving 100% GFSI-recognised certification or equivalent throughout its food production and distribution chain.
Child labour In its Global Human Rights Statement the company states that it ‘expects its suppliers to eliminate child labour’ in its operations. However, this statement does not translate to a commitment by the company to prohibit the use of child labour.
Forced labour The company commits to prohibiting forced labour in its operations and requires its suppliers to adhere to the same standard. It also prohibits suppliers from retaining workers’ personal documents and restricting workers’ freedom of movement. However, it has an opportunity to disclose a commitment to respect workers’ rights to freedom of association and collective bargaining as well as specify that it does not interfere with workers seeking to exercise these rights.
Living wage The company does not disclose that it pays its workers a living wage or requires its suppliers to do the same. Neither has it set targets to do so in the future.
Farmer and fisher productivity and resilience The company discloses qualitative information and scoping details of its activities on this matter. Its efforts include social development investments, farmer support centres and loan programmes as well as ethical sourcing of its raw materials. The company can improve its performance by also systematically measuring and disclosing the outcomes and impact of all its support activities, as part of a holistic strategic approach.
Core social indicators
The core social indicators are part of the social inclusion measurement area. These indicators assess societal expectations of business conduct that companies should meet if they aspire to be part of a system transformation that leaves no one behind.
Respect human rights
Starbucks discloses commitments towards human rights and the ILO core labour rights, covering its own operations and its supply chain. It also has a grievance mechanism that is accessible to both internal and external individuals. However, the company does not disclose evidence concerning a human rights due diligence process or how it engages with affected and potentially affected stakeholders.
Provide and promote decent work
Starbucks commits to providing a safe and healthy environment for its workers, and some evidence of this was found for a portion of its supply chain. The company also discloses metrics regarding workforce diversity, and gender equality and women’s empowerment, with a commitment to the latter. However, the company does not publicly show a commitment to living wages, decent working hours or collective bargaining.
Act ethically
Starbucks discloses both a commitment to and statement on data protection. It also has commitment regarding a tax strategy and an anti-corruption and anti-bribery policy, even though insufficient disclosure concerning these topics was found. Furthermore, the company does not disclose commitments regarding lobbying and allows political contributions to be made.
More about the company

This company is part of the SDG2000, the 2.000 most influential companies
Brought to you by:

Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal
By: Nancy F. Koehn, Kelly McNamara, Nora N. Khan, Elizabeth Legris
Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal analyzes the turnaround and reconstruction of Starbucks Coffee Company from 2008 to 2014 as led by CEO and co-founder Howard Schultz. The case…
- Length: 71 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jun 2, 2014
- Discipline: Entrepreneurship
- Product #: 314068-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Same page, Teaching Note
- Same page, Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal analyzes the turnaround and reconstruction of Starbucks Coffee Company from 2008 to 2014 as led by CEO and co-founder Howard Schultz. The case offers executives and students an opportunity to examine in depth how Schultz and his team saved Starbucks from near-collapse, by both executing a deep, comprehensive return to its core values and, at the same time, investing in a range of new products, customer experiences and organizational capabilities designed to make the company fit for enduring success in a turbulent global economy. Set against the backdrop of the Great Recession, the case also considers the impact of unprecedented important shifts in consumer spending and confidence as well as new competitive forces on Starbucks' transformation. The case concludes by examining Schultz's own leadership journey, the lessons he learned personally during Starbucks transformation, and how he is using these lessons-within Starbucks and on the national stage-to redefine the roles and responsibilities of a public corporation in the 21st century.
Based on extensive interviews conducted with Schultz and other Starbucks executives conducted from 2011 to 2014, the case offers a range of vital lessons on leadership, organizational transformation, restructuring, strategy, innovation, entrepreneurial vision, and customer service.
Learning Objectives
Learning Objective is to help executives and students analyze and understand in depth how Howard Schultz and his team saved and transformed Starbucks Coffee Company from 2008-2014 by both executing a deep, comprehensive return to its core values and, at the same time, investing in a range of new products, customer experiences and organizational capabilities designed to make the company fit for enduring success in a turbulent global economy. The powerful lessons from this study apply to a wide range of leaders and organizations in the turbulent global economy of the 21st century.
Jun 2, 2014
Discipline:
Entrepreneurship
Geographies:
United States
Industries:
Beverage industry, Retail and consumer goods, Retail trade
Harvard Business School
314068-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

COMMENTS
Strong Market Position and Global Brand Recognition: Starbucks has a significant geographical presence across the globe and maintain a 36.7% market share in the United States (Appendix 1) and has operations in over 60 countries. Starbucks is also the most recognized brand in the coffeehouse segment and is ranked 91st in
This case study examines the key components of Starbucks international strategy, including cultural adaptation, strategic expansion phases, partnership models, and lessons that can be drawn from its international success.
Starbucks competes with local coffee shops through a multifaceted strategy that leverages its global brand, extensive resources, and standardized customer experience. Here’s how Starbucks maintains its competitive edge: Consistent Quality and Standardization: Starbucks offers a consistent product and experience across all its locations. This ...
The global coffee giant Starbucks uses big data and artificial intelligence to drive marketing, sales and business decisions. With a highly successful mobile app and rewards program, the company...
The tool enables Starbucks to evaluate massive amounts of data including variables such as population, income levels, traffic, competitor presence, and proximity to other Starbucks locations before recommending a new store location.
PDF | this report is a case study analysis of Starbucks sustainability plan with reference to TBL approach | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
This is a four-module course, one module per week, and at the end of each module, we have an assessment: to write a case study analysis about a given topic. In the first week, I had to write...
Starbucks outperforms most of its peers in the food service segment. Apart from its commitments to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction, Starbucks also shows its responsibility towards sourcing its most relevant commodities, coffee and cocoa, achieving close to 100% sustainable sourcing practices – although it has an opportunity to ...
This visual case study delves into the key factors that have propelled Starbucks to unparalleled success, examining its innovative strategies, customer-centric approach, and global expansion.
The case offers executives and students an opportunity to examine in depth how Schultz and his team saved Starbucks from near-collapse, by both executing a deep, comprehensive return to its core values and, at the same time, investing in a range of new products, customer experiences and organizational capabilities designed to make the company ...