
Study of Osmosis by Potato Osmometer
A study of osmosis can be done using a potato osmometer. Osmosis is a phenomenon in which water moves from high solvent to low solvent concentration. The movement of water occurs between two compartments, separated by a semipermeable membrane .
The cell membrane of living organisms behaves as a semipermeable or selective membrane. The permeability of a selective membrane differs based on the size, charge and mass of different molecules.
Biological membranes are impermeable to large biomolecules and polar molecules like ions. But, non-polar molecules (lipids) and small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide etc.) can cross the selective barrier.
Water is the solvent that travels down or up the cell concentration gradient through osmosis. We can study water diffusion by creating two compartments and a semipermeable membrane in between.
The difference in the concentration of solutes or solvents between two compartments is the driving force responsible for water movement. Here, we need to note that only solvents can pass the selective barrier, not solutes.
Thus, the diffusion or distribution of water is related to osmosis . This post describes the meaning, requirements, procedure and results of the potato osmometer experiment.
Content: Study of Osmosis by Potato Osmometer
Potato osmometer, materials required, precautions.
It is a common experiment to demonstrate both endosmosis and exosmosis using a potato. Using a potato Osmoscope, we can study osmosis in a living system.
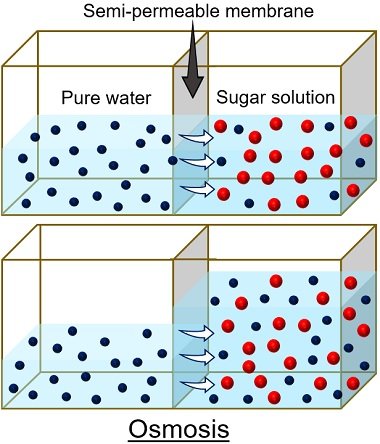
Here, a potato is used because the porous outer surface of the potato acts as a selective membrane .
- The contents within the cell form one compartment.
- The solution surrounding the cell forms another compartment.
Thus, a selective membrane separates two compartments and allows the process of osmosis .
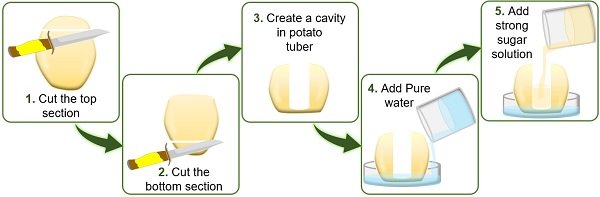
- High solvent concentration in the cell surrounding.
- Low solvent concentration in the cavity of potato tuber.
Following the rule of osmosis, water in the cell surrounding enters the tuber cavity via the cell membrane.
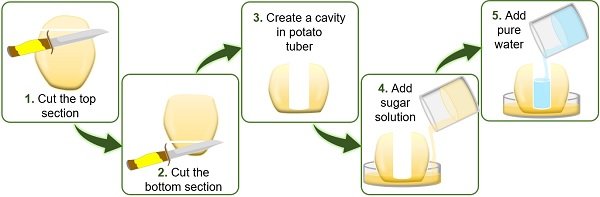
- High solvent concentration in the cavity of potato tuber.
- Low solvent concentration in the cell surrounding.
Following the rule of osmosis, water in the potato cavity enters the surrounding solution via the cell membrane.
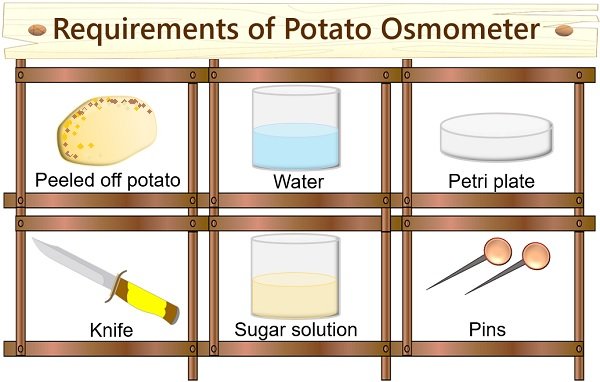
- Peeled off potato
- Concentrated sugar solution
- Petri plate
Video: Study of Osmosis
To perform the potato osmometer experiment, we need to follow the given procedure:
- First, peel off the large-sized potato using a peeler or knife.
- Then cut the upper and lower portions of the peeled potato using a knife. Through this step, we can easily place the potato on the Petri plate.
- Using a knife, make a cavity from the centre of the potato deep into the bottom, leaving some space. Here, the bottom of the potato will function as a selective membrane.
- Then, keep the potato on the Petri plate.
- To study endosmosis , pour water into half of the Petri plate. Next, pour the concentrated sugar solution into half of the cavity created in the potato.
- To study exosmosis , add concentrated sugar solution on the Petri plate and water into the cavity of the potato tuber.
- Then, fix a pin into the potato tuber-A and B to mark the level of sugar solution and water added into the cavity.
- Leave the plate undisturbed for some time until you notice any change.
Observation
- Observe the level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A.
- Notice the level of water in the cavity of the potato tuber-B.
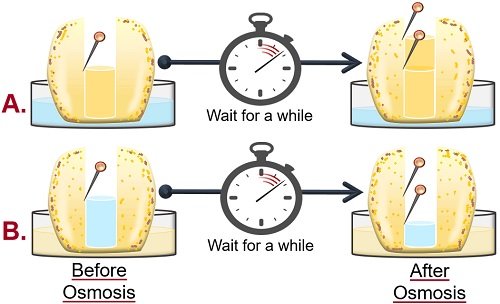
Potato Osmosis Experiment Results
- The level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A increases . It occurs because the water in the Petri plate will move towards the cell with a high solute or low solvent concentration. This experiment shows endosmosis , as water goes into the cell or potato tuber.
- In contrast, the level of water in the cavity of potato tuber-B decreases . Here, water in the cavity moves toward the solution in the Petri plate due to the high solute concentration in the surrounding. This experiment shows exosmosis as water leaves the cell or potato tuber.
- The cavity should be deep enough by leaving a minimum thickness at the bottom.
- The sugar solution should have a high osmotic concentration.
The water movement from the Petri plate to the potato cavity or vice versa is due to the difference in the solvent or solute concentration between the two compartments.
Related Topics:
- Germination of Plant
- Difference Between Root and Stem
- Nerve Impulse
- Ozone Formation
- Examples of Adsorption in Daily Life
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Start typing and press enter to search
- No category
Biology – Potatoes Osmosis Lab Report

Related documents

Study collections
- education if my future

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
- Biology Article
- Study Of Osmosis By Potato Osmometer
Understanding Osmosis Using Potato Osmometer
To study by demonstrating the osmosis process by potato osmometer.
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is the phenomena in which solvent molecules pass through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The process continues until the quantity of fluid is balanced or equalized in both regions, the region of higher concentration and the region of lower concentration of the semipermeable membrane. In other words, osmosis is the diffusion or movement of water from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential.
In osmosis, what are solvent and solute?
The fluid that permeates through the semipermeable membrane is called the solvent, whereas the solute is the dissolved particles in the fluid.
What is the solution?
The mixture of solute and solvent form the solution.
List the different types of solutions.
The following are the types of solutions:
- Hypertonic solution – It is a solution with a high solute level. If living cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, because of lower concentration water moves out of the cell causing it to shrink and becomes plasmolyzed.
- Hypotonic solution – It is a solution with low concentration levels of solute. If living cells are placed in this solution, water passes into the cells because of higher water concentration in comparison to the cell causing the cells to swell and turn turgid.
- Isotonic solution – A solution is said to be isotonic if both solutions have an equal concentration of solute. If living cells are placed in an isotonic solution, no change is shown as there is the equal concentration on both the regions hence the cell retains its original shape.
Material Required
- A fresh large-sized potato tuber
- 20% sucrose solution
- Scalpel/blade
- A Bell pin needle that is labelled with a waterproof ink
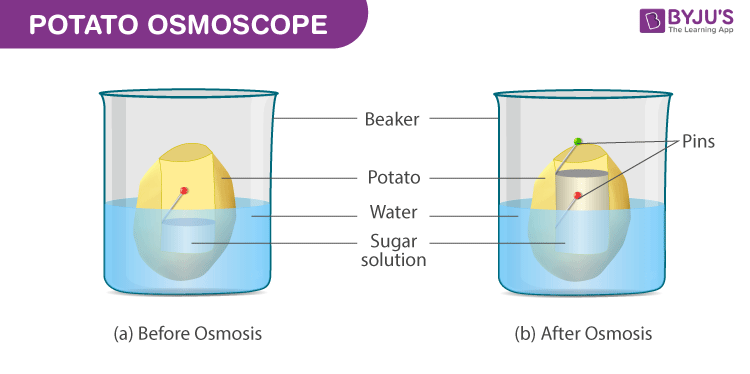
- Slice the potato tuber into two equal halves with the help of a scalpel or a blade. The outer skin is to be peeled off. Since the tuber shape is irregular, slice the halves into squares
- From the mid-region of the tuber, scoop from the soft parenchyma, so as to form a tiny cavity of a square or a circular shape. At the base, the cavity prepared should have a minimum thickness.
- Fill up half the cavity with the freshly prepared 20% sugar solution. Into the cavity, fix a pin in a way that the mark is in the same line with the layer of the sucrose solution.
- Set up the osmometer in a Petri dish/beaker that is filled with water in a way such that 75% of the potato osmometer is immersed in water
- The set up should remain uninterrupted for close to 1 hour.
- Notice the sugar solution in the osmometer towards the end of the experiment
- Carry out the experiment with the help of water in the cavity and the sucrose solution in the petri dish/beaker.
Observation
After a period of time, within the osmoscope, the sugar solution rises and is seen coloured.
- An increase in the level of sucrose solution is observed in the osmometer. It is because of the entrance of water due to endosmosis from the beaker.
- Also, a water potential gradient is built between the sucrose solution in the external water and the osmometer.
- Though both the liquids are divided by living cells of the potato tuber, they allow the entrance of water into the sugar solution.
- This demonstrates the entrance of water into the sugar solution through the tissues of potato serving as a selectively permeable membrane.
Viva Questions
Q.1. What is plasmolysis?
A.1. It is a process, wherein the protoplasm of the plant cell turns round as a result of contraction when placed in a hypertonic solution due to exosmosis resulting in the decline in the tension of the cell wall.
Q.2. What is the significance of osmosis?
A.2. Osmosis maintains cell turgidity. It causes the transportation of nutrients and discharge of metabolic waste products. It preserves the interior environment of a living entity to maintain an equilibrium between the intracellular fluid levels and water.
Q.3. What is diffusion?
A.3. The movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion.
For more information on related biological concepts and experiments, please register at BYJU’S.
Related Links:

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Good Thank you BYJU’S!!
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Vanderbilt University

Hello world!
Dec. 5, 2023— Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this activity, we are going to explore osmosis by looking at a dataset produced with a classic classroom experiment. The experiment uses pieces of potato that are placed in six different solutions of water each with a different solute concentration.
Osmosis - Potatoes 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 SUMMARY In this experiment, we are trying to find the isotonic point of potatoes by soaking them into different concentrations of salt water solutions, then using percent-weight-change to …
To study and analyze the process of osmosis using potato osmometer. Explore more in detail about Osmosis and Diffusion of water only at BYJU'S.
The aim of the potato experiment is to investigate the effects of different solute concentrations changing various results in the osmosis process. In this experiment we will see how water moves with osmosis and how it effects the …
The shrinking and expanding of the potato strips is due to osmosis. Potatoes are made of cells and their cells have cell walls that act as semipermeable membranes. The 0 grams saltwater …
Osmosis required practical. Aim: To investigate the range of concentrations of salt or sugar solutions on the mass of plant tissue. Procedure: Prepare samples of potatoes (or other plant tissue) and place in different …
Experiment: Osmosis in Potatoes. Distribute two slices potato to each group. Give each pair: 1 Potato Activity Sheet, one 100 mL beaker of distilled water, 1 container of salt, 1 spoon, 1 petri …